- Windows Command Line Output Error To File
- command line — Redirect Windows cmd stdout and stderr to a .
- How to Redirect Command Prompt Output to a File [Easy]
- How to save command output to file using Command Prompt or .
- Solved: output batch errors to log files Tech Support Guy
- Batch files — How To . Display and Redirect Output
- Reading the output of a command into a batch file variable .
- Windows Batch Script: Redirect ALL output to a file .
- How to Fix Command Prompt Not Working in Windows 10 Error
- How to save command output to file from Command Prompt and .
- Windows Command Line Output Error To File Fixes & Solutions
- Redirect Output from the Windows Command Line to a Text File
- How Windows Command Prompt Output Works
- Redirect Standard Output Write to New File
- Redirect Standard Output Writes to the Same File
- Redirect Standard Error To a File
- Redirect All Output Writes to a Same File
- Silencing Standard or Error Output Streams
- VS Code: command-line error:missing source file name
- 4 Answers 4
- Redirect Windows cmd stdout and stderr to a single file
- 7 Answers 7
- Background info from MSKB
- From MSKB110930
- Redirecting Error Messages from Command Prompt: STDERR/STDOUT
- Summary
- Example
Windows Command Line Output Error To File

We have collected for you the most relevant information on Windows Command Line Output Error To File, as well as possible solutions to this problem. Take a look at the links provided and find the solution that works. Other people have encountered Windows Command Line Output Error To File before you, so use the ready-made solutions.
command line — Redirect Windows cmd stdout and stderr to a .
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1420965/redirect-windows-cmd-stdout-and-stderr-to-a-single-file
- You can print the errors and standard output to a single file by using the «&1» command to redirect the output for STDERR to STDOUT and then sending the output from STDOUT to a …
How to Redirect Command Prompt Output to a File [Easy]
- https://www.lifewire.com/how-to-redirect-command-output-to-a-file-2618084
- Apr 05, 2020 · To save the command output to a file in a specific folder that doesn’t yet exist, first, create the folder and then run the command. Make folders without leaving Command Prompt with the mkdir command. ping 10.1.0.12 > «C:\Users\jonfi\Desktop\Ping Results.txt» Redirecting «ping» Results to a TXT File in a Different Folder.Estimated Reading Time: 3 mins
How to save command output to file using Command Prompt or .
- https://www.windowscentral.com/how-save-command-output-file-using-command-prompt-or-powershell
- Feb 12, 2019 · On Windows 10, the ability to save the output of a PowerShell or Command Prompt command to a text file can come in handy in many scenarios.For example, when you’re troubleshooting a …Estimated Reading Time: 3 mins
Solved: output batch errors to log files Tech Support Guy
- https://forums.techguy.org/threads/solved-output-batch-errors-to-log-files.749357/
- Sep 16, 2008 · The only thing that will appear on the Command Prompt window are errors. By default, the redirection only redirects STDOUT, not STDERR. You can redirect STDERR to a file as well, but not the same file to which the STDOUT is being sent. And, you can’t output to both a file and the Command Prompt window at the same time, at least not natively.
Batch files — How To . Display and Redirect Output
- https://www.robvanderwoude.com/battech_redirection.php
- Standard Output is the stream where all, well, standard output of commands is being sent to. The ECHO command sends all its output to Standard Output. Standard Error is the stream where many (but not all) commands send their error messages.
Reading the output of a command into a batch file variable .
- https://devblogs.microsoft.com/oldnewthing/20120731-00/?p=7003
- Jul 31, 2012 · The Windows command processor does not have direct backquoting, but you can fake it by abusing the FOR command. Here’s the evolution: Here’s the evolution: The /F flag to the FOR command says that it should open the file you pass in parentheses and set the loop variable to the contents of each line.
Windows Batch Script: Redirect ALL output to a file .
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15346863/windows-batch-script-redirect-all-output-to-a-file
- Just as «command > file» redirects STDOUT to a file, you may also redirect arbitrary file descriptors to each other. The >& operator redirects between file descriptors. So, 2 >& 1 redirects all STDERR output to STDO…
How to Fix Command Prompt Not Working in Windows 10 Error
- https://www.guidingtech.com/fix-command-prompt-not-working/
- Jul 05, 2019 · Sometimes, the SFC command fails to perform its duty because it fails to find or access the correct files from the Windows image. That is when you will …
How to save command output to file from Command Prompt and .
- https://www.addictivetips.com/windows-tips/save-command-output-to-file-command-prompt-powershell-windows-10/
- Apr 05, 2019 · In PowerShell, you can send command output to a file the same way you can in Command Prompt. Enter the command you want to run and before you tap Enter, add the following at the end. Again, you won’t have to create the text file. PowerShell will do that for you.
Windows Command Line Output Error To File Fixes & Solutions
We are confident that the above descriptions of Windows Command Line Output Error To File and how to fix it will be useful to you. If you have another solution to Windows Command Line Output Error To File or some notes on the existing ways to solve it, then please drop us an email.
