- Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
- Introduction
- Benefits of Windows Image Acquisition 2.0
- For Application Writers
- For Device Manufactures
- For Scanner Users
- Development of Windows Image Acquisition
- Overview of Windows Image Acquisition
- Facts about Windows Image Acquisition 2.0
- Developer Audience
- Run-Time Requirements
- WIA Topics
- What’s New in Windows Server 2016
- Compute
- General
- Hyper-V
- Nano Server
- Shielded Virtual Machines
- Identity and Access
- Active Directory Certificate Services
- Active Directory Domain Services
- Active Directory Federation Services
- Web Application Proxy
- Administration
- PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC) in Windows Management Framework (WMF) 5
- PackageManagement unified package management for software discovery, installation, and inventory
- PowerShell enhancements to assist digital forensics and help reduce security breaches
- Networking
- Software-Defined Networking
- TCP performance improvements
- Security and Assurance
- Just Enough Administration
- Credential Guard
- Remote Credential Guard
- Device Guard (Code Integrity)
- Windows Defender
- Control Flow Guard
- Storage
- Storage Spaces Direct
- Storage Replica
- Storage Quality of Service (QoS)
- Failover Clustering
- Cluster Operating System Rolling Upgrade
- Cloud Witness
- Health Service
- Application development
- Internet Information Services (IIS) 10.0
- Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)
Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
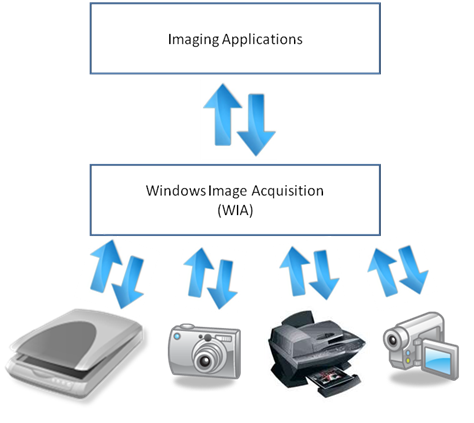
Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) is the still image acquisition platform in the Windows family of operating systems starting with WindowsВ Millennium Edition (WindowsВ Me) and WindowsВ XP.
Introduction
The WIA platform enables imaging/graphics applications to interact with imaging hardware and standardizes the interaction between different applications and scanners. This allows those different applications to talk to and interact with those different scanners without requiring the application writers and scanner manufactures to customize their application or drivers for each application-device combination.
Benefits of Windows Image Acquisition 2.0
WIA provides benefits to application developers, device manufacturers, and scanner users who need to interact with imaging hardware.
For Application Writers
- Windows runs a certification process for WIA drivers so WIA applications are guaranteed to be base-level compatible with all WIA-based scanners.
- WIA drivers are loaded in the WIA service process, thus providing a more stable driver environment.
- Applications can be initiated from the scanner scan button via push events supported by the WIA subsystem.
- The WIA includes a default segmentation filter that all drivers can take advantage of; this way, applications do not have to write code for multi-region scanning for purposes such as separating out a large number of photos spread over a flatbed scanner.
For Device Manufactures
- WIA driver certification process helps driver developers in establishing that their driver is WIA-compliant.
- WIA drivers can take advantage of a built-in segmentation filter, image processing filter and error handler, if they choose to do so.
- WIA-based scanners work right out of the box on Windows with Windows scanning applications such as Windows Fax and Scan and Paint.
- WIA drivers offer better integration with Windows such as the full device experience.
- WindowsВ Vista release includes a WSD-WIA class driver that enables all devices compliant with Web Services for Scanner (WS-Scan) protocol to work with WIA applications without any additional driver or software.
For Scanner Users
- WIA-based scanners can be used from Windows applications such Windows Fax and Scan and Paint without the need for any additional software.
- WIA-based applications and scanners can also take advantage of WIA add-ons such as the segmentation filter which enables such features as processing a number of pictures on the scanner and scanning them all to individual files without user intervention.
- WIA-based devices offers a much better integration with other Windows features such as the Device Stage feature for WindowsВ 7.
- WIA provides a more robust, stable and reliable scanning experience by isolating the driver and the application.
Development of Windows Image Acquisition
The imaging architecture in WindowsВ 2000 and WindowsВ 95 or later consisted of a low-level hardware abstraction, Still Image Architecture (STI), and a high-level set of APIs known as TWAIN. In WindowsВ XP and WindowsВ MeВ WIA was introduced. WIA is an imaging architecture that builds on STI and does not require TWAIN, although TWAIN is still supported alongside WIA.
WIA 1.0 was introduced in WindowsВ Me and WindowsВ XP and supports scanners, digital cameras and digital video equipment. WIA 2.0 was released with WindowsВ Vista. WIA 2.0 is targeted towards scanners but continues to offer support for legacy WIA 1.0 applications and devices through a WIA 1.0 to WIA 2.0 compatibility layer provided by the WIA service. However, video content support was removed from WIA for WindowsВ Vista. We recommend Windows Portable Devices (WPD) API for digital cameras and digital video equipment in the future. WIA 1.0 as well as STI TWAIN drivers are still supported directly on WindowsВ Vista and WindowsВ 7 alongside native WIA 2.0 device drivers and imaging applications.
Overview of Windows Image Acquisition
WIA provides a framework that allows a device to present its unique capabilities to the operating system and allows imaging applications to invoke those unique capabilities.
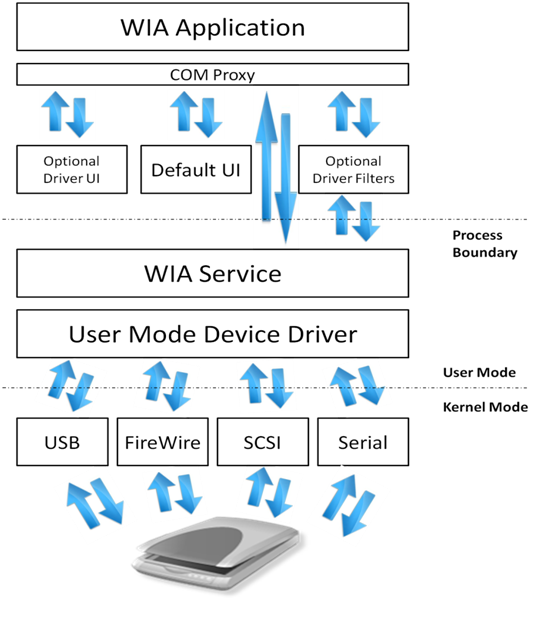
The WIA platform includes a data acquisition protocol, a Device Driver Model and Interface (DDI), an API and a dedicated WIA service. The platform also includes a set of built-in kernel mode drivers that support communication with imaging devices locally connected through USB, serial/parallel, SCSI and FireWire interfaces. The WIA subsystem also includes a transparent compatibility layer which allows TWAIN compatible applications to employ and use WIA-driver-based devices.
Network connected imaging devices that support Web Services for Devices (WSD) protocol can also be used from WIA-compliant imaging applications on WindowsВ Vista and WindowsВ 7 out of the box via a WSD-WIA class driver that shipped as part of WindowsВ Vista. The class driver converts WIA calls to WSD calls and vice versa and makes already existing WIA applications work with WSD based scanners without any additional driver.
WIA drivers are made up of a user interface (UI) component and a core driver component, loaded into two different process spaces: UI in the application space and the driver core in the WIA service space. The service runs in Local System context in WindowsВ XP and runs in Local Service context starting with Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ Vista for enhanced security against buggy or malicious drivers.
The WIA API set exposes imaging applications to still image acquisition hardware functionality by providing support for:
- Enumeration of available image acquisition devices.
- Creating connections to multiple devices simultaneously.
- Querying properties of devices in a standard and expandable manner.
- Acquiring device data by using standard and high performance transfer mechanisms.
- Maintaining image properties across data transfers.
- Notification of device status and scan event handling.
Windows added scripting support to WIA by releasing the WIA Automation Library in 2002 that was incorporated in WindowsВ Vista as Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) Automation Layer and continues to be a part of WindowsВ 7. The WIA Automation Library provides end-to-end image acquisition capabilities to automation-enabled application development environments and programming languages such as Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0, Active Server Pages (ASP), VBScript and C#.
For WindowsВ 7, WIAВ APIs have additional support to complement the already existing push-scanning support.
- Auto-configured device initiated scanning with scan parameters configured at the scanner on the device front panel.
- Automatic source selection for device-initiated scan.
Facts about Windows Image Acquisition 2.0
- The data transfer mechanism in WIA 2.0 is stream based. The stream abstraction removes the distinction between different transfer types and also allows exchange of mutually agreed-upon metadata between device and application.
- WIA 2.0 subsystem also includes a basic image processing filter driver add-on that is optionally replaceable by the scanner driver, if the driver chooses to provide a customized image processing filter. The built-in filter enables post processing of images acquired through the scanner. Image processing filter also enables live software previews when small settings such as brightness and contrast are adjusted.
- The segmentation filter is another handy WIA component that can be replaced by a more customized filter by the scanner driver. The segmentation filter can be used for multi-region scanning. Multi-region scanning, as an example, allows an application to automatically detect different scan regions without any user intervention, such as identifying a bunch of photos lying randomly on the scanner flatbed.
- WIA 2.0 provides a replaceable/extensible error handler to gracefully handle, and possibly recover from, software, hardware and configuration errors and delays. The error handler is another WIA component that can be replaced with a more customized version by the scanner driver. This extension provides status and error messages during data acquisitions such as «Lamp warming up,» «Cover open,» «Paper jam,» and so on. This extension also allows cleaner support for «Cancel operations.»
Developer Audience
The WIA API is designed for use by C/C++ programmers. Familiarity with the WindowsВ GUI and Component Object Model (COM) interfaces is required.
For developers familiar with Microsoft Visual BasicВ 6.0, Active Server Pages (ASP), or scripting, WIA provides an automation layer for WindowsВ XPВ Service PackВ 1 (SP1) or later that builds upon and simplifies access to the foundation provided by C/C++. For information about the automation layer, see Windows Image Acquisition Automation Layer.
The WIA Automation Layer supersedes Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)В 1.0 scripting.
Run-Time Requirements
Applications that use the WIAВ API require WindowsВ XP or later.
WIA Topics
The WIA topics are organized as shown in the following table.
What’s New in Windows Server 2016
Applies to: Windows Server 2016

Compute
The Virtualization area includes virtualization products and features for the IT professional to design, deploy, and maintain Windows Server.
General
Physical and virtual machines benefit from greater time accuracy due to improvements in the Win32 Time and Hyper-V Time Synchronization Services. Windows Server can now host services that are compliant with upcoming regulations which require a 1ms accuracy with regards to UTC.
Hyper-V
What’s new in Hyper-V on Windows Server 2016. This topic explains the new and changed functionality of the Hyper-V role in Windows Server 2016, Client Hyper-V running on Windows 10, and Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016.
Windows Containers: Windows Server 2016 container support adds performance improvements, simplified network management, and support for Windows containers on Windows 10. For some additional information on containers, see Containers: Docker, Windows and Trends.
Nano Server
What’s New in Nano Server. Nano Server now has an updated module for building Nano Server images, including more separation of physical host and guest virtual machine functionality as well as support for different Windows Server editions.
There are also improvements to the Recovery Console, including separation of inbound and outbound firewall rules as well as the ability to repair the configuration of WinRM.
Shielded Virtual Machines
Windows Server 2016 provides a new Hyper-V-based Shielded Virtual Machine to protect any Generation 2 virtual machine from a compromised fabric. Among the features introduced in Windows Server 2016 are the following:
New «Encryption Supported» mode that offers more protections than for an ordinary virtual machine, but less than «Shielded» mode, while still supporting vTPM, disk encryption, Live Migration traffic encryption, and other features, including direct fabric administration conveniences such as virtual machine console connections and Powershell Direct.
Full support for converting existing non-shielded Generation 2 virtual machines to shielded virtual machines, including automated disk encryption.
Hyper-V Virtual Machine Manager can now view the fabrics upon which a shielded virtual is authorized to run, providing a way for the fabric administrator to open a shielded virtual machine’s key protector (KP) and view the fabrics it is permitted to run on.
You can switch Attestation modes on a running Host Guardian Service. Now you can switch on the fly between the less secure but simpler Active Directory-based attestation and TPM-based attestation.
End-to-end diagnostics tooling based on Windows PowerShell that is able to detect misconfigurations or errors in both guarded Hyper-V hosts and the Host Guardian Service.
A recovery environment that offers a means to securely troubleshoot and repair shielded virtual machines within the fabric in which they normally run while offering the same level of protection as the shielded virtual machine itself.
Host Guardian Service support for existing safe Active Directory – you can direct the Host Guardian Service to use an existing Active Directory forest as its Active Directory instead of creating its own Active Directory instance
For more details and instructions for working with shielded virtual machines, see Shielded VMs and Guarded Fabric Validation Guide for Windows Server 2016 (TPM).
Identity and Access
New features in Identity improve the ability for organizations to secure Active Directory environments and help them migrate to cloud-only deployments and hybrid deployments, where some applications and services are hosted in the cloud and others are hosted on premises.
Active Directory Certificate Services
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) in Windows Server 2016 increases support for TPM key attestation: You can now use Smart Card KSP for key attestation, and devices that are not joined to the domain can now use NDES enrollment to get certificates that can be attested for keys being in a TPM.
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory Domain Services includes improvements to help organizations secure Active Directory environments and provide better identity management experiences for both corporate and personal devices. For more information, see What’s new in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) in Windows Server 2016.
Active Directory Federation Services
What’s New in Active Directory Federation Services. Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) in Windows Server 2016 includes new features that enable you to configure AD FS to authenticate users stored in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories. For more information, see What’s New in AD FS for Windows Server 2016.
Web Application Proxy
The latest version of Web Application Proxy focuses on new features that enable publishing and preauthentication for more applications and improved user experience. Check out the full list of new features that includes preauthentication for rich client apps such as Exchange ActiveSync and wildcard domains for easier publishing of SharePoint apps. For more information, see Web Application Proxy in Windows Server 2016.
Administration
The Management and Automation area focuses on tool and reference information for IT pros who want to run and manage Windows Server 2016, including Windows PowerShell.
Windows PowerShell 5.1 includes significant new features, including support for developing with classes and new security features that extend its use, improve its usability, and allow you to control and manage Windows-based environments more easily and comprehensively. See New Scenarios and Features in WMF 5.1 for details.
New additions for Windows Server 2016 include: the ability to run PowerShell.exe locally on Nano Server (no longer remote only), new Local Users & Groups cmdlets to replace the GUI, added PowerShell debugging support, and added support in Nano Server for security logging & transcription and JEA.
Here are some other new administration features:
PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC) in Windows Management Framework (WMF) 5
Windows Management Framework 5 includes updates to Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC), Windows Remote Management (WinRM), and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI).
For more info about testing the DSC features of Windows Management Framework 5, see the series of blog posts discussed in Validate features of PowerShell DSC. To download, see Windows Management Framework 5.1.
PackageManagement unified package management for software discovery, installation, and inventory
Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 includes a new PackageManagement feature (formerly called OneGet) that enables IT Professionals or DevOps to automate software discovery, installation, and inventory (SDII), locally or remotely, no matter what the installer technology is and where the software is located.
PowerShell enhancements to assist digital forensics and help reduce security breaches
To help the team responsible for investigating compromised systems — sometimes known as the «blue team» — we’ve added additional PowerShell logging and other digital forensics functionality, and we’ve added functionality to help reduce vulnerabilities in scripts, such as constrained PowerShell, and secure CodeGeneration APIs.
Networking
This area addresses networking products and features for the IT professional to design, deploy, and maintain Windows Server 2016.
Software-Defined Networking
You can now both mirror and route traffic to new or existing virtual appliances. Together with a distributed firewall and Network security groups, this enables you to dynamically segment and secure workloads in a manner similar to Azure. Second, you can deploy and manage the entire Software-defined networking (SDN) stack using System Center Virtual Machine Manager. Finally, you can use Docker to manage Windows Server container networking, and associate SDN policies not only with virtual machines but containers as well. For more information, see Plan a Software Defined Network Infrastructure.
TCP performance improvements
The default Initial Congestion Window (ICW) has been increased from 4 to 10 and TCP Fast Open (TFO) has been implemented. TFO reduces the amount of time required to establish a TCP connection and the increased ICW allows larger objects to be transferred in the initial burst. This combination can significantly reduce the time required to transfer an Internet object between the client and the cloud.
In order to improve TCP behavior when recovering from packet loss we have implemented TCP Tail Loss Probe (TLP) and Recent Acknowledgment (RACK).В TLP helps convert Retransmit TimeOuts (RTOs) to Fast Recoveries and RACK reduces the time required for Fast Recovery to retransmit a lost packet.В
Security and Assurance
Includes security solutions and features for the IT professional to deploy in your datacenter and cloud environment. For information about security in Windows Server 2016 generally, see Security and Assurance.
Just Enough Administration
Just Enough Administration in Windows Server 2016 is security technology that enables delegated administration for anything that can be managed with Windows PowerShell. Capabilities include support for running under a network identity, connecting over PowerShell Direct, securely copying files to or from JEA endpoints, and configuring the PowerShell console to launch in a JEA context by default. For more details, see JEA on GitHub.
Credential Guard
Credential Guard uses virtualization-based security to isolate secrets so that only privileged system software can access them. See Protect derived domain credentials with Credential Guard.
Remote Credential Guard
Credential Guard includes support for RDP sessions so that the user credentials remain on the client side and are not exposed on the server side. This also provides Single Sign On for Remote Desktop. See Protect derived domain credentials with Windows Defender Credential Guard.
Device Guard (Code Integrity)
Device Guard provides kernel mode code integrity (KMCI) and user mode code integrity (UMCI) by creating policies that specify what code can run on the server. See Introduction to Windows Defender Device Guard: virtualization-based security and code integrity policies.
Windows Defender
Windows Defender Overview for Windows Server 2016. Windows Server Antimalware is installed and enabled by default in Windows Server 2016, but the user interface for Windows Server Antimalware is not installed. However, Windows Server Antimalware will update antimalware definitions and protect the computer without the user interface. If you need the user interface for Windows Server Antimalware, you can install it after the operating system installation by using the Add Roles and Features Wizard.
Control Flow Guard
Control Flow Guard (CFG) is a platform security feature that was created to combat memory corruption vulnerabilities. See Control Flow Guard for more information.
Storage
Storage in Windows Server 2016 includes new features and enhancements for software-defined storage, as well as for traditional file servers. Below are a few of the new features, for more enhancements and further details, see What’s New in Storage in Windows Server 2016.
Storage Spaces Direct
Storage Spaces Direct enables building highly available and scalable storage using servers with local storage. It simplifies the deployment and management of software-defined storage systems and unlocks use of new classes of disk devices, such as SATA SSD and NVMe disk devices, that were previously not possible with clustered Storage Spaces with shared disks.
Storage Replica
Storage Replica enables storage-agnostic, block-level, synchronous replication between servers or clusters for disaster recovery, as well as stretching of a failover cluster between sites. Synchronous replication enables mirroring of data in physical sites with crash-consistent volumes to ensure zero data loss at the file-system level. Asynchronous replication allows site extension beyond metropolitan ranges with the possibility of data loss.
Storage Quality of Service (QoS)
You can now use storage quality of service (QoS) to centrally monitor end-to-end storage performance and create management policies using Hyper-V and CSV clusters in Windows Server 2016.
Failover Clustering
Windows Server 2016 includes a number of new features and enhancements for multiple servers that are grouped together into a single fault-tolerant cluster using the Failover Clustering feature. Some of the additions are listed below; for a more complete listing, see What’s New in Failover Clustering in Windows Server 2016.
Cluster Operating System Rolling Upgrade
Cluster Operating System Rolling Upgrade enables an administrator to upgrade the operating system of the cluster nodes from Windows Server 2012 R2 to Windows Server 2016 without stopping the Hyper-V or the Scale-Out File Server workloads. Using this feature, the downtime penalties against Service Level Agreements (SLA) can be avoided.
Cloud Witness
Cloud Witness is a new type of Failover Cluster quorum witness in Windows Server 2016 that leverages Microsoft Azure as the arbitration point. The Cloud Witness, like any other quorum witness, gets a vote and can participate in the quorum calculations. You can configure cloud witness as a quorum witness using the Configure a Cluster Quorum Wizard.
Health Service
The Health Service improves the day-to-day monitoring, operations, and maintenance experience of cluster resources on a Storage Spaces Direct cluster.
Application development
Internet Information Services (IIS) 10.0
New features provided by the IIS 10.0 web server in Windows Server 2016 include:
- Support for HTTP/2 protocol in the Networking stack and integrated with IIS 10.0, allowing IIS 10.0 websites to automatically serve HTTP/2 requests for supported configurations. This allows numerous enhancements over HTTP/1.1 such as more efficient reuse of connections and decreased latency, improving load times for web pages.
- Ability to run and manage IIS 10.0 in Nano Server. See IIS on Nano Server.
- Support for Wildcard Host Headers, enabling administrators to set up a web server for a domain and then have the web server serve requests for any subdomain.
- A new PowerShell module (IISAdministration) for managing IIS.
For more details see IIS.
Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)
Three new features are added in Microsoft Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016:
A new interface for Resource Manager Rejoin can be used by a resource manager to determine the outcome of an in-doubt transaction after a database restarts due to an error. See IResourceManagerRejoinable::Rejoin for details.
Improved tracing allowing you to set a registry key to include an image file path in the trace log file name so you can tell which trace log file to check. See How to enable diagnostic tracing for MS DTC on a Windows-based computer for details on configuring tracing for MSDTC.