- Frequently Asked Questions about using Python on Windows
- Trouble installing a package with pip install
- Trouble installing pip with WSL
- What is py.exe?
- Why does running python.exe open the Microsoft Store?
- Why don’t file paths work in Python when I copy-paste them?
- What is PYTHONPATH?
- Where can I find help with packaging and deployment?
- What if I need to work across different machines?
- What if I’m used to using PyCharm, Atom, Sublime Text, Emacs, or Vim?
- How do Mac shortcut keys map to Windows shortcut keys?
- Часто задаваемые вопросы об использовании Python в Windows
- Проблемы при установке пакета с помощью установщика pip
- Проблемы при установке pip с помощью WSL
- Что такое py.exe?
- Почему при запуске python.exe открывается Microsoft Store?
- Почему пути к файлам не работают в Python, когда я копирую и вставляю их?
- Что такое PYTHONPATH?
- Где можно найти справку по упаковке и развертыванию?
- Что делать, если мне нужно работать на разных компьютерах?
- Что делать, если я использую PyCharm, Atom, Sublime Text, Emacs или Vim?
- Насколько сочетания клавиш в Mac соответствуют сочетаниям клавиш в Windows?
- Get started using Python on Windows for beginners
- Set up your development environment
- Install Python
- Install Visual Studio Code
- Install Git (optional)
- Hello World tutorial for some Python basics
- Hello World tutorial for using Python with VS Code
- Create a simple game with Pygame
- Resources for continued learning
- Online courses for learning Python
- Working with Python in VS Code
Frequently Asked Questions about using Python on Windows
Trouble installing a package with pip install
There are a number of reasons why an installation will fail—in many cases the right solution is to contact the package developer.
A common cause for trouble is trying to install into a location that you do not have permission to modify. For example, the default install location might require Administrative privileges, but by default Python will not have them. The best solution is to create a virtual environment and install there.
Some packages include native code that requires a C or C++ compiler to install. In general, package developers should publish pre-compiled versions, but often do not. Some of these packages might work if you install Build Tools for Visual Studio and select the C++ option, however in most cases you will need to contact the package developer.
Trouble installing pip with WSL
When installing a package (like Flask) with pip on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL or WSL2), for example python3 -m pip install flask , you may specifically encounter an error like this:
When researching this problem you may be led down several rabbit holes, none of which are particularly productive with a WSL linux distribution. (Warning: on WSL do not try editing resolv.conf , that file is a symbolic link and modifying it is a can of worms). Unless you are running an aftermarket firewall, the likely solution is to simply re-install pip:
*Further discussion in the WSL product repo on GitHub. Thanks to our user community for contributing this issue to the docs.
What is py.exe?
You may end up with multiple versions of Python installed on your machine because you are working on different types of Python projects. Because these all use the python command, it may not be obvious which version of Python you are using. As a standard, it is recommended to use the python3 command (or python3.7 to select a specific version).
The py.exe launcher will automatically select the most recent version of Python you’ve installed. You can also use commands like py -3.7 to select a particular version, or py —list to see which versions can be used. HOWEVER, the py.exe launcher will only work if you are using a version of Python installed from python.org. When you install Python from the Microsoft Store, the py command is not included. For Linux, macOS, WSL and the Microsoft Store version of Python, you should use the python3 (or python3.7 ) command.
Why does running python.exe open the Microsoft Store?
To help new users find a good installation of Python, we added a shortcut to Windows that will take you directly to the latest version of the community’s package published in the Microsoft Store. This package can be installed easily, without administrator permissions, and will replace the default python and python3 commands with the real ones.
Running the shortcut executable with any command-line arguments will return an error code to indicate that Python was not installed. This is to prevent batch files and scripts from opening the Store app when it was probably not intended.
If you install Python using the installers from python.org and select the «add to PATH» option, the new python command will take priority over the shortcut. Note that other installers may add python at a lower priority than the built-in shortcut.
You can disable the shortcuts without installing Python by opening «Manage app execution aliases» from Start, finding the «App Installer» Python entries and switching them to «Off».
Why don’t file paths work in Python when I copy-paste them?
Python strings use “escapes” for special characters. For example, to insert a new line character into a string, you would type \n . Because file paths on Windows use backslashes, some parts might be being converted into special characters.
To paste a path as a string in Python, add the r prefix. This indicates that it is a raw string, and no escape characters will be used except for \” (you might need to remove the last backslash in your path). So your path might look like: r»C:\Users\MyName\Documents\Document.txt»
When working with paths in Python, we recommend using the standard pathlib module. This will let you convert the string to a rich Path object that can do path manipulations consistently whether it uses forward slashes or backslashes, making your code work better across different operating systems.
What is PYTHONPATH?
The PYTHONPATH environment variable is used by Python to specify a list of directories that modules can be imported from. When running, you can inspect the sys.path variable to see which directories will be searched when you import something.
To set this variable from the Command Prompt, use: set PYTHONPATH=list;of;paths .
To set this variable from PowerShell, use: $env:PYTHONPATH=’list;of;paths’ just before you launch Python.
Setting this variable globally through the Environment Variables settings is not recommended, as it may be used by any version of Python instead of the one that you intend to use.
Where can I find help with packaging and deployment?
Docker: VSCode extension helps you quickly package and deploy with Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml templates (generate the proper Docker files for your project).
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) enables you to deploy and manage containerized applications while scaling resources on demand.
What if I need to work across different machines?
Settings Sync allows you to synchronize your VS Code settings across different installations using GitHub. If you work on different machines, this helps keep your environment consistent across them.
What if I’m used to using PyCharm, Atom, Sublime Text, Emacs, or Vim?
The VSCode extension Keymaps can help your environment feel right at home.
How do Mac shortcut keys map to Windows shortcut keys?
Some of the keyboard buttons and system shortcuts are slightly different between a Windows machine and a Macintosh. This Mac to Windows transition guide covers the basics.
Часто задаваемые вопросы об использовании Python в Windows
Проблемы при установке пакета с помощью установщика pip
Есть ряд причин, по которым установка может завершиться сбоем. Во многих случаях правильным будет обратиться к разработчику пакета.
Распространенная причина проблем — попытка установки в расположение, для которого у вас нет разрешения на изменение. Например, для расположения установки по умолчанию могут потребоваться права администратора, но по умолчанию в Python их нет. Лучшее решение — создать виртуальную среду и установить пакет в ней.
Некоторые пакеты содержат машинный код, для установки которого требуется компилятор C или C++. Как правило, разработчики пакетов должны публиковать предварительно скомпилированные версии, но зачастую они этого не делают. Некоторые из этих пакетов могут работать, если установить средства сборки для Visual Studio и выбрать вариант C++, но в большинстве случаев необходимо обратиться к разработчику пакета.
Проблемы при установке pip с помощью WSL
При установке пакета (например, Flask) с использованием pip в подсистеме Windows для Linux (WSL или WSL2), например python3 -m pip install flask , может поступить примерно такое сообщение об ошибке:
При исследовании этой проблемы вы можете пойти несколькими путями, ни один из которых не работает с дистрибутивом WSL Linux достаточно продуктивно (предупреждение: в WSL не изменяйте файл resolv.conf , так как он является символьной ссылкой, при изменении которой может возникнуть уязвимость для червей). Если вы не используете неоригинальный брандмауэр, возможное решение — переустановить pip:
*Дальнейшее обсуждение можно найти в репозитории продуктов WSL в GitHub. Благодарим наше сообщество пользователей за добавление сведений об этой проблеме в документацию.
Что такое py.exe?
На компьютере может быть установлено несколько версий Python, потому что вы работаете с различными типами проектов Python. Так как все версии применяют команду python , может быть неясно, какая версия Python используется. В качестве стандарта рекомендуется использовать команду python3 (или python3.7 ), чтобы выбрать конкретную версию.
Средство запуска py.exe автоматически выберет последнюю установленную версию Python. Вы также можете выполнить такие команды, как py -3.7 , чтобы выбрать конкретную версию, или py —list , чтобы узнать, какие версии можно использовать. Но средство запуска py.exe будет работать только при использовании версии Python, установленной с сайта python.org. При установке Python из Microsoft Store команда py не поддерживается. Для версий Python для Linux, macOS, WSL и Microsoft Store следует использовать команду python3 (или python3.7 ).
Почему при запуске python.exe открывается Microsoft Store?
Чтобы помочь новым пользователям найти хорошую установку Python, мы добавили ярлык для Windows, который сразу же переведет вас к последней версии пакета сообщества, опубликованного в Microsoft Store. Этот пакет можно легко установить без прав администратора, и он заменит команды по умолчанию python и python3 на реальные.
Если запустить исполняемый файл ярлыка с любыми аргументами командной строки, будет возвращен код ошибки, указывающий на то, что Python не установлен. Это необходимо для того, чтобы пакетные файлы и скрипты не открывали приложение Store, если это не требуется.
Если вы устанавливаете Python с помощью установщиков с сайта python.org и выбираете параметр «Добавить в PATH», новая команда python будет иметь приоритет над ярлыком. Обратите внимание, что другие установщики могут добавлять python с более низким приоритетом, чем при использовании встроенного ярлыка.
Вы можете отключить ярлыки, не устанавливая Python. Для этого откройте в меню «Пуск» раздел Manage app execution aliases (Управление псевдонимами выполнения приложений), найдите записи «Установщик приложений» для Python и переключите их в режим «Отключено».
Почему пути к файлам не работают в Python, когда я копирую и вставляю их?
В строках Python для специальных символов используются escape-знаки. Например, чтобы вставить символ новой строки в строку, введите \n . Так как пути к файлам в Windows используют символы обратной косой черты, некоторые части могут быть преобразованы в специальные символы.
Чтобы вставить путь в виде строки в Python, добавьте префикс r . Это означает, что это строка raw , и escape-символы не будут использоваться, за исключением «» (вам может потребоваться удалить последний символ обратной косой черты в пути). Так что ваш путь может выглядеть следующим образом: r»C:\Users\MyName\Documents\Document.txt» .
При работе с путями в Python рекомендуется использовать стандартный модуль pathlib. Это позволит вам преобразовать строку в расширенный объект Path, который может последовательно выполнять манипуляции с путями, независимо от того, использует ли он символ косой или обратной косой черты, что улучшает выполнение вашего кода в разных операционных системах.
Что такое PYTHONPATH?
Переменная среды PYTHONPATH используется в Python для указания списка каталогов, из которых можно импортировать модули. При запуске можно проверить переменную sys.path , чтобы узнать, по каким каталогам будет выполняться поиск при импорте чего-либо.
Чтобы задать эту переменную из командной строки, используйте: set PYTHONPATH=list;of;paths .
Чтобы задать эту переменную из PowerShell, используйте $env:PYTHONPATH=’list;of;paths’ непосредственно перед запуском Python.
Глобальная установка этой переменной через параметры Переменные среды****не рекомендуется, так как она может использоваться любой версией Python вместо нужной.
Где можно найти справку по упаковке и развертыванию?
Расширение VS Code для Docker помогает быстро упаковать и развернуть шаблоны Dockerfile и docker-compose.yml (создайте соответствующие файлы Docker для проекта).
Служба Azure Kubernetes (AKS) позволяет развертывать контейнерные приложения и управлять ими при масштабировании ресурсов по требованию.
Что делать, если мне нужно работать на разных компьютерах?
Синхронизация параметров позволяет синхронизировать параметры VS Code в разных установках с помощью GitHub. Если вы работаете на разных компьютерах, это обеспечит согласованность среды между ними.
Что делать, если я использую PyCharm, Atom, Sublime Text, Emacs или Vim?
Расширение VS Code Keymaps может содействовать эффективной работе вашей среды.
Насколько сочетания клавиш в Mac соответствуют сочетаниям клавиш в Windows?
Некоторые кнопки клавиатуры и системные сочетания клавиш в компьютерах Windows и Macintosh несколько отличаются друг от друга. В этом руководстве по переходу с Mac на Windows рассматриваются основные сведения.
Get started using Python on Windows for beginners
The following is a step-by-step guide for beginners interested in learning Python using Windows 10.
Set up your development environment
For beginners who are new to Python, we recommend you install Python from the Microsoft Store. Installing via the Microsoft Store uses the basic Python3 interpreter, but handles set up of your PATH settings for the current user (avoiding the need for admin access), in addition to providing automatic updates. This is especially helpful if you are in an educational environment or a part of an organization that restricts permissions or administrative access on your machine.
If you are using Python on Windows for web development, we recommend a different set up for your development environment. Rather than installing directly on Windows, we recommend installing and using Python via the Windows Subsystem for Linux. For help, see: Get started using Python for web development on Windows. If you’re interested in automating common tasks on your operating system, see our guide: Get started using Python on Windows for scripting and automation. For some advanced scenarios (like needing to access/modify Python’s installed files, make copies of binaries, or use Python DLLs directly), you may want to consider downloading a specific Python release directly from python.org or consider installing an alternative, such as Anaconda, Jython, PyPy, WinPython, IronPython, etc. We only recommend this if you are a more advanced Python programmer with a specific reason for choosing an alternative implementation.
Install Python
To install Python using the Microsoft Store:
Go to your Start menu (lower left Windows icon), type «Microsoft Store», select the link to open the store.
Once the store is open, select Search from the upper-right menu and enter «Python». Open «Python 3.9» from the results under Apps. Select Get.
Once Python has completed the downloading and installation process, open Windows PowerShell using the Start menu (lower left Windows icon). Once PowerShell is open, enter Python —version to confirm that Python3 has installed on your machine.
The Microsoft Store installation of Python includes pip, the standard package manager. Pip allows you to install and manage additional packages that are not part of the Python standard library. To confirm that you also have pip available to install and manage packages, enter pip —version .
Install Visual Studio Code
By using VS Code as your text editor / integrated development environment (IDE), you can take advantage of IntelliSense (a code completion aid), Linting (helps avoid making errors in your code), Debug support (helps you find errors in your code after you run it), Code snippets (templates for small reusable code blocks), and Unit testing (testing your code’s interface with different types of input).
VS Code also contains a built-in terminal that enables you to open a Python command line with Windows Command prompt, PowerShell, or whatever you prefer, establishing a seamless workflow between your code editor and command line.
To install VS Code, download VS Code for Windows: https://code.visualstudio.com.
Once VS Code has been installed, you must also install the Python extension. To install the Python extension, you can select the VS Code Marketplace link or open VS Code and search for Python in the extensions menu (Ctrl+Shift+X).