Redirect Output from the Windows Command Line to a Text File
Avoid scrolling and/or save the generated output
One of the most useful ways to log and troubleshoot the behavior of commands or batch jobs that you run on Windows is to redirect output to a file.
However, there are a few different ways you can redirect command line writes to a file. The option you choose depends on how you want to view your command output.
How Windows Command Prompt Output Works
When you type a command in the Windows console (command prompt), the output from that command goes to two separate streams.
- STDOUT: Standard Out is where any standard responses from commands go. For example the standard response for the DIR command is a list of files inside a directory.
- STDERR: Standard Error is where any error messages go if there’s a problem with the command. For example if there aren’t any files in the directory, the DIR command will output “File Not Found” to the Standard Error stream.
You can redirect output to a file in Windows for both of these output streams.
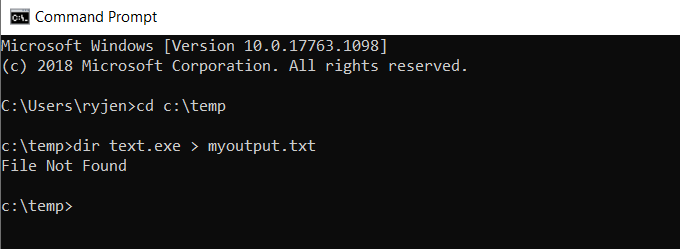
Redirect Standard Output Write to New File
There are two ways you can redirect standard output of a command to a file. The first is to send the command output write to a new file every time you run the command.
To do this, open the command prompt and type:
The > character tells the console to output STDOUT to the file with the name you’ve provided.
When you run this command, you’ll notice that there isn’t any response in the command window except the error that the file doesn’t exist.
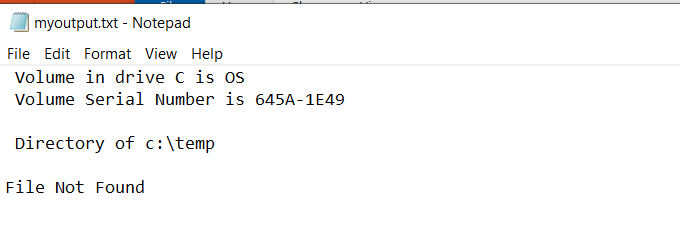
This is because the standard output for the command was redirected to a file called myoutput.txt. The file now exists in the same directory where you ran the command. The standard error output still displays as it normally does.
Note: Be careful to change the active directory for the command prompt before running the command. This way you’ll know where the output files are stored.
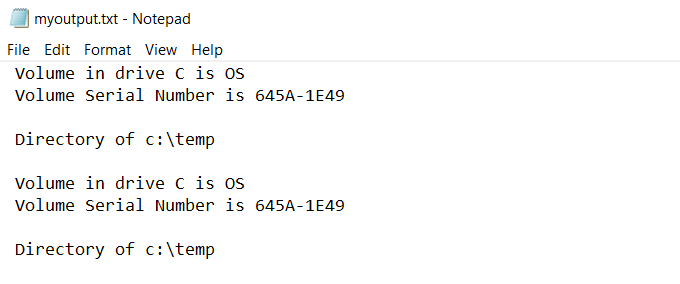
You can view the standard output that went to the file by typing “myoutput.txt” in the command window. This will open the text file in your default text file viewer. For most people, this is usually Notepad.exe.
The next time you run the same command, the previous output file will be deleted. A new output file will be recreated with the latest command’s output.
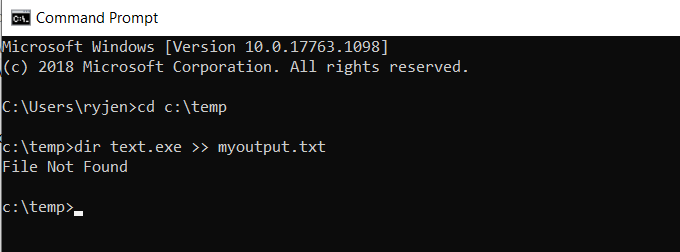
Redirect Standard Output Writes to the Same File
What if you don’t want to overwrite the same file? Another option is to use >> rather than > to redirect to an output file. In the case of this example, you would type:
You’ll see the same output (the error only).
But in this case, instead of overwriting the output file, this command appends the new output to the existing output file.
Every time you run a command and append the output to a file, it’ll write the new standard output to the end of the existing file.
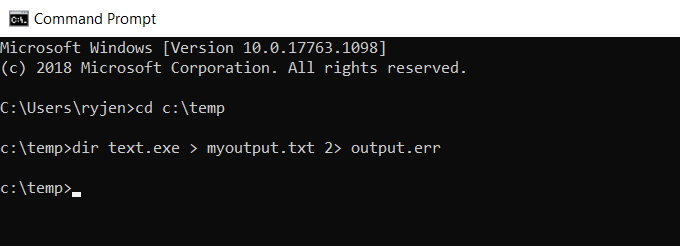
Redirect Standard Error To a File
The same way you can redirect standard output writes to a file, you can also output the standard error stream to a file.
To do this, you’ll need to add 2> to the end of the command, followed by the output error file you want to create.
In this example, you’ll type the command:
This sends the standard output stream to myoutput.txt, and the standard error stream to output.err. The result is that no output stream at all gets displayed in the console window.
However, you can see the error messages by typing output.err. This will open the file in your default text file viewer.
As you can see, any error messages from the command are output to the error file. Just as with the standard output, you can use >> instead to append the error to errors from previously run commands.
Redirect All Output Writes to a Same File
All of the approaches above result in multiple files. One file is for the standard output stream and the other is for the standard error stream.
If you want to include both of these outputs to the same file, you can do that too. To do this, you just need to redirect all output to the same file using the following command.
Here’s how this command works:
- The standard output is directed to the output file identified by output number 1.
- The standard error output identified by the number 2 is redirected to the output file identified by number 1.
This will append the error output to the end of the standard output.
This is a useful way to see all output for any command in one file.
Silencing Standard or Error Output Streams
You can also turn off either Standard Output or Standard Error by redirecting the output to a NUL instead of a file.
Using the example above, if you only want Standard Output and no Standard Error at all, you can use the following command:
This will result in the same output file as the first example above where you only redirected the Standard Output, but with this command the error won’t echo inside the console. It won’t create an error log file either.
This is useful if you don’t care about any errors and don’t want them to become a nuisance.
You can perform any of the same output commands above from inside a BAT file and the output from that line will go to the output file you specify. This is a useful way to see whether any commands within a BAT file had any errors when they tried to run.
Ryan has been writing how-to and other technology-based articles online since 2007. He has a BSc degree in Electrical Engineering and he’s worked 13 years in automation engineering, 5 years in IT, and now is an Apps Engineer. Read Ryan’s Full Bio
VS Code: command-line error:missing source file name
This is picture of my screen: 
I use gcc. gcc -o outputname filename.c and using C/C++ IntelliSense, debugging, and code browsing extension by Microsoft.
4 Answers 4
As you didn’t explain the question well. I think that there is a macro in the build options that is not defined so it gets inserted into the build command as a blank string. Does your project use some macros in the build options maybe something for 55x CSL directory?
If so make sure to define these macros on the macro tab of the build options dialog.
Various things may contribute to this error:
- unclosed quotes in preprocessor definitions, macros or even c_cpp_properties.json
- file encoding
- the VS Code cpp extension
It has come and gone in my c/c++ development, and I don’t know if anything specific I’ve done fixes it or if just restarting VS Code is the solution.
Most recently, I
- changed the encoding of all files from UTF-8 to ANSI (in case there were any hidden unicode characters in the file, which happens with copy & paste sometimes)
- restarted VS Code
- it then complained that the c/c++ extension wasn’t installed (it was?) and so I installed it again, and the error is gone.
Redirect Windows cmd stdout and stderr to a single file
I’m trying to redirect all output (stdout + stderr) of a DOS command to a single file:
Is it possible, or should I just redirect to two separate files?
7 Answers 7
The syntax 2>&1 will redirect 2 (stderr) to 1 (stdout). You can also hide messages by redirecting to NUL , more explanation and examples on MSDN.
Anders Lindahl’s answer is correct, but it should be noted that if you are redirecting stdout to a file and want to redirect stderr as well then you MUST ensure that 2>&1 is specified AFTER the 1> redirect, otherwise it will not work.
Background info from MSKB
While the accepted answer to this question is correct, it really doesn’t do much to explain why it works, and since the syntax is not immediately clear I did a quick google to find out what was actually going on. In the hopes that this information is helpful to others, I’m posting it here.
From MSKB110930
Redirecting Error Messages from Command Prompt: STDERR/STDOUT
Summary
When redirecting output from an application using the ‘>’ symbol, error messages still print to the screen. This is because error messages are often sent to the Standard Error stream instead of the Standard Out stream.
Output from a console (Command Prompt) application or command is often sent to two separate streams. The regular output is sent to Standard Out (STDOUT) and the error messages are sent to Standard Error (STDERR). When you redirect console output using the «>» symbol, you are only redirecting STDOUT. In order to redirect STDERR you have to specify ‘2>’ for the redirection symbol. This selects the second output stream which is STDERR.
Example
The command dir file.xxx (where file.xxx does not exist) will display the following output:
If you redirect the output to the NUL device using dir file.xxx > nul , you will still see the error message part of the output, like this:
To redirect (only) the error message to NUL , use the following command:
Or, you can redirect the output to one place, and the errors to another.
You can print the errors and standard output to a single file by using the «&1» command to redirect the output for STDERR to STDOUT and then sending the output from STDOUT to a file: