- How to create a Python library
- How to install dlib library for Python in Windows 10
- Preparation
- Install
- Sasiwut Chaiyadecha — Senior Consultant — EY | LinkedIn
- Sasiwut is a Senior Consultant working on Performance Improvement (PI) at EY Thailand. Currently, the main focus is on…
- Analytics Vidhya
- Windows python build library
How to create a Python library
Ever wanted to create a Python library, albeit for your team at work or for some open source project online? In this blog you will learn how to!
The tutorial is easiest to follow when you are using the same tools, however it is also possible for you to use different ones.
The tools used in this tutorial are:
— Linux command prompt
— Visual Studio Code
Step 1: Create a directory in which you want to put your library
Open your command prompt and create a folder in which you will create your Python library.
Remember:
— With pwd you can see your present working directory.
— With ls you can list the folders and files in your directory.
— With cd
you can change the current present directory you are in.
— With mkdir you can create a new folder in your working directory.
In my case, the folder I will be working with is mypythonlibrary . Change the present working directory to be your folder.
Step 2: Create a virtual environment for your folder
When starting your project, it is always a good idea to create a virtual environment to encapsulate your project. A virtual environment consists of a certain Python version and some libraries.
Virtual environments prevent the issue of running into dependency issues later on. For example, in older projects you might have worked with older versions of the numpy library. Some old code, that once worked beautifully, might stop working once you update its version. Perhaps parts of numpy are no longer compatible with other parts of your program. Creating virtual environments prevents this. They are also useful in cases when you are collaborating with someone else, and you want to make sure that your application is working on their computer, and vice versa.
(Make sure you changed the present working directory to the folder you are going to create your Python library in ( cd
Go ahead and create a virtual environment by typing:
> python3 -m venv venv
Once it is created, you must now activate the environment by using:
> source venv/bin/activate
Activating a virtual environment modifies the PATH and shell variables to point to the specific isolated Python set-up you created. PATH is an environmental variable in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that tells the shell which directories to search for executable files (i.e., ready-to-run programs) in response to commands issued by a user. The command prompt will change to indicate which virtual environment you are currently in by prepending ( yourenvname ).
In your environment, make sure you have pip installed wheel , setuptools and twine . We will need them for later to build our Python library.
> pip install wheel
> pip install setuptools
> pip install twine
Step 3: Create a folder structure
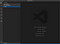
In Visual Studio Code, open your folder mypythonlibrary (or any name you have given your folder). It should look something like this:
You now can start adding folders and files to your project. You can do this either through the command prompt or in Visual Studio Code itself.
- Create an empty file called setup.py . This is one of the most important files when creating a Python library!
- Create an empty file called README.md . This is the place where you can write markdown to describe the contents of your library for other users.
- Create a folder called mypythonlib , or whatever you want your Python library to be called when you pip install it. (The name should be unique on pip if you want to publish it later.)
- Create an empty file inside mypythonlib that is called __init__.py . Basically, any folder that has an __init__.py file in it, will be included in the library when we build it. Most of the time, you can leave the __init__.py files empty. Upon import, the code within __init__.py gets executed, so it should contain only the minimal amount of code that is needed to be able to run your project. For now, we will leave them as is.
- Also, in the same folder, create a file called myfunctions.py .
- And, finally, create a folder tests in your root folder. Inside, create an empty __init__.py file and an empty test_myfunctions.py .
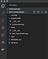
Your set-up should now look something like this:
Step 4: Create content for your library
To put functions inside your library, you can place them in the myfunctions.py file. For example, copy the haversine function in your file:
This function will give us the distance in meters between two latitude and longitude points.
Whenever you write any code, it is highly encouraged to also write tests for this code. For testing with Python you can use the libraries pytest and pytest-runner . Install the library in your virtual environment:
> pip install pytest==4.4.1
> pip install pytest-runner==4.4
Let’s create a small test for the haversine function. Copy the following and place it inside the test_myfunctions.py file:
Finally, let’s create a setup.py file, that will help us to build the library. A limited version of setup.py will look something like this:
The name variable in setup holds whatever name you want your package wheel file to have. To make it easy, we will gave it the same name as the folder.
Set the packages you would like to create
While in principle you could use find_packages() without any arguments, this can potentially result in unwanted packages to be included. This can happen, for example, if you included an __init__.py in your tests/ directory (which we did). Alternatively, you can also use the exclude argument to explicitly prevent the inclusion of tests in the package, but this is slightly less robust. Let’s change it to the following:
Set the requirements your library needs
Note that pip does not use requirements.yml / requirements.txt when your project is installed as a dependency by others. Generally, for that, you will have to specify dependencies in the install_requires and tests_require arguments in your setup.py file.
Install_requires should be limited to the list of packages that are absolutely needed. This is because you do not want to make users install unnecessary packages. Also note that you do not need to list packages that are part of the standard Python library.
However, since we have only defined the haversine function so far and it only uses the math library (which is always available in Python), we can leave this argument empty.
Maybe you can remember us installing the pytest library before. Of course, you do not want to add pytest to your dependencies in install_requires : it isn’t required by the users of your package. In order to have it installed automatically only when you run tests you can add the following to your setup.py :
Running:
> python setup.py pytest
will execute all tests stored in the ‘tests’ folder.
Step 5: Build your library
Now that all the content is there, we want to build our library. Make sure your present working directory is /path/to/mypythonlibrary (so the root folder of your project). In your command prompt, run:
> python setup.py bdist_wheel
Your wheel file is stored in the “dist” folder that is now created. You can install your library by using:
> pip install /path/to/wheelfile.whl
Note that you could also publish your library to an internal file system on intranet at your workplace, or to the official PyPI repository and install it from there.
Once you have installed your Python library, you can import it using:
import mypythonlib
from mypythonlib import myfunctions
How to install dlib library for Python in Windows 10
Hi! This is my first blog (or article depending on what you call) in English. Anyway, I am writing this blog because I have been facing with the trouble of this package for a while. I was trying to google it for the solution but I could not find the alternative one. So! this is my solution to install dlib library in Windows 10.
Some people might say that why don’t you just use conda install which is already complied. It is much easy to install. Well… I agree and I could do it. However, other packages, such as face_recognition could not leverage dlib when you used conda install . Hence, we need to use pip install .
Preparation
First thing first, there are two things required (really need it indeed!).
- CMake: This is because dlib was developed in C based programming language, so it needs this program to use it. It can be found in the link https://cmake.org/download/. To make sure matching with your operation system, in our case is Windows 10 64-bit version.
Sometimes we need manage the Windows PATH environment for CMake. (If you already added during installation, you can skip this section).
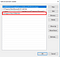
For checking whether the PATH already added or not, you can go to Environment Variables on Windows by go to This PC > Properties > Advance system settings. Then, go to Tab Advanced and click on Environment Variables.
Another windows will pop-up and click Edit…
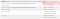
If you are unable to find CMake path, you should add the CMake installed directory like image below.
Install
Everything is looking good so far. Now we can install dlib into our python environment. First of all, you need to install CMake library.
Then, you can install dlib library using pip install .
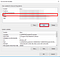
After passing enter, you laptop or desktop will run the C, C++ Compiler. If you got something like image below, you would be fine.
After these all, you will get dilb installed on your Windows 10 by not using conda install compiler.
For further discussion or anyone would like to contact me. We could do it over the LinkdIn below.
Sasiwut Chaiyadecha — Senior Consultant — EY | LinkedIn
Sasiwut is a Senior Consultant working on Performance Improvement (PI) at EY Thailand. Currently, the main focus is on…
See you next time!
Analytics Vidhya
Analytics Vidhya is a community of Analytics and Data…
Windows python build library
A collection of Python frameworks, libraries and software.
Libraries for Python version and environment management.
- pyenv — Simple Python version management.
- virtualenv — A tool to create isolated Python environments.
- virtualenvwrapper — A set of extensions to virtualenv.
- virtualenv-api — An API for virtualenv and pip.
- pew — A set of tools to manage multiple virtual environments.
- Vex — Run a command in the named virtualenv.
- PyRun — A one-file, no-installation-needed version of Python.
Libraries for package and dependency management.
- pip — The Python package and dependency manager.
- Python Package Index
- conda — Cross-platform, Python-agnostic binary package manager.
- Curdling — Curdling is a command line tool for managing Python packages.
- wheel — The new standard of Python distribution and are intended to replace eggs.
Local PyPI repository server and proxies.
- warehouse — Next generation Python Package Repository (PyPI).
- Warehouse
- devpi — PyPI server and packaging/testing/release tool.
- localshop — PyPI server which mirrors official packages on-demand, and also supports local (private) package uploads.
Libraries to create packaged executables for release distribution.
- cx-Freeze — Freezes Python scripts (cross-platform).
- py2exe — Freezes Python scripts (Windows).
- pynsist — A tool to build Windows installers, installers bundle Python itself.
- py2app — Freezes Python scripts (Mac OS X).
- PyInstaller — Converts Python programs into stand-alone executables (cross-platform).
- dh-virtualenv — Build and distribute a virtualenv as a Debian package.
- Nuitka — Compile scripts, modules, packages to an executable or extension module.
Compile software from source code.
- buildout — A build system for creating, assembling and deploying applications from multiple parts, some of which may be non-Python-based.
- SCons — A software construction tool.
- PlatformIO — A console tool to build code with different development platforms.
- BitBake — A make-like build tool with the special focus of distributions and packages for embedded Linux.
- fabricate — A build tool that finds dependencies automatically for any language.
Interactive Python interpreters.
- IPython — A rich toolkit to help you make the most out of using Python interactively.
- bpython – A fancy interface to the Python interpreter.
- python-prompt-toolkit — A Library for building powerful interactive command lines.
- ptpython — advanced Python REPL built on top of the prompt_toolkit library
Libraries for file manipulation and MIME type detection.
- mimetypes — (Python standard library) Map filenames to MIME types.
- imghdr — (Python standard library) Determine the type of an image.
- python-magic — A Python interface to the libmagic file type identification library.
- path.py — A module wrapper for os.path.
- watchdog — API and shell utilities to monitor file system events.
- Unipath — An object-oriented approach to file/directory operations.
- pathlib — (Python standard library in Python 3.4+) An cross-platform, object-oriented path library.
Libraries for working with dates and times.
- arrow — Better dates & times for Python.
- Chronyk — A Python 3 library for parsing human-written times and dates.
- dateutil — Extensions to the standard Python datetime module.
- delorean — A library for clearing up the inconvenient truths that arise dealing with datetimes.
- when.py — Providing user-friendly functions to help perform common date and time actions.
- moment — A Python library for dealing with dates/times. Inspired by Moment.js.
- pytz — World timezone definitions, modern and historical. Brings the tz database into Python.
Libraries for parsing and manipulating plain texts.
- General
- difflib — (Python standard library) Helpers for computing deltas.
- Levenshtein — Fast computation of Levenshtein distance and string similarity.
- fuzzywuzzy — Fuzzy String Matching.
- esmre — Regular expression accelerator.
- shortuuid — A generator library for concise, unambiguous and URL-safe UUIDs.
- ftfy — Makes Unicode text less broken and more consistent automagically.
- unidecode — ASCII transliterations of Unicode text.
- chardet — Python 2/3 compatible character encoding detector.
- xpinyin — A library to translate Chinese hanzi (漢字) to pinyin (拼音).
- pangu.py — Spacing texts for CJK and alphanumerics.
- pyfiglet — An implementation of figlet written in Python.
- uniout — Print readable chars instead of the escaped string.
- Slugify
- awesome-slugify — A Python slugify library that can preserve unicode.
- python-slugify — A Python slugify library that translates unicode to ASCII.
- unicode-slugify — A slugifier that generates unicode slugs with Django as a dependency.
- Parser
- PLY — Implementation of lex and yacc parsing tools for Python
- phonenumbers — Parsing, formatting, storing and validating international phone numbers.
- python-user-agents — Browser user agent parser.
- sqlparse — A non-validating SQL parser.
- Pygments — A generic syntax highlighter.
- python-nameparser — Parsing human names into their individual components.
- pyparsing — A general purpose framework for generating parsers.
Specific Formats Processing
Libraries for parsing and manipulating specific text formats.
- General
- tablib — A module for Tabular Datasets in XLS, CSV, JSON, YAML.
- Office
- python-docx — Reads, queries and modifies Microsoft Word 2007/2008 docx files.
- xlwt / xlrd — Writing and reading data and formatting information from Excel files.
- XlsxWriter — A Python module for creating Excel .xlsx files.
- xlwings — A BSD-licensed library that makes it easy to call Python from Excel and vice versa.
- Marmir — Takes Python data structures and turns them into spreadsheets.
- PDF
- PDFMiner — A tool for extracting information from PDF documents.
- PyPDF2 — A library capable of splitting, merging and transforming PDF pages.
- Markdown
- Python-Markdown — A Python implementation of John Gruber’s Markdown.
- Mistune — Fastest and full featured pure Python parsers of Markdown.
- YAML
- PyYAML — YAML implementations for Python.
- CSV
- csvkit — Utilities for converting to and working with CSV.
- Archive
- unp — A command line tool that can unpack archives easily.
Natural Language Processing
Libraries for working with human languages.
- NLTK — A leading platform for building Python programs to work with human language data.
- Pattern — A web mining module for the Python. It has tools for natural language processing, machine learning, among others.
- TextBlob — Providing a consistent API for diving into common NLP tasks. Stands on the giant shoulders of NLTK and Pattern.
- jieba — Chinese Words Segmentation Utilities.
- SnowNLP — A library for processing Chinese text.
- loso — Another Chinese segmentation library.
- genius — A Chinese segment base on Conditional Random Field.
Libraries for generating project documentation.
- Sphinx — Python Documentation generator.
- awesome-sphinxdoc
- reStructuredText — Markup Syntax and Parser Component of Docutils.
- MkDocs — Markdown friendly documentation generator.
- Pycco — The original quick-and-dirty, hundred-line-long, literate-programming-style documentation generator.
- pdoc — Epydoc replacement to auto generate API documentation for Python libraries.
Libraries for storing configuration options.
- ConfigParser — (Python standard library) INI file parser.
- ConfigObj — INI file parser with validation.
- config — Hierarchical config from the author of logging.
- profig — Config from multiple formats with value conversion.
Libraries for building command-line application.
- Command-line Application Development
- cement — Cement provides a light-weight and fully featured foundation to build anything from single file scripts to complex and intricately designed applications.
- click — A package for creating beautiful command line interfaces in a composable way.
- clint — Python Command-line Application Tools.
- cliff — A framework for creating command-line programs with multi-level commands.
- Clime – Clime lets you convert any module into a multi-command CLI program without any configuration.
- docopt — Pythonic command line arguments parser.
- colorama — Cross-platform colored terminal text.
- pyCLI — Command-line applications supporting standard command line parsing, logging, unit and functional testing.
- Gooey — Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line
- Productivity Tools
- cookiecutter — A command-line utility that creates projects from cookiecutters (project templates). E.g. Python package projects, jQuery plugin projects.
- httpie — A command line HTTP client, a user-friendly cURL replacement.
- percol — Adds flavor of interactive selection to the traditional pipe concept on UNIX.
- RainbowStream — Smart and nice Twitter client on terminal.
- caniusepython3 — Determine what projects are blocking you from porting to Python 3.
Libraries for downloading.
- s3cmd — A command line tool for managing Amazon S3 and CloudFront.
- youtube-dl — A small command-line program to download videos from YouTube.
- you-get — A YouTube/Youku/Niconico video downloader written in Python 3.
- coursera — Script for downloading Coursera.org videos and naming them.
- WikiTeam — Tools for downloading and preserving wikis.
- subliminal — Library and command line tool to search and download subtitles.
Libraries for manipulating images.
- pillow — Pillow is the friendly PIL fork.
- wand — Python bindings for MagickWand, C API for ImageMagick.
- thumbor — A smart imaging service. It enables on-demand crop, resizing and flipping of images.
- imgSeek — A project for searching a collection of images using visual similarity.
- python-qrcode — A pure Python QR Code generator.
- pyBarcode — Create barcodes in Python without needing PIL.
- pygram — Instagram-like image filters.
- Quads — Computer art based on quadtrees.
- nude.py — Nudity detection.
- scikit-image — A Python library for (scientific) image processing.
- hmap — Image histogram remapping.
Libraries for Optical Character Recognition.
- [python-tesseract] (https://code.google.com/p/python-tesseract) — A wrapper class for Google Tesseract OCR.
- pytesseract — Another wrapper for Google Tesseract OCR.
- pyocr — A wrapper for Tesseract and Cuneiform.
Libraries for manipulating audio.
- audiolazy — Expressive Digital Signal Processing (DSP) package for Python.
- audioread — Cross-library (GStreamer + Core Audio + MAD + FFmpeg) audio decoding.
- beets — A music library manager and MusicBrainz tagger.
- dejavu — Audio fingerprinting and recognition.
- django-elastic-transcoder — Django + Amazon Elastic Transcoder.
- eyeD3 — A tool for working with audio files, specifically MP3 files containing ID3 metadata.
- id3reader — A Python module for reading MP3 meta data.
- mutagen — A Python module to handle audio metadata.
- pydub — Manipulate audio with a simple and easy high level interface.
- pyechonest — Python client for the Echo Nest API.
- talkbox — A Python library for speech/signal processing.
- TimeSide — Open web audio processing framework.
- tinytag — A library for reading music meta data of MP3, OGG, FLAC and Wave files.
- m3u8 — A module for parsing m3u8 file.
Libraries for manipulating video and GIFs.
- moviepy — A module for script-based movie editing with many formats, including animated GIFs.
- shorten.tv — Video summarization.
- scikit-video — Video processing routines for SciPy.
Libraries for geocoding addresses and working with latitudes and longitudes.
- GeoDjango — A world-class geographic web framework.
- geopy — Python Geocoding Toolbox.
- pygeoip — Pure Python GeoIP API.
- GeoIP — Python API for MaxMind GeoIP Legacy Database.
- geojson — Python bindings and utlities for GeoJSON.
- django-countries — A Django app that provides country choices for use with forms, flag icons static files, and a country field for models.
Libraries for working with HTTP.
- requests — HTTP Requests for Humans™.
- grequests — requests + gevent for asynchronous HTTP requests.
- urllib3 — A HTTP library with thread-safe connection pooling, file post support, sanity friendly.
- httplib2 — Comprehensive HTTP client library.
- treq — Python requests like API built on top of Twisted’s HTTP client.
Databases implemented in Python.
- ZODB — A native object database for Python. A key-value and object graph database.
- pickleDB — A simple and lightweight key-value store for Python.
- TinyDB — A tiny, document-oriented database.
Libraries for connecting and operating databases.
- Relational Databases
- mysql-python — The MySQL database connector for Python.
- mysqlclient — mysql-python fork supporting Python 3.
- PyMySQL — Pure Python MySQL driver compatible to mysql-python.
- mysql-connector-python — A pure Python MySQL driver from Oracle.
- oursql — A better MySQL connector with support for native prepared statements and BLOBs.
- psycopg2 — The most popular PostgreSQL adapter for Python.
- txpostgres — Twisted based asynchronous driver for PostgreSQL.
- queries — A wrapper of the psycopg2 library for interacting with PostgreSQL.
- dataset — Store Python dicts in a database — works with SQLite, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
- NoSQL Databases
- cassandra-python-driver — Python driver for Cassandra.
- pycassa — Python Thrift driver for Cassandra.
- HappyBase — A developer-friendly library for Apache HBase.
- PyMongo — The official Python client for MongoDB.
- Plyvel — A fast and feature-rich Python interface to LevelDB.
- redis-py — The Redis Python Client.
- py2neo — Python wrapper client for Neo4j’s restful interface.
- telephus — Twisted based client for Cassandra.
- txRedis — Twisted based client for Redis.
Libraries that implement Object-Relational Mapping or datamapping techniques.
- Relational Databases
- Django Models — A part of Django.
- SQLAlchemy — The Python SQL Toolkit and Object Relational Mapper.
- awesome-sqlalchemy
- peewee — A small, expressive ORM.
- PonyORM — ORM that provides a generator-oriented interface to SQL.
- NoSQL Databases
- MongoEngine — A Python Object-Document-Mapper for working with MongoDB.
- django-mongodb-engine — Django MongoDB Backend.
- redisco — A Python Library for Simple Models and Containers Persisted in Redis.
- flywheel — Object mapper for Amazon DynamoDB.
- Others
- butterdb — A Python ORM for Google Drive Spreadsheets.
Full stack web frameworks.
- Django — The most popular web framework in Python.
- awesome-django
- Flask — A microframework for Python.
- awesome-flask
- Bottle — A fast, simple and lightweight WSGI micro web-framework.
- Pyramid — A small, fast, down-to-earth, open source Python web framework.
- awesome-pyramid
- web2py — A full stack web framework and platform focused in the ease of use.
- web.py — A web framework for Python that is as simple as it is powerful.
- TurboGears — The Web Framework that starts as a microframework and scales up to a fullstack solution.
- CherryPy — A Minimalist Python Web Framework, HTTP/1.1-compliant and WSGI thread-pooled.
- Grok — A framework built on the existing Zope 3 libraries.
- Bluebream — An open-source web application server, framework and library, formerly known as Zope 3.
- guava — A lightweight and high performance web framework for Python written in C.
Libraries that allow or deny users access to data or functionality.
- django-guardian — Implementation of per object permissions for Django 1.2+
- Carteblanche — Module to align code with thoughts of users and designers. Also magically handles navigation and permissions.
Content Management Systems.
- django-cms — An Open source enterprise CMS based on the Django.
- djedi-cms — A lightweight but yet powerful Django CMS with plugins, inline editing and performance in mind.
- FeinCMS — One of the most advanced Content Management Systems built on Django.
- Kotte — A high-level, Pythonic web application framework built on Pyramid.
- Mezzanine — A powerful, consistent, and flexible content management platform.
- Opps — A Django-based CMS for magazines, newspapers websites and portals with high-traffic.
- Plone — A CMS built on top of the open source application server Zope.
- Quokka — Flexible, extensible, small CMS powered by Flask and MongoDB.
- Wagtail — A Django content management system.
- Widgy — Last CMS framework, based on Django.
Frameworks and libraries for e-commerce and payments.
- django-oscar — An open-source e-commerce framework for Django.
- django-shop — A Django based shop system.
- merchant — A Django app to accept payments from various payment processors.
- money — Money class with optional CLDR-backed locale-aware formatting and an extensible currency exchange solution.
- python-currencies — Display money format and its filthy currencies.
Libraries for developing RESTful APIs.
- cornice — A REST framework for Pyramid.
- django-rest-framework — A powerful and flexible toolkit that makes it easy to build Web APIs.
- django-tastypie — Creating delicious APIs for Django apps.
- django-formapi — Create JSON APIs with HMAC authentication and Django form-validation.
- flask-api — An implementation of the same web browsable APIs that django-rest-framework provides.
- flask-restful — An extension for Flask that adds support for quickly building REST APIs.
- flask-restless — A Flask extension for generating ReSTful APIs for database models defined with SQLAlchemy (or Flask-SQLAlchemy).
- flask-api-utils — Flask extension that takes care of API representation and authentication.
- falcon — A high-performance Python framework for building cloud APIs and web app backends.
- eve — REST API framework powered by Flask, MongoDB and good intentions.
- sandman — Automated REST APIs for existing database-driven systems.
- restless — Framework agnostic REST framework based on lessons learned from TastyPie.
- savory-pie — REST API building library (django, and others)
Libraries for implementing authentications schemes.
- OAuth
- Authomatic — Simple but powerful framework agnostic authentication/authorization client package.
- OAuthLib — A generic, spec-compliant, thorough implementation of the OAuth request-signing logic.
- rauth — A Python library for OAuth 1.0/a, 2.0, and Ofly.
- python-oauth2 — A fully tested, abstract interface to creating OAuth clients and servers.
- python-social-auth — An easy-to-setup social authentication mechanism.
- django-oauth-toolkit — OAuth2 goodies for the Djangonauts.
- django-oauth2-provider — Providing OAuth2 access to Django app.
- django-allauth — Authentication app for Django that «just works.»
- Flask-OAuthlib — OAuth 1.0/a, 2.0 implementation of client and provider for Flask.
- sanction — A dead simple OAuth2 client implementation.
- Others
- PyJWT — Implementation of the JSON Web Token draft 01.
- python-jwt — Module for generating and verifying JSON Web Tokens.
- python-jws — Implementation of JSON Web Signatures draft 02.
- jose — JavaScript Object Signing and Encryption draft implementation.
Libraries and tools for templating and lexing.
- Jinja2 — A modern and designer friendly templating language.
- Genshi — Python templating toolkit for generation of web-aware output.
- Mako — Hyperfast and lightweight templating for the Python platform.
- Chameleon — An HTML/XML template engine. Modeled after ZPT, optimized for speed.
- Spitfire — A very fast Python template compiler.
Libraries for working with event and task queues.
- celery — An asynchronous task queue/job queue based on distributed message passing.
- huey — Little multi-threaded task queue.
- mrq — Mr. Queue — A distributed worker task queue in Python using Redis & gevent.
- rq — Simple job queues for Python.
- simpleq — A simple, infinitely scalable, Amazon SQS based queue.
Libraries and software for indexing and performing search queries on data.
- django-haystack — Modular search for Django.
- elasticsearch-py — The official low-level Python client for Elasticsearch.
- solrpy — A Python client for solr.
- Whoosh — A fast, pure Python search engine library.
Libraries for building user’s activities.
- Feedly — A library to build newsfeed and notification systems using Cassandra and Redis.
- django-activity-stream — Generate generic activity streams from the actions on your site.
Tools for managing, compressing and minifying website assets.
- django-compressor — Compresses linked and inline javascript or CSS into a single cached file.
- jinja-assets-compressor — A Jinja extension to compile and compress your assets.
- webassets — Bundles, optimizes, and manages unique cache-busting URLs for static resources.
- fanstatic — Packages, optimizes, and serves static file dependencies as Python packages.
- fileconveyor — Monitors changes, processes, and transports assets to CDNs and file storage systems.
- django-storages — A collection of custom storage backends for Django.
- glue — Glue is a simple command line tool to generate CSS sprites.
- libsass-python — A Python binding of libsass, the reference implementation of SASS/SCSS.
- Flask-Assets — Helps you integrate webassets into your Flask app.
Libraries for caching data.
- Beaker — A library for caching and sessions for use with web applications and stand-alone Python scripts and applications.
- dogpile.cache — dogpile.cache is next generation replacement for Beaker made by same authors.
- HermesCache — Python caching library with tag-based invalidation and dogpile effect prevention.
- django-cache-machine — Automatic caching and invalidation for Django models through the ORM.
- django-cacheops — A slick ORM cache with automatic granular event-driven invalidation.
- johnny-cache — A caching framework for django applications.
- django-viewlet — Render template parts with extended cache control.
- pylibmc — A Python wrapper around the libmemcached interface.
Libraries for sending and parsing email.
- inbox.py — Python SMTP Server for Humans.
- imbox — Python IMAP for Humans.
- inbox — The open source email toolkit.
- lamson — Pythonic SMTP Application Server.
- flanker — A email address and Mime parsing library.
- marrow.mailer — High-performance extensible mail delivery framework.
- django-celery-ses — Django email backend with AWS SES and Celery.
- modoboa — A mail hosting and management platform including a modern and simplified Web UI.
- envelopes — Mailing for human beings.
- mailjet — Mailjet API implementation for batch mailing, statistics and more.
- Talon — Mailgun library to extract message quotations and signatures.
- pyzmail — Compose, send and parse emails.
Libraries for woking with i18n.
- Babel — An internationalization library for Python.
- Korean — A library for Korean morphology.
Libraries for parsing URLs.
- furl — A small Python library that makes manipulating URLs simple.
- purl — A simple, immutable URL class with a clean API for interrogation and manipulation.
- pyshorteners — A pure Python URL shortening lib.
- short_url — Python implementation for generating Tiny URL and bit.ly-like URLs.
- webargs — A friendly library for parsing HTTP request arguments, with built-in support for popular web frameworks, including Flask, Django, Bottle, Tornado, and Pyramid.
Libraries for working with HTML and XML.
- BeautifulSoup — Providing Pythonic idioms for iterating, searching, and modifying HTML or XML.
- lxml — A very fast, easy-to-use and versatile library for handling HTML and XML.
- html5lib — A standards-compliant library for parsing and serializing HTML documents and fragments.
- pyquery — A jQuery-like library for parsing HTML.
- cssutils — A CSS library for Python.
- MarkupSafe — Implements a XML/HTML/XHTML Markup safe string for Python.
- bleach — A whitelist-based HTML sanitization and text linkification library.
- xmltodict — Working with XML feel like you are working with JSON.
- xhtml2pdf — HTML/CSS to PDF converter.
- untangle — Converts XML documents to Python objects for easy access.
Libraries for scraping websites.
- Scrapy — A fast high-level screen scraping and web crawling framework.
- portia — Visual scraping for Scrapy.
- feedparser — Universal feed parser.
- RoboBrowser — A simple, Pythonic library for browsing the web without a standalone web browser.
- MechanicalSoup — A Python library for automating interaction with websites.
- mechanize — Stateful programmatic web browsing.
- Demiurge — PyQuery-based scraping micro-framework.
- cola — A distributed crawling framework.
- pyspider — A powerful spider system.
Web Content Extracting
Libraries for extracting web contents.
- newspaper — News extraction, article extraction and content curation in Python.
- html2text — Convert HTML to Markdown-formatted text.
- python-goose — HTML Content/Article Extractor.
- lassie — Web Content Retrieval for Humans.
- micawber — A small library for extracting rich content from URLs.
- sumy — A module for automatic summarization of text documents and HTML pages.
- Haul — An Extensible Image Crawler.
- python-readability — Fast Python port of arc90’s readability tool.
- opengraph — A Python module to parse the Open Graph Protocol
- textract — Extract text from any document, Word, PowerPoint, PDFs, etc.
- sanitize — Bringing sanity to world of messed-up data.
Libraries for working with forms.
- WTForms — A flexible forms validation and rendering library.
- WTForms-JSON — A WTForms extension for JSON data handling.
- Deform — Python HTML form generation library influenced by the formish form generation library.
- django-bootstrap3 — Bootstrap 3 integration with Django.
- django-crispy-forms — A Django app which lets you create beautiful forms in a very elegant and DRY way.
- django-remote-forms — A platform independent Django form serializer.
Libraries for validating data. Used for forms in many cases.
- voluptuous — A Python data validation library. It is primarily intended for validating data coming into Python as JSON, YAML, etc.
- colander — A system for validating and deserializing data obtained via XML, JSON, an HTML form post or any other equally simple data serialization.
- schema — A library for validating Python data structures.
- Schematics — Data Structure Validation.
- kmatch — A language for matching/validating/filtering Python dictionaries.
- valideer — Lightweight extensible data validation and adaptation library.
Libraries for fighting spam.
- Stopspam — Intelligent spam detection for Python.
- django-simple-spam-blocker — Simple spam blocker for Django.
- django-simple-captcha — A simple and highly customizable Django app to add captcha images to any Django form.
Libraries for tagging items.
Libraries for administrative interfaces.
- Ajenti — The admin panel your servers deserve.
- Grappelli – A jazzy skin for the Django Admin-Interface.
- django-suit — Alternative Django Admin-Interface (free only for Non-commercial use).
- django-xadmin — Drop-in replacement of Django admin comes with lots of goodies.
- flask-admin — Simple and extensible administrative interface framework for Flask.
- flower — Real-time monitor and web admin for Celery.
Static Site Generator
Static site generator is a software that takes some text + templates as input and produces html files on the output.
- Pelican — Uses Markdown or ReST for content and Jinja 2 for themes. Supports DVCS, Disqus. AGPL.
- Cactus – Static site generator for designers.
- Hyde — Jinja2-based static web site generator.
- Nikola — A static website and blog generator.
- Tags — The simplest static site generator.
- Tinkerer — Tinkerer is a blogging engine/.static website generator powered by Sphinx.
Processes and Threads
Libraries for woking with processes or threads
- multiprocessing — (Python standard library) Process-based «threading» interface.
- threading — (Python standard library) Higher-level threading interface.
- envoy — Python Subprocesses for Humans™.
- sh — A full-fledged subprocess replacement for Python.
- sarge — A wrapper for subprocess.
Concurrency and Networking
Libraries for concurrency and network programming.
- asyncio — (Python standard library in Python 3.4+) Asynchronous I/O, event loop, coroutines and tasks.
- gevent — A coroutine-based Python networking library that uses greenlet.
- Twisted — An event-driven networking engine.
- Tornado — A Web framework and asynchronous networking library.
- pulsar — Event-driven concurrent framework for Python.
- diesel — Greenlet-based event I/O Framework for Python.
- eventlet — Asynchronous framework with WSGI support.
- pyzmq — A Python wrapper for the 0MQ message library.
- txZMQ — Twisted based wrapper for the 0MQ message library.
- Crossbar — Open-source Unified Application Router (Websocket & WAMP for Python on Autobahn).
Libraries for woking with WebSocket.
- AutobahnPython — WebSocket & WAMP for Python on Twisted and asyncio.
- WebSocket-for-Python — WebSocket client and server library for Python 2 and 3 as well as PyPy.
WSGI-compatible web servers.
- wsgiref — (Python standard library) WSGI reference implementation, single-threaded.
- Werkzeug — A WSGI utility library for Python that powers Flask and can easily be embedded into your own projects.
- paste — Multi-threaded, stable, tried and tested.
- rocket — Multi-threaded.
- waitress — Multi-threaded, poweres Pyramid.
- netius — Asynchronous, very fast.
- gunicorn — Pre-forked, partly written in C.
- fapws3 — Asynchronous (network side only), written in C.
- meinheld — Asynchronous, partly written in C.
- bjoern — Asynchronous, very fast and written in C.
- SimpleXMLRPCServer — (Python standard library) Simple XML-RPC server implementation, single-threaded.
- SimpleJSONRPCServer — This library is an implementation of the JSON-RPC specification.
- zeroRPC — zerorpc is a flexible RPC implementation based on ZeroMQ and MessagePack.
- PyCrypto — The Python Cryptography Toolkit.
- Paramiko — A Python (2.6+, 3.3+) implementation of the SSHv2 protocol, providing both client and server functionality.
- cryptography — A package designed to expose cryptographic primitives and recipes to Python developers.
- PyNacl — Python binding to the Networking and Cryptography (NaCl) library.
- hashids — Implementation of hashids in Python.
- Passlib — Secure password storage/hashing library, very high level.
Libraries for working with graphical user interface applications.
- PyQt — Python bindings for the Qt cross-platform application and UI framework, with support for both Qt v4 and Qt v5 frameworks.
- PySide — Python bindings for the Qt cross-platform application and UI framework, supporting the Qt v4 framework.
- wxPython — A blending of the wxWidgets C++ class library with the Python.
- kivy — A library for creating NUI applications, running on Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, Android and iOS.
- curses — Built-in wrapper for ncurses used to create terminal GUI applications.
- urwid — A library for creating terminal GUI applications with strong support for widgets, events, rich colors, etc.
- pyglet — A cross-platform windowing and multimedia library for Python.
- Tkinter — Tkinter is Python’s de-facto standard GUI package.
- enaml — Creating beautiful user-interfaces with Declaratic Syntax like QML.
- Toga — A Python native, OS native GUI toolkit.
Awesome game development libraries.
- Pygame — Pygame is a set of Python modules designed for writing games.
- Cocos2d — cocos2d is a framework for building 2D games, demos, and other graphical/interactive applications. It is based on pyglet.
- PySDL2 — A ctypes based wrapper for the SDL2 library.
- Panda3D — 3D game engine developed by Disney and maintained by Carnegie Mellon’s Entertainment Technology Center. Written in C++, completely wrapped in Python.
- PyOgre — Python bindings for the Ogre 3D render engine, can be used for games, simulations, anything 3D.
- PyOpenGL — Python ctypes bindings for OpenGL and it’s related APIs.
- PySFML — Python bindings for SFML
- RenPy — A Visual Novel engine.
Libraries for generating and working with log files.
- logging — (Python standard library) Logging facility for Python.
- logbook — Logging replacement for Python.
- Sentry — A realtime logging and aggregation server.
- Raven — The Python client for Sentry.
Libraries for testing codebases and generating test data.
- Testing Frameworks
- unittest — (Python standard library) Unit testing framework.
- nose — nose extends unittest.
- pytest — A mature full-featured Python testing tool.
- mamba — The definitive testing tool for Python. Born under the banner of BDD.
- contexts — A BDD framework for Python 3.3+. Inspired by C#’s Machine.Specifications .
- pyshould — Should style asserts based on PyHamcrest.
- pyvows — BDD style testing for Python. Inspired by Vows.js.
- Web Testing
- Selenium — Python bindings for Selenium WebDriver.
- splinter — Open source tool for testing web applications.
- locust — Scalable user load testing tool written in Python.
- sixpack — A language-agnostic A/B Testing framework.
- Mock
- mock — A Python Mocking and Patching Library for Testing.
- responses — A utility library for mocking out the requests Python library.
- doublex — Powerful test doubles framework for Python.
- freezegun — Travel through time by mocking the datetime module.
- httpretty — HTTP request mock tool for Python.
- httmock — A mocking library for requests for Python 2.6+ and 3.2+.
- Code Coverage
- coverage — Code coverage measurement.
- Fake Data
- faker — A Python package that generates fake data.
- fake2db — Fake database generator.
- mixer — Generating fake data and creating random fixtures for testing in Django ORM, SQLAlchemy, Peewee, MongoEngine, Pony ORM and etc.
- model_mommy — Creating random fixtures for testing in Django.
- ForgeryPy — An easy to use forged data generator for Python. It’s a port of forgery.
- radar — Generate random datetime / time.
- Error Handler
- FuckIt.py — FuckIt.py uses state-of-the-art technology to make sure your Python code runs whether it has any right to or not.
Code Analysis and Linter
Libraries and tools for analysing, parsing and manipulation codebases.
- Code Analysis
- pysonar2 — A type inferencer and indexer for Python.
- pycallgraph — A library that visualises the flow (call graph) of your Python application.
- code2flow — Turn your Python and JavaScript code into DOT flowcharts.
- Linter
- Flake8 — The modular source code checker: pep8, pyflakes and co.
- pylama — Code audit tool for Python and JavaScript.
- Pylint — A source code analyzer.
Libraries for debugging code.
- pdb — (Python standard library) The Python Debugger.
- ipdb — IPython-enabled pdb.
- winpdb — A Platform Independent Python Debugger with GUI.
- pudb – A full-screen, console-based Python debugger.
- pyringe — Debugger capable of attaching to and injecting code into Python processes.
- python-statsd — Python Client for the statsd server.
- memory_profiler — Monitor Memory usage of Python code.
- profiling — An interactive Python profiler.
- django-debug-toolbar — Display various debug information about the current request/response.
- django-devserver — A drop-in replacement for Django’s runserver.
- flask-debugtoolbar — A port of the django-debug-toolbar to flask.
- pyelftools — A pure-Python library for parsing and analyzing ELF files and DWARF debugging information.
Science and Data Analysis
Libraries for scientific computing and data analyzing.
- SciPy — A Python-based ecosystem of open-source software for mathematics, science, and engineering.
- NumPy — A fundamental package for scientific computing with Python.
- Numba — Python JIT (just in time) complier to LLVM aimed at scientific Python by the developers of Cython and NumPy.
- NetworkX — A high-productivity software for complex networks.
- Pandas — A library providing high-performance, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools.
- Open Mining — Business Intelligence (BI) in Python (Pandas web interface)
- PyMC — Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling toolkit.
- zipline — A Pythonic algorithmic trading library.
- PyDy — Short for Python Dynamics, used to assist with workflow in the modeling of dynamic motion based around NumPy, SciPy, IPython, and matplotlib.
- SymPy — A Python library for symbolic mathematics.
- statsmodels — Statistical modeling and econometrics in Python.
- astropy — A community Python library for Astronomy.
- orange — Data mining, data visualization, analysis and machine learning through visual programming or Python scripting.
- RDKit — Cheminformatics and Machine Learning Software.
- Open Babel — A chemical toolbox designed to speak the many languages of chemical data.
- cclib — A library for parsing and interpreting the results of computational chemistry packages.
- Biopython — Biopython is a set of freely available tools for biological computation.
- bccb — Collection of useful code related to biological analysis.
- bcbio-nextgen — A toolkit providing best-practice pipelines for fully automated high throughput sequencing analysis.
- blaze — NumPy and Pandas interface to Big Data.
Libraries for visualizing data. See: awesome-javascript.
- matplotlib — A Python 2D plotting library.
- bokeh — Interactive Web Plotting for Python.
- plotly — Collaborative web plotting for Python and matplotlib.
- vincent — A Python to Vega translator.
- d3py — A plottling library for Python, based on D3.js.
- ggplot — Same API as ggplot2 for R.
- Kartograph.py — Rendering beautiful SVG maps in Python.
- pygal — A Python SVG Charts Creator.
- pygraphviz — Python interface to Graphviz.
- PyQtGraph — Interactive and realtime 2D/3D/Image plotting and science/engineering widgets.
Libraries for computer vision.
- OpenCV — Open Source Computer Vision Library.
- SimpleCV — An open source framework for building computer vision applications.
- scikit-learn — A Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy.
- pattern — Web mining module for Python.
- NuPIC — Numenta Platform for Intelligent Computing.
- Pylearn2 — A Machine Learning library based on Theano.
- hebel — GPU-Accelerated Deep Learning Library in Python.
- gensim — Topic Modelling for Humans.
- PyBrain — Another Python Machine Learning Library.
- Crab — A flexible, fast recommender engine.
- python-recsys — A Python library for implementing a Recommender System.
- vowpal_porpoise — A lightweight Python wrapper for Vowpal Wabbit.
Framworks and libraries for MapReduce.
- PySpark — The Spark Python API.
- dpark — Python clone of Spark, a MapReduce alike framework in Python.
- luigi — A module that helps you build complex pipelines of batch jobs.
- mrjob — Run MapReduce jobs on Hadoop or Amazon Web Services.
- dumbo — Python module that allows one to easily write and run Hadoop programs.
- streamparse — Run Python code against real-time streams of data. Integrates with Apache Storm.
Functional Programming with Python.
- fn.py — Functional programming in Python: implementation of missing features to enjoy FP.
- funcy — A fancy and practical functional tools.
- Toolz — A collection of functional utilities for iterators, functions, and dictionaries.
- CyToolz — Cython implementation of Toolz: High performance functional utilities.
Libraries for accessing third party services APIs. See: List of Python API Wrappers and Libraries.
- apache-libcloud — One Python library for all clouds.
- boto — Python interface to Amazon Web Services.
- twython — A Python wrapper for the Twitter API.
- google-api-python-client — Google APIs Client Library for Python.
- gspread — Google Spreadsheets Python API.
- facebook-sdk — Facebook Platform Python SDK.
- facepy — Facepy makes it really easy to interact with Facebook’s Graph API
- gmail — A Pythonic interface for Gmail.
- django-wordpress — WordPress models and views for Django.
Software and libraries for DevOps.
- OpenStack — Open source software for building private and public clouds.
- Ansible — A radically simple IT automation platform.
- SaltStack — Infrastructure automation and management system.
- Fabric — A simple, Pythonic tool for remote execution and deployment.
- Fabtools — Tools for writing awesome Fabric files.
- cuisine — Chef-like functionality for Fabric.
- psutil — A cross-platform process and system utilities module.
- pexpect — Controlling interactive programs in a pseudo-terminal like GNU expect.
- provy — An easy-to-use provisioning system in Python.
- honcho — A Python port of Foreman, a tool for managing Procfile-based applications.
- gunnery — Multipurpose task execution tool for distributed systems with web-based interface.
- fig — Fast, isolated development environments using Docker.
- hgapi — Pure-Python API for Mercurial.
- gitapi — Pure-Python API for git.
- supervisor — Supervisor process control system for UNIX.
Libraries for scheduling jobs.
- APScheduler — A light but powerful in-process task scheduler that lets you schedule functions.
- django-schedule — A calendaring app for Django.
- doit — A task runner/build tool.
- Joblib — A set of tools to provide lightweight pipelining in Python.
- Plan — Writing crontab file in Python like a charm.
- Spiff — A powerful workflow engine implemented in pure Python.
- schedule — Python job scheduling for humans.
- TaskFlow — A Python library that helps to make task execution easy, consistent and reliable.
Foreign Function Interface
Libraries for providing foreign function interface.
- ctypes — (Python standard library) Foreign Function Interface for Python calling C code.
- cffi — Foreign Function Interface for Python calling C code.
- SWIG — Simplified Wrapper and Interface Generator.
- PyCUDA — A Python wrapper for Nvidia’s CUDA API.
Libraries for making Python faster.
- Cython — Optimizing Static Complier for Python. Uses type mixins to compile Python into C or C++ modules resulting in large performance gains.
- PyPy — An implementation of Python in Python. The interpreter uses black magic to make Python very fast without having to add in additional type information.
- Stackless Python — An enhanced version of the Python.
- Pyston — A Python implementation built using LLVM and modern JIT techniques with the goal of achieving good performance.
Python programming on Microsoft Windows.
- pythonlibs — Unofficial Windows(32/64-bit) binaries for Python extension packages
- Python(x,y) — Scientific-applications-oriented Python Distribution based on Qt and Spyder.
- spyder — IDE for the Python language with advanced editing, interactive testing, debugging and introspection features (also comes with Anaconda).
Network Virtualization and SDN
Tools and libraries for Virtual Networking and SDN (Software Defined Networking).
- Mininet — A popular network emulator and API written in Python.
- POX — An open source development platform for Python-based Software Defined Networking (SDN) control applications, such as OpenFlow SDN controllers.
- Pyretic — A member of the Frenetic family of SDN programming languages that provides powerful abstractions over network switches or emulators.
- SDX Platform — SDN based IXP implementation that leverages Mininet, POX and Pyretic.
Libraries for programming with hardware.
- PyUserInput — A module for cross-platform control of the mouse and keyboard.
- wifi — A Python library and command line tool for working with WiFi on Linux.
- scapy — A brilliant packet manipulation library.
- ino — Command line toolkit for working with Arduino.
- Pyro — Python Robotics.
Libraries for migrating from Python 2 to 3.
- Six — Python 2 and 3 compatibility utilities.
- Python-Future — The missing compatibility layer between Python 2 and Python 3.
- Python-Modernize — Modernizes Python code for eventual Python 3 migration.
Useful libraries or tools that don’t fit in the categories above.
- pluginbase — A simple but flexible plugin system for Python.
- itsdangerous — Various helpers to pass trusted data to untrusted environments.
- blinker — A fast Python in-process signal/event dispatching system.
- Pychievements — A framework for creating and tracking achievements.
Algorithms and Design Patterns
Python implementation of algorithms and design patterns.
- python-patterns — A collection of design patterns in Python.
- algorithms — module of algorithms for Python.
Plugins for editors and IDEs.
- Vim
- Python-mode — An all in one plugin for turning Vim into a Python IDE.
- Jedi-vim — Vim bindings for the Jedi autocompletion library for Python.
- YouCompleteMe — Includes Jedi-based completion engine for Python
- Emacs
- Elpy — Emacs Python Development Environment.
- Sublime Text
- SublimeJEDI — A Sublime Text plugin to the awesome autocomplete library Jedi.
- Anaconda — Anaconda turns your Sublime Text 3 in a full featured Python development IDE.
- Atom
- Linter — A static code analysis tool for Atom.
- Linter-flake8 — An addon to linter , that acts as an interface for flake8 .
- virtualenv — Atom package for virtualenv management.