Python is an interpreted language, and in order to run Python code, you must tell VS Code which interpreter to use. We recommend sticking with Python 3.7 unless you have a specific reason for choosing something different. Once you’ve installed the Python extension, select a Python 3 interpreter by opening the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), start typing the command Python: Select Interpreter to search, then select the command. You can also use the Select Python Environment option on the bottom Status Bar if available (it may already show a selected interpreter). The command presents a list of available interpreters that VS Code can find automatically, including virtual environments. If you don’t see the desired interpreter, see Configuring Python environments.
To open the terminal in VS Code, select View > Terminal, or alternatively use the shortcut Ctrl+` (using the backtick character). The default terminal is PowerShell.
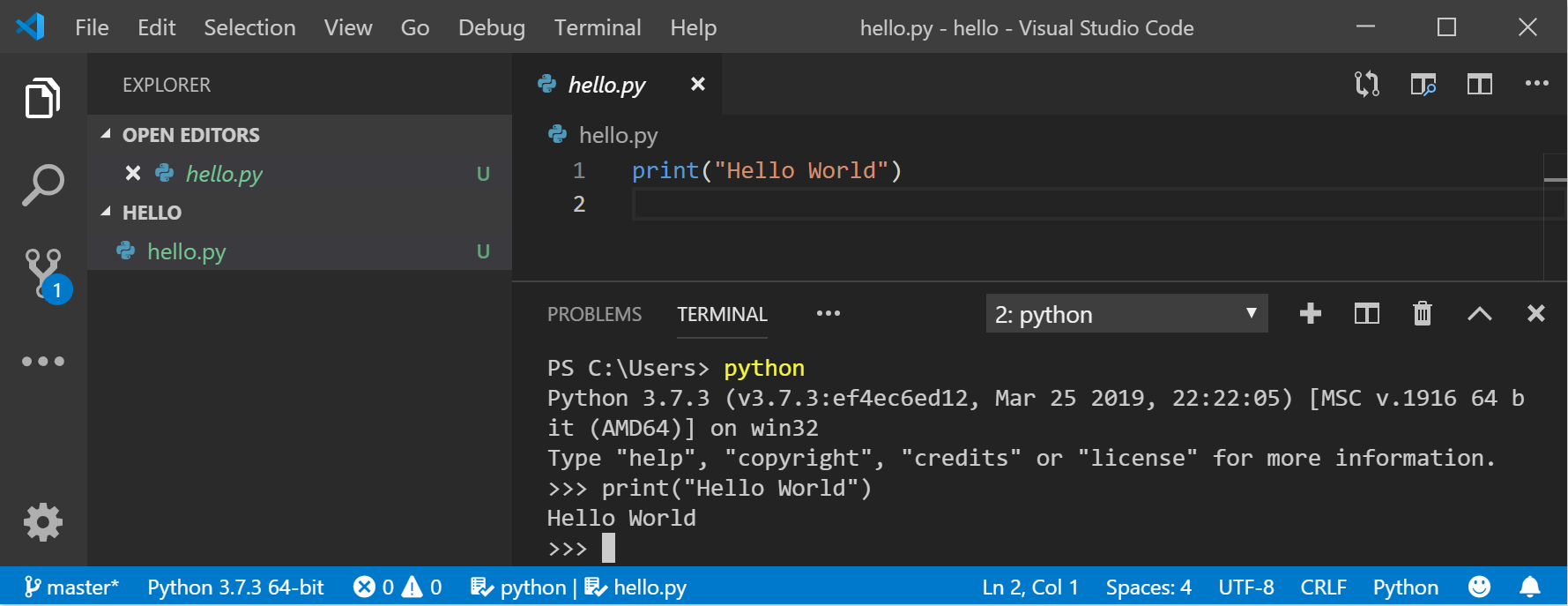
Inside your VS Code terminal, open Python by simply entering the command: python
Try the Python interpreter out by entering: print(«Hello World») . Python will return your statement «Hello World».
Install Git (optional)
If you plan to collaborate with others on your Python code, or host your project on an open-source site (like GitHub), VS Code supports version control with Git. The Source Control tab in VS Code tracks all of your changes and has common Git commands (add, commit, push, pull) built right into the UI. You first need to install Git to power the Source Control panel.
Download and install Git for Windows from the git-scm website.
An Install Wizard is included that will ask you a series of questions about settings for your Git installation. We recommend using all of the default settings, unless you have a specific reason for changing something.
If you’ve never worked with Git before, GitHub Guides can help you get started.
Hello World tutorial for some Python basics
Python, according to its creator Guido van Rossum, is a “high-level programming language, and its core design philosophy is all about code readability and a syntax which allows programmers to express concepts in a few lines of code.”
Python is an interpreted language. In contrast to compiled languages, in which the code you write needs to be translated into machine code in order to be run by your computer’s processor, Python code is passed straight to an interpreter and run directly. You just type in your code and run it. Let’s try it!
With your PowerShell command line open, enter python to run the Python 3 interpreter. (Some instructions prefer to use the command py or python3 , these should also work). You will know that you’re successful because a >>> prompt with three greater-than symbols will display.
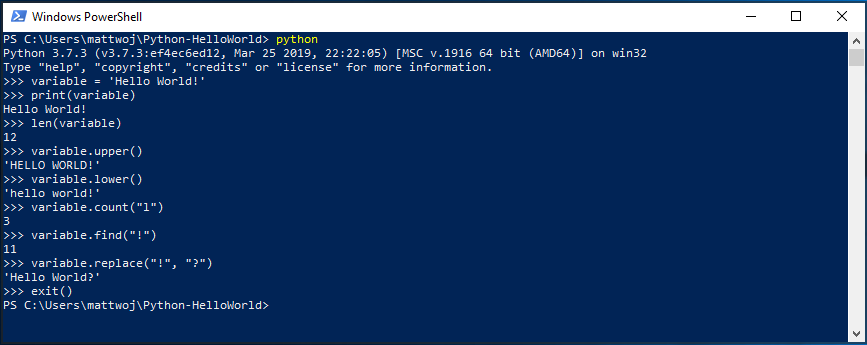
There are several built-in methods that allow you to make modifications to strings in Python. Create a variable, with: variable = ‘Hello World!’ . Press Enter for a new line.
Print your variable with: print(variable) . This will display the text «Hello World!».
Find out the length, how many characters are used, of your string variable with: len(variable) . This will display that there are 12 characters used. (Note that the blank space it counted as a character in the total length.)
Convert your string variable to upper-case letters: variable.upper() . Now convert your string variable to lower-case letters: variable.lower() .
Count how many times the letter «l» is used in your string variable: variable.count(«l») .
Search for a specific character in your string variable, let’s find the exclamation point, with: variable.find(«!») . This will display that the exclamation point is found in the 11th position character of the string.
Replace the exclamation point with a question mark: variable.replace(«!», «?») .
To exit Python, you can enter exit() , quit() , or select Ctrl-Z.
Hope you had fun using some of Python’s built-in string modification methods. Now try creating a Python program file and running it with VS Code.
Hello World tutorial for using Python with VS Code
The VS Code team has put together a great Getting Started with Python tutorial walking through how to create a Hello World program with Python, run the program file, configure and run the debugger, and install packages like matplotlib and numpy to create a graphical plot inside a virtual environment.
Open PowerShell and create an empty folder called «hello», navigate into this folder, and open it in VS Code:
Once VS Code opens, displaying your new hello folder in the left-side Explorer window, open a command line window in the bottom panel of VS Code by pressing Ctrl+` (using the backtick character) or selecting View > Terminal. By starting VS Code in a folder, that folder becomes your «workspace». VS Code stores settings that are specific to that workspace in .vscode/settings.json, which are separate from user settings that are stored globally.
Continue the tutorial in the VS Code docs: Create a Python Hello World source code file.
Create a simple game with Pygame
Pygame is a popular Python package for writing games — encouraging students to learn programming while creating something fun. Pygame displays graphics in a new window, and so it will not work under the command-line-only approach of WSL. However, if you installed Python via the Microsoft Store as detailed in this tutorial, it will work fine.
Once you have Python installed, install pygame from the command line (or the terminal from within VS Code) by typing python -m pip install -U pygame —user .
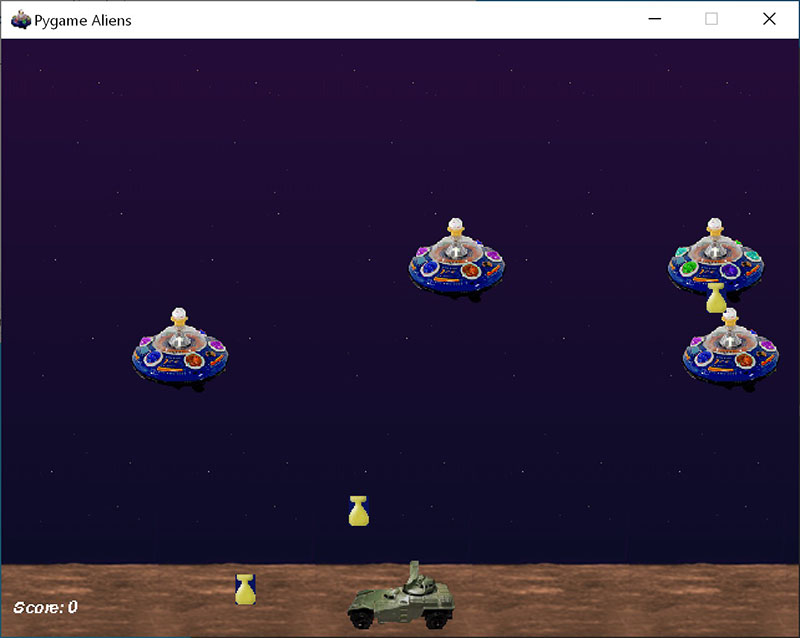
Test the installation by running a sample game : python -m pygame.examples.aliens
All being well, the game will open a window. Close the window when you are done playing.
Here’s how to start writing your own game.
Open PowerShell (or Windows Command Prompt) and create an empty folder called «bounce». Navigate to this folder and create a file named «bounce.py». Open the folder in VS Code:
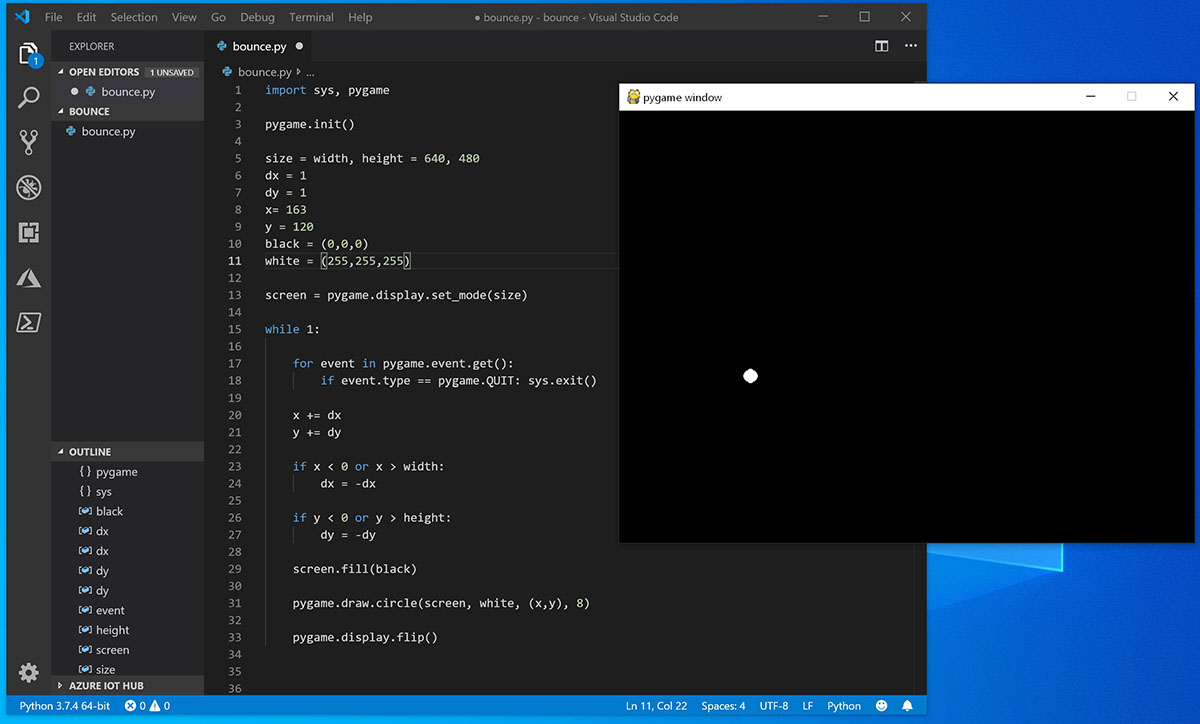
Using VS Code, enter the following Python code (or copy and paste it):
Save it as: bounce.py .
From the PowerShell terminal, run it by entering: python bounce.py .
Try adjusting some of the numbers to see what effect they have on your bouncing ball.
Read more about writing games with pygame at pygame.org.
Resources for continued learning
We recommend the following resources to support you in continuing to learn about Python development on Windows.
Online courses for learning Python
Introduction to Python on Microsoft Learn: Try the interactive Microsoft Learn platform and earn experience points for completing this module covering the basics on how to write basic Python code, declare variables, and work with console input and output. The interactive sandbox environment makes this a great place to start for folks who don’t have their Python development environment set up yet.
Python on Pluralsight: 8 Courses, 29 Hours: The Python learning path on Pluralsight offers online courses covering a variety of topics related to Python, including a tool to measure your skill and find your gaps.
LearnPython.org Tutorials: Get started on learning Python without needing to install or set anything up with these free interactive Python tutorials from the folks at DataCamp.
The Python.org Tutorials: Introduces the reader informally to the basic concepts and features of the Python language and system.
Learning Python on Lynda.com: A basic introduction to Python.
Working with Python in VS Code
Editing Python in VS Code: Learn more about how to take advantage of VS Code’s autocomplete and IntelliSense support for Python, including how to customize their behavior. or just turn them off.
Linting Python: Linting is the process of running a program that will analyse code for potential errors. Learn about the different forms of linting support VS Code provides for Python and how to set it up.
Debugging Python: Debugging is the process of identifying and removing errors from a computer program. This article covers how to initialize and configure debugging for Python with VS Code, how to set and validate breakpoints, attach a local script, perform debugging for different app types or on a remote computer, and some basic troubleshooting.
Unit testing Python: Covers some background explaining what unit testing means, an example walkthrough, enabling a test framework, creating and running your tests, debugging tests, and test configuration settings.