- How to Check Linux Kernel Version on Ubuntu & Linux Mint
- Check Kernel Version
- Find Linux Kernel Version
- View Even More Linux Kernel Info
- Am I Running the Latest Linux Version?
- Bonus Tip: Use Neofetch to check
- How To Find Which Linux Kernel Version Is Installed On My System
- Commands to find your Linux Kernel Version
- How to check kernel version on Linux server/desktop/laptop
- Understanding uname command options
- Find Linux kernel using /proc/version file
- How to find your Linux Kernel version using hostnamect
- Related media
- Conclusion
- 3 Ways to Check Linux Kernel Version in Command Line
- How to find Linux kernel version
- 1. Find Linux kernel using uname command
- 2. Find Linux kernel using /proc/version file
- 3. Find Linux kernel version using dmesg commad
- How do you check your Linux kernel version and other information?
- Ubuntu kernels from Canonical
- Identifying a kernel
- Kernel and OS releases
- Kernel security
- General Availability (GA) and variant Ubuntu kernels
- Custom kernels
How to Check Linux Kernel Version on Ubuntu & Linux Mint
Learn how to check Linux kernel version on Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and related Linux distributions, simply by running one single command.
All you need is a working keyboard, a few fingers, and a terminal app of your choice.
Before we share the command to run to check your kernel version, let’s quickly recap the reasons why you might want to find your Linux kernel version in the first place.
Check Kernel Version
One thing unites every Linux distro out there, from Ubuntu to Fedora, Solus to Arch: the Linux kernel.
But what is the Linux kernel?
Well, there are plenty of in-depth, super complex definitions which describe what the Linux kernel is in detail. But the ‘for dummies’ way to describe it is as the engine of your operating system, atop which everything else sits.
The Linux kernel is what allows everything you see on your computer to be there; it’s responsible for managing hardware resources, allocating memory, allowing processes to run, to communicate and to do what you need them to do.
New versions of the Linux kernel are released regularly, including both major releases with new features, performance optimisations, and hardware support, and minor releases that carry critical security fixes or bug patches.
Security issues and hardware support mean it’s important to know which kernel you’re on
Sometimes (like this month, with the whole Spectre and Meltdown security issues) it can be helpful to know what version of Linux you’re running on as different security issues affect different kernel versions.
By knowing which kernel version your Linux distro is using, you’ll be better placed to tell whether you should upgrade your kernel or not (and if you do, you’ll then know how to double-check to make sure you’re in the clear).
Of course, there may be other reasons why you want to know which version of Linux you’re running. Support for new hardware is often kernel-specific too. You need to upgrade the Linux kernel to get your latest gadget or peripheral working just right.
Explanation over, lets see how to quickly find your Ubuntu kernel version number (or that of any other distro)
Find Linux Kernel Version
The quickest way to find the Linux kernel version you’re currently using is to use the command line.
Open the Terminal app from your systems application menu (or press ctrl + alt + t ) and run the following command:
The uname command instantly tells you which Linux kernel version you’re using. The output will look similar to this (but with different numbers, of course)
What do these Linux kernel version numbers mean?
- 4. – Kernel version
- 14. – Major revision
- 0 – Minor revision
- –16 – Bug fix/revision detail
- –generic — architecture/build specific
The first number is the kernel version. This number changes the least frequently. At present Linux 4.x is the current series.
The second number is the major revision. In years past an even revision number would denote a stable release, and an odd number a development release however this is no longer the case.
The third and fourth numbers relate to which minor revision and security/bug fix release you’re using.
View Even More Linux Kernel Info
To get even more information about your kernel, such as whether it’s 32-bit or 64-bit, you can run the same command again, but this time add the -a flag to the end (‘a’ stands for ‘all’):
The uname command will instantly tell you what need to know, including more details on the specific kernel version, your OS, and even the date the kernel was installed!
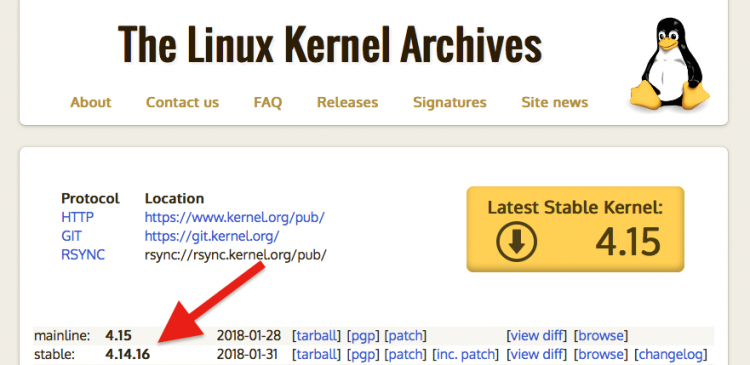
Am I Running the Latest Linux Version?
Check your kernel number against that of the latest mainline and stable Linux kernel releases on the following website:
Bonus Tip: Use Neofetch to check
The uname command is my go-to suggestion for checking kernel details. But my top tip for those who want to see more system info on the command line or check Ubuntu version, is to install Neofetch,
Neofetch is a great utility. It gives you an organized overview of pretty much everything your system is running, including distro name, desktop shell, GTK theme, plus details on ubuntu version, uptime, and memory.
You can install Neofetch on Ubuntu from the Ubuntu Software. The app is also available in the repos of other major Linux distros too, including Arch and Linux Mint.
Once installed just run the neofetch command from a terminal app:
This article is part of our Ubuntu Basics series. If you have a topic or tutorial suggestion you think we help new Ubuntu users do get in touch using our contact form.
Home » How To » How to Check Linux Kernel Version on Ubuntu & Linux Mint
Источник
How To Find Which Linux Kernel Version Is Installed On My System
I am a new proud Linux user. My question to you is – how do I check Linux Kernel version? How do I find my Linux Kernel Version installed on my PC? Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Introduction : The Linux kernel is the central (core) component of Linux operating systems. Its responsibilities include managing the system’s resources and the communication between hardware and software components. It also maintains the security of your system. Hence, finding out the version information is a good idea for patching and other sysadmin management tasks.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | None |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
Commands to find your Linux Kernel Version
To check Linux Kernel version, try the following commands:
- uname -r : Find Linux kernel version
- cat /proc/version : Show Linux kernel version with help of a special file
- hostnamectl | grep Kernel : For systemd based Linux distro you can use hotnamectl to display hostname and running Linux kernel version
Let us see all commands and examples in details.
How to check kernel version on Linux server/desktop/laptop
You need to use then uname command to print certain system information including kernel name. Type the following command to print kernel version number:
$ uname -r
Sample outputs:
So my Linux kernel version is 4.15.0-39, where:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- 4 : Kernel version
- 15 : Major revision
- 0 : Minor revision
- 39 : Patch level or number
- generic : Linux distro/kernel specific additional info
Understanding uname command options
To print certain system information you use uname command. It has the following options:
| -a, OR —all | print all information |
| -s, OR —kernel-name | print the kernel name |
| -n, OR —nodename | print the network node hostname |
| -r, OR —kernel-release | print the Linux kernel release |
| -v, OR —kernel-version | print the kernel version |
| -m, OR —machine | print the machine hardware name |
| -p, OR —processor | print the processor type or “unknown” |
| -i, OR —hardware-platform | print the hardware platform or “unknown” |
| -o, OR —operating-system | print the operating system |
Find Linux kernel using /proc/version file
Another option is to type the following cat command:
$ cat /proc/version
Sample outputs:
How to find your Linux Kernel version using hostnamect
Type the hostnamectl command along with grep command:
$ hostnamectl
$ hostnamectl | grep Kernel
Related media
This tutorial is also available in a quick video format:
Conclusion
You learned three diffent commands to display and show Linux kernel version on screen. For more info see the following pages too:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
3 Ways to Check Linux Kernel Version in Command Line
Last updated October 29, 2020 By Abhishek Prakash 25 Comments
Brief: Wondering which Linux kernel version your system uses? Here are several ways to check your kernel version in the Linux terminal.
You may find yourself in a situation where you need to know the exact Linux kernel version being used on your system. Thanks to the powerful Linux command line, you can easily find that out.
Quick way to check Linux kernel version
You can use the following command to get the Linux kernel version:
uname -r
There are other ways to get even more detailed information about kernel. Read the rest of the article to learn it in detail.
In this article, I’ll show you various methods for finding out your kernel version and tell you what those numbers actually mean. If you prefer videos, here’s a quick one. Don’t forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel for more Linux tips.
How to find Linux kernel version
I am using Ubuntu while writing this article. But these commands are generic and can be used on Fedora, Debian, CentOS, SUSE Linux or any other Linux distribution.
1. Find Linux kernel using uname command
uname is the Linux command for getting system information. You can also use it to find out whether you’re using a 32-bit or 64-bit system.
Open a terminal and type in the following command:
The output will be something similar to this:
This means that you’re running Linux kernel 4.4.0-97, or in more generic terms, you are running Linux kernel version 4.4.
But what do the other digits mean here? Let me explain:
- 4 – Kernel version
- 4 – Major revision
- 0 – Minor revision
- 97 – Bug fix
- generic – Distribution-specific string. For Ubuntu, it means I’m using the desktop version. For Ubuntu server edition, it would be ‘server’.
You can also use the uname command with the option -a. This will provide more system information if you need it.
The output of the command should like this:
Let me explain the output and what it means:
- Linux – Kernel name. If you run the same command on BSD or macOS, the result will be different.
- itsfoss – Hostname.
- 4.4.0-97-generic – Kernel release (as we saw above).
- #120-Ubuntu SMP Tue Sep 19 17:28:18 UTC 2017 – This means that Ubuntu has compiled 4.4.0-97-generic 120 times. A timestamp for the last compilation is also there.
- x86_64 – Machine architecture.
- x86_64 – Processor architecture.
- x86_64 – Operating system architecture (you can run a 32-bit OS on a 64-bit processor).
- GNU/Linux – Operating system (and no, it won’t show the distribution name).
But I’ll save you from information overload. Let’s see some other commands to find your Linux kernel version.
2. Find Linux kernel using /proc/version file
In Linux, you can also find the kernel information in the file /proc/version. Just look at the contents of this file:
You’ll see an output similar to what you saw with uname.
You can see the kernel version 4.4.0-97-generic here.
3. Find Linux kernel version using dmesg commad
dmesg is a powerful command used for writing kernel messages. It’s also very useful for getting system information.
Since dmesg provides an awful lot of information, you should normally use a command like less to read it. But since we’re here just to check the Linux kernel version, grepping on ‘Linux’ should give the desired output.
The output will have a few lines but you should be able to identify the Linux kernel version there easily.
How do you check your Linux kernel version and other information?
Of the three ways discussed here, I use uname all the time. It’s the most convenient.
What about you? Which command do you prefer for getting Linux kernel information?
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
Ubuntu kernels from Canonical
At the core of the Ubuntu operating system is the Linux kernel, which manages and controls the hardware resources like I/O (networking, storage, graphics and various user interface devices, etc.), memory and CPU for your device or computer. It is one of the first software programs a booting device loads and runs on the central processing unit (CPU). The Linux kernel manages the system’s hardware environment so other programs like the operating system’s user space programs and application software programs can run well without modification on a variety of different platforms and without needing to know very much about that underlying system.
Identifying a kernel
The easiest way to determine the kernel you’re running is to type cat /proc/version_signature on the terminal. For example:
Ubuntu 5.4.0-12.15-generic 5.4.8
This output provides important information about the kernel:
- Canonical adds » Ubuntu «
- Ubuntu kernel-release = 5.4.0-12.15-generic
- kernel version is 5.4 , which is identical to upstream stable kernel version
- .0 is an obsolete parameter left over from older upstream kernel version naming practices
- -12 application binary interface (ABI) bump for this kernel
- .15 upload number for this kernel
- -generic is kernel flavour parameter, where -generic is the default Ubuntu kernel flavour
- Mainline kernel-version = 5.4.8
Kernel and OS releases
Canonical provides long-term support (LTS) kernels for Ubuntu LTS releases. Canonical also provides interim operating system releases with updated kernels every 6 months.
For customers and business partners that don’t have specialised bleeding-edge workloads or latest hardware needs, the latest LTS release «-generic» kernel is the best option for them such as the 4.15 default kernel in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. Customers who need the latest hardware support capability can install the latest HWE kernel such as the ones contained in interim releases, keeping in mind the shorter support lifespan associated with these kernels (9 months). HWE kernel customers are recommended to upgrade to a newer LTS release that supports their hardware and/or software needs as soon as it is available. Another option for customers is to use point releases. For example, there is an 18.04.4 point release as of February 2020, which includes an updated 5.3.x kernel but is also considered LTS, exactly like the original GA 4.15 kernel in 18.04.
Kernel security
The Canonical Kernel Team’s primary focus is the careful maintenance of kernels and their variants for regular delivery via the Ubuntu SRU process and the Canonical livepatch service. This includes rigorous management of all Linux kernel Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) lists (with a focus on patching all high and critical CVEs) review and application of all relevant patches for all critical and serious kernel defects in the mailing lists and then rigorously testing newly updated kernels end-to-end each SRU cycle.
General Availability (GA) and variant Ubuntu kernels
The complete functionality of any given kernel is determined by the included modules and the kernel configuration for both hardware and the expected workloads that are run on it.
Kernel modules are binary programs that extend a kernel’s ability to control the computing system’s hardware or add additional system capabilities like high-performance networking or non-standard graphics, etc. The GA kernel that is shipped by default, with the Canonical Ubuntu Long Term Support (LTS) and Hardware Enablement (HWE) releases, are tuned for stable, reliable, secure, high-performance operation over a wide variety of hardware platforms and workloads.
A kernel variant is a kernel that deviates from the generic GA kernel by changes to its configuration, and/or by having modules added and/or removed.
Custom kernels
Canonical advocates for customers to use the GA kernel shipped with Ubuntu as the best and most cost-effective option in their business environment. We also offer the option for customers to customize their own Ubuntu kernels. Several of our enterprise, Telco and cloud provider customers have systems and workload needs, which justify both the time investment to optimise their kernels and the pay to develop and maintain those custom kernels over time.
© 2021 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Источник