- Batch File Loop Skip File if name contains
- 5 Answers 5
- How to verify if a file exists in a batch file?
- 3 Answers 3
- IF… OR IF… in a windows batch file
- 14 Answers 14
- Batch file: Find if substring is in string (not in a file)
- 10 Answers 10
- Batch file commands
- Batch file commands: Windows/DOS
- List of batch file commands
- ASSOC
- ATTRIB
- CD
- CHKDSK
- CHOICE
- CLS
- CMD
- COMP
- CONVERT
- COPY
- DATE
- DEL
- DIR
- DISKPART
- DRIVERQUERY
- ECHO
- EXIT
- EXPAND
- FC
- FIND
- FORMAT
- HELP
- IPCONFIG
- LABEL
- MD
- MORE
- MOVE
- NET
- PATH
- PAUSE
- PING
- RD
- REM
- REN
- SET
- SHUTDOWN
- SORT
- START
- SYSTEMINFO
- TASKKILL
- TASKLIST
- TIME
- TITLE
- TREE
- TYPE
- VER
- VOL
- XCOPY
Batch File Loop Skip File if name contains
I am creating this batch file, that works with handbrakecli, to batch convert avi to mp4.
However I am stuck in how to continue the loop and skip the current file inside a loop.
This currently doesn’t work in skipping the files that contain trailer or sample
I have tried using find or findstr and both fail to skip.
Here is for sample.
If a file contains either trailer or sample, I do not want to do any handbrakecli conversions, but to just skip it.
I do echo’s to display which files get converted, and it does include files with Sample or sample in the name.
I have tried using find or findstr and both fail to set skip to yes
if skip == No do ( rem do conversion )
I only want to convert non-trailer/sample avi files.
Thank you for your time.
5 Answers 5
try this, put your conversion commands in the loop and remove the word echo before handbrakecli if the output is OK:
The file name+file path is in the variable «!fpath!» .
Added some code concerning the needs of the OP:
This should work:
nG . Findstr will certainly be slower but I suspect each AVI encode will take longer than an hour, so time isn’t a factor. 🙂 – foxidrive Jun 3 ’13 at 8:41
It’s difficult to see where your post is pseudocode and where actual code.
The first sample contains only REM statements, so it’s not surprising it apparently does nothing.
Your second and third sample are effectively identical — the only difference is the target string. It’s not surprising that the variable skip isn’t set to Yes since the correct syntax is
The syntax you’ve posted will REPORT that skip is not defined — it ignores the Yes
HOWEVER this syntax is only usable OUTSIDE of a «block statement» — that is, a multiple-instruction statement (enclosed in parentheses) or cascaded&by&ersands. Batch first PARSES a complete statement — from the FOR or if through to the appropriate closing-parenthesis and THEN executes it. As part of the PARSING phase, any %var% — including %errorlevel% is replaced by its value as it stands at the time the entire statement is parsed — not as it changes due to the operation of the for .
In order to use the value as it changes, you need to use
where do_something and do_something_else) may themselves be compound statements.
where the variable either is defined or not
But it’s quite possible that
will give you an appropriate skeleton.
Echo the filename through FINDSTR and look for «sample» or «trailer» /i case-insensitive. Findstr sets errorlevel 0 if either target string is found, 1 otherwise — and the if errorlevel x syntax works on the dynamic value of errorlevel within a loop.
How to verify if a file exists in a batch file?
I have to create a .BAT file that does this:
- If C:\myprogram\sync\data.handler exists, exit;
- If C:\myprogram\html\data.sql does not exist, exit;
- In C:\myprogram\sync\ delete all files and folders except ( test , test3 and test2 )
- Copy C:\myprogram\html\data.sql to C:\myprogram\sync\
- Call other batch file with option sync.bat myprogram.ini .
If it was in the Bash environment it was easy for me, but I do not know how to test if a file or folder exists and if it is a file or folder.
3 Answers 3
You can use IF EXIST to check for a file:
If you do not need an «else», you can do something like this:
Here’s a working example of searching for a file or a folder:
Type IF /? to get help about if, it clearly explains how to use IF EXIST.
To delete a complete tree except some folders, see the answer of this question: Windows batch script to delete everything in a folder except one
Finally copying just means calling COPY and calling another bat file can be done like this:
Here is a good example on how to do a command if a file does or does not exist:
We will take those three files and put it in a temporary place. After deleting the folder, it will restore those three files.
Use the XCOPY command:
I will explain what the /c /d /h /e /i /y means:
Call other batch file with option sync.bat myprogram.ini.
I am not sure what you mean by this, but if you just want to open both of these files you just put the path of the file like
If it was in the Bash environment it was easy for me, but I do not know how to test if a file or folder exists and if it is a file or folder.
You are using a batch file. You mentioned earlier you have to create a .bat file to use this:
I have to create a .BAT file that does this:
IF… OR IF… in a windows batch file
Is there a way to write an IF OR IF conditional statement in a windows batch-file?
14 Answers 14
The zmbq solution is good, but cannot be used in all situations, such as inside a block of code like a FOR DO(. ) loop.
An alternative is to use an indicator variable. Initialize it to be undefined, and then define it only if any one of the OR conditions is true. Then use IF DEFINED as a final test — no need to use delayed expansion.
You could add the ELSE IF logic that arasmussen uses on the grounds that it might perform a wee bit faster if the 1st condition is true, but I never bother.
Addendum — This is a duplicate question with nearly identical answers to Using an OR in an IF statement WinXP Batch Script
Final addendum — I almost forgot my favorite technique to test if a variable is any one of a list of case insensitive values. Initialize a test variable containing a delimitted list of acceptable values, and then use search and replace to test if your variable is within the list. This is very fast and uses minimal code for an arbitrarily long list. It does require delayed expansion (or else the CALL %%VAR%% trick). Also the test is CASE INSENSITIVE.
The above can fail if VAR contains = , so the test is not fool-proof.
If doing the test within a block where delayed expansion is needed to access current value of VAR then
FOR options like «delims=» might be needed depending on expected values within VAR
The above strategy can be made reliable even with = in VAR by adding a bit more code.
But now we have lost the ability of providing an ELSE clause unless we add an indicator variable. The code has begun to look a bit «ugly», but I think it is the best performing reliable method for testing if VAR is any one of an arbitrary number of case-insensitive options.
Finally there is a simpler version that I think is slightly slower because it must perform one IF for each value. Aacini provided this solution in a comment to the accepted answer in the before mentioned link
The list of values cannot include the * or ? characters, and the values and %VAR% should not contain quotes. Quotes lead to problems if the %VAR% also contains spaces or special characters like ^ , & etc. One other limitation with this solution is it does not provide the option for an ELSE clause unless you add an indicator variable. Advantages are it can be case sensitive or insensitive depending on presence or absence of IF /I option.
Batch file: Find if substring is in string (not in a file)
In a batch file, I have a string abcdefg . I want to check if bcd is in the string.
Unfortunately it seems all of the solutions I’m finding search a file for a substring, not a string for a substring.
Is there an easy solution for this?
10 Answers 10
Yes, you can use substitutions and check against the original string:
The %str1:bcd=% bit will replace a bcd in str1 with an empty string, making it different from the original.
If the original didn’t contain a bcd string in it, the modified version will be identical.
Testing with the following script will show it in action:
And the results of various runs:
A couple of notes:
- The if statement is the meat of this solution, everything else is support stuff.
- The x before the two sides of the equality is to ensure that the string bcd works okay. It also protects against certain «improper» starting characters.
You can pipe the source string to findstr and check the value of ERRORLEVEL to see if the pattern string was found. A value of zero indicates success and the pattern was found. Here is an example:
When this is run in CMD.EXE, we get:
I usually do something like this:
I don’t know if this is the best way.
For compatibility and ease of use it’s often better to use FIND to do this.
You must also consider if you would like to match case sensitively or case insensitively.
The method with 78 points (I believe I was referring to paxdiablo’s post) will only match Case Sensitively, so you must put a separate check for every case variation for every possible iteration you may want to match.
( What a pain! At only 3 letters that means 9 different tests in order to accomplish the check! )
In addition, many times it is preferable to match command output, a variable in a loop, or the value of a pointer variable in your batch/CMD which is not as straight forward.
For these reasons this is a preferable alternative methodology:
Use: Find [/I] [/V] «Characters to Match»
[/I] (case Insensitive) [/V] (Must NOT contain the characters)
As mentioned this is great for things which are not in variables which allow string substitution as well:
Batch file commands
In this tutorial, you will learn about batch file commands and how they are used in batch file scripting or programming.
As discussed in the previous tutorial, a batch file is an unformatted text file or script file which contains multiple batch file commands or instructions to achieve a certain task. It has extension of .bat or .cmd .
Batch file commands: Windows/DOS
For the ease of learning, we have listed all the batch file commands with relevant examples and explanations below. Please click on the commands to know the details.
List of batch file commands
Note: Batch file commands are not case sensitive
ASSOC
The batch command ASSOC associates a file extension with a file type, or list all associations.
Example
Output
As shown in above output, it displays the file association for .txt extension.
If only ASSOC is written and executed, it will display all the file associations for every extension, instead of just .txt extension.
ATTRIB
The batch command ATTRIB is used to display the file attributes or set an attribute to a file in the working directory.
Example
Now let us suppose we have a file note.txt in our working directory. We will display its file attributes and then make it hidden and read only by adding ‘ah’ and ‘r’ attributes to it. And finally, we will remove some attributes we added as well.
Output
Here in this output, A means Archived, R means Read only and AH means Hidden file.
CD
The batch command CD helps in navigating through different directories and changing directories or displaying current directory.
Example
Output
CHKDSK
The batch command CHKDSK is used for checking error in the disk.
Example
CHOICE
The batch command CHOICE provides a list of options to the user.
Example
Output
Now that script will produce following output.
Now the console waits for your input and once you enter your answer it will terminate.
CLS
The batch command CLS clears the screen.
Example
This command just clears all the logs in command prompt screen.
CMD
The batch command CMD invokes a new command prompt window.
Example
COMP
The batch command COMP compares the size of two files and checks if they are different in size.
Example
CONVERT
The batch command CONVERTS the volumes or drives from one format to another i.e from FAT to NTFS.
Example
COPY
The batch command COPY is used for copying files from one location to another.
Example
DATE
The batch command DATE displays the current date in the system.
Example
Output
This command DATE displays system date in command prompt as shown above.
DEL
The batch command DEL is used for deleting files.
Example
Note: DEL command only deletes files, not directories.
DIR
The batch command DIR lists all the contents of directories.
Example
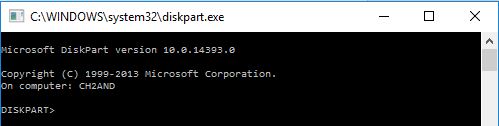
DISKPART
The batch command DISKPART shows the properties of a disk partition.
Example
This script will ask for users permission to check the properties of disk partition and if allowed, will display following output in the console depending on disk properties.
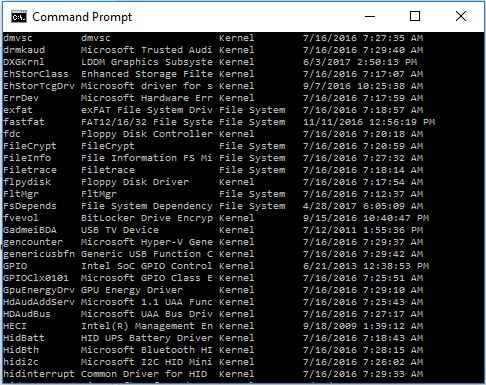
DRIVERQUERY
The batch command DRIVERQUERY displays all the drivers installed and their properties.
Example
Output
This output shows the fraction of drivers list with their properties and installed date. DRIVERQUERY command shows all the drivers list, which is huge.
ECHO
The batch command ECHO is used for echoing commands on/off and printing message to the console.
Example
Output
This command ECHO displays Hello in the console as shown above.
Besides printing message, echo is also used for deciding whether or not to display the command itself. Like in this example as well, in the first line we have turned OFF echo, which makes sure that commands themselves are not printed.
If that echo wasn’t turned off, then the output would have been like:
EXIT
The batch command EXIT terminates and exits the console.
Example
In this example, as soon as HI is printed in the console, EXIT command will terminate the program and close the output console.
EXPAND
The batch command EXPAND extracts the contents of .cab file.
Example
This script will extract all the contents of xyz.cab file to the same location where xyz.cab is located.
FC
The batch command FC finds the difference between the two files and displays them to console.
Example
This script will find the difference in the content of both files and list out all of them.
FIND
The batch command FIND search the given file to find the desired string and if located, it displays the corresponding line in which the string exists.
Example
This script will search for the string “find me” in example.txt file and if it exists in example.txt, it will display the corresponding line on the console.
FORMAT
The batch command FORMAT is used for formatting a drive of format FAT 16/32 or NTFS in Windows.
Example
This script will format E drive and overwrite previous contents.
HELP
This might be the one of the most important batch file commands because with this HELP command we can know about all the other commands used in batch file or command prompt.
Example
Now this will display all the available commands with their functionalities in the console.
Since the list of commands is so much more, we have sliced the list and shown few here.
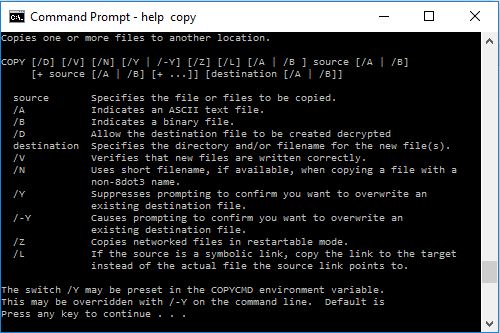
Now that we have a list of batch file commands, we can also view details of their syntax and functionalities in following way:
Now this will display details of the copy command.
As you can see, it HELP COPY displays all the details about COPY command.
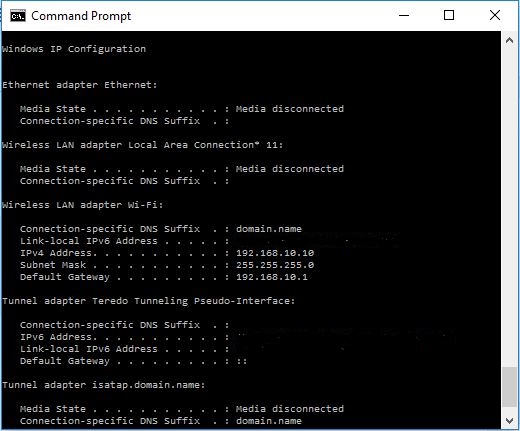
IPCONFIG
The batch command IPCONFIG displays Windows IP configuration.
Example
This script will generate following output.
P.S: We have hidden iPV6 address in above output.
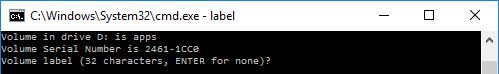
LABEL
The batch command LABEL displays the label of a drive or volume and is also is used for adding, setting or removing a disk label.
Example
Now this will display the label of your working directory and you can set, remove or add another label.
For example, my working directory is D: and has label ‘apps’. So, it will generate following output:
MD
The batch command MD creates a new directory or folder in the working directory.
Example
This program will create a new directory abc in current working location.
MORE
The batch command MORE displays the content of a file one by one.
Example
This program will display the contents of example.txt line by line, one at a time.
MOVE
This batch command moves files from one directory to another, rename the directories and move the directories as well.
Example
In this way, MOVE command can be used to move files, directories and rename directories.
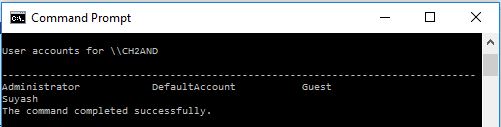
NET
The batch command NET is used for many network functionalities depending upon the commands used.
Example
To display the users:
This will generate following output:
Like users, there are many other commands:
- net accounts
- net computer
- net config
- net continue
- net file
- net group
- net help
- net name
- net pause
- net print
- net send
- net session
- net share
- net start
- net statistics
- net stop
- net time
- net use
- net view
PATH
The batch command PATH displays the path variable or it can be used to set path variable.
Example
This program will display the path of the current working directory.
PAUSE
The batch command PAUSE is used for holding the output screen till user enters a variable or a value.
Example
This program will print hi in the console and show the message ‘Press any key to continue..’ and wait for the input from the user.
PING
The batch command PING is used for sending ICMP/IP packets to the designated address over the network.
Example
Output
This script will send packets to address 127.0.1.1 and output will be displayed as follows:
RD
The batch command RD is used for removing the empty directories, directories with contents or files inside cannot be removed with RD command.
Example
REM
The batch command REM signifies comments in the batch script.
Example
Anything written after REM is interpreted as a comment and is not executed in batch programs.
REN
The batch command REN is used for renaming files and directories.
Example
SET
The batch command SET displays the list of environment variables of the system.
Example
SHUTDOWN
The batch command SHUTDOWN when invoked, shuts down the computer.
Example
SORT
The batch command SORT is used to sort the content of the file alphabetically.
Example
This script will sort the content of example.txt alphabetically either in ascending or descending order.
START
The batch command START is used to open a file or start a new program.
Example
This program will start the application paint if it is in the working location, else you will have to explicitly indicate the path of that program as well.
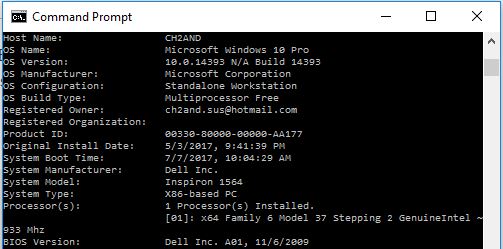
SYSTEMINFO
The batch command SYSTEMINFO displays all the configuration of the computer and operating system.
Example
This will generate following output depending upon the computer:
Of course, the details will be much more than this, but please try and look on your PC.
TASKKILL
The batch command TASKKILL is used to terminate a running task
Example
If you were to terminate the notepad running in your PC, then following script is used.
TASKLIST
The batch command TASKLIST lists all the running tasks in the console.
Example
TIME
The batch command TIME is used to display or set the system time.
Example
Output
The current time is displayed in the console.
TITLE
The batch command TITLE sets new title for output console.
Example
This script will set the title of output console to ‘New Console’. Thus the output console will look like:
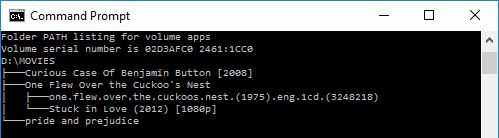
TREE
The batch command TREE displays the tree diagram of the subdirectories to the last level.
Example
I have a folder movies. SO, if I were to run TREE in that movie folder, it will create a tree of movies inside that folder and also the subdirectories where there is movie file and subtitle file.
Output
This script will generate following output.
TYPE
The batch command TYPE is used for displaying the content of a file to an output console.
Example
This program will display all the contents of notes.txt to the console.
VER
The batch command VER displays the version of Windows or MS-DOS.
Example
Output
VOL
The batch command VOL displays the current volume label of Windows.
Example
Output
XCOPY
The batch command XCOPY is similar to COPY command but COPY command copies single file whereas XCOPY command copies entire directories including subdirectories.
Example
This script will copy test.txt from D drive to E drive.
So, these are the batch file commands along with examples.
We hope you find these batch file commands easy to learn. We will discuss more advanced concepts in next tutorials.