- Фундаментальные основы Linux. Часть IV. Программные каналы и команды
- Глава 16. Перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
- Потоки данных stdin, stdout и stderr
- Перенаправление стандартного потока вывода
- Перенаправление стандартного потока ошибок
- Перенаправление стандартного потока вывода и программные каналы
- Объединение стандартных потоков вывода stdout и ошибок stderr
- Перенаправление стандартного потока ввода
- Неоднозначное перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
- Быстрая очистка содержимого файла
- Практическое задание: перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
- Корректная процедура выполнения практического задания: перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
- What are stdin, stderr and stdout in Bash
- stdin, stdout and stderr
- stdin, stdout, and stderr in action
- Piping
- Redirecting streams
- Redirecting Stdout and Stderr
- Final thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
- What is Linux standard input output error and how to redirect stdout and stderr to file in Linux
- Linux standard input output error
- How to redirect stdin
- How to redirect standard error stderr and standard out stdout in one go
Фундаментальные основы Linux. Часть IV. Программные каналы и команды
Оригинал: Linux Fundamentals
Автор: Paul Cobbaut
Дата публикации: 16 октября 2014 г.
Перевод: А.Панин
Дата перевода: 15 декабря 2014 г.
Глава 16. Перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
Одной из мощных возможностей командной оболочки системы Unix является механизм перенаправления потоков ввода/вывода с возможностью задействования программных каналов .
В данной главе даются пояснения относительно перенаправления стандартных потоков ввода, вывода и ошибок.
Потоки данных stdin, stdout и stderr
Командная оболочка bash поддерживает три типа базовых потоков данных; она принимает данные из стандартного потока ввода stdin (поток 0 ), отправляет данные в стандартный поток вывода stdout (поток 1 ), а также отправляет сообщения об ошибках в стандартный поток ошибок stderr (поток 2 ).
Приведенная ниже иллюстрация является графической интерпретацией этих трех потоков данных.
Клавиатура обычно служит источником данных для стандартного потока ввода stdin , в то время, как стандартные потоки вывода stdout и ошибок stderr используются для вывода данных. Новых пользователей Linux может смущать подобное разделение, так как не существует очевидного способа дифференцирования стандартных потоков вывода stdout и ошибок stderr . Опытные же пользователи знают о том, что разделение стандартных потоков вывода и ошибок может оказаться весьма полезным.
В следующем разделе будет рассказано о том, как осуществляется перенаправление упомянутых потоков данных.
Перенаправление стандартного потока вывода
Операция перенаправления потока данных stdout (>)
Перенаправление стандартного потока вывода stdout может быть осуществлено с помощью символа знака «больше» . В том случае, если при разборе строки команды командная оболочка обнаруживает символ знака >, она удаляет данные из файла и перенаправлет данные из стандартного потока вывода в него.
командная оболочка будет рассматривать только два аргумента (echo = аргумент 0, привет = аргумент 1). Описание операции перенаправления потока данных удаляется перед началом подсчета количества аргументов.
Содержимое выходного файла удаляется
Параметр командной оболочки noclobber
Нейтрализация влияния параметра командной оболочки noclobber
Перенаправление стандартного потока ошибок
Операция перенаправления потока данных stderr (2>)
Перенаправление стандартного потока ошибок осуществляется с помощью оператора 2> . Такое перенаправление может оказаться очень полезным для предотвращения заполнения вашего экрана сообщениями об ошибках.
Операция перенаправления нескольких потоков данных 2>&1
позволяет перенаправить только данные из стандартного потока вывода в файл dirlist, так как с помощью данной команды осуществляется копирование дескриптора стандартного потока вывода в дескриптор стандартного потока ошибок перед тем, как стандартный поток вывода перенаправляется в файл dirlist.
Перенаправление стандартного потока вывода и программные каналы
Объединение стандартных потоков вывода stdout и ошибок stderr
Перенаправление стандартного потока ввода
Операция перенаправления потока данных stdin ( стандартного потока ввода stdin осуществляется с помощью оператора here document (иногда называемая структурой here-is-document) является механизмом для ввода данных до момента обнаружения определенной последовательности символов (обычно EOF). Маркер EOF может быть либо введен вручную, либо вставлен автоматически при нажатии комбинации клавиш Ctrl-D.
Структура here string может использоваться для непосредственной передачи строк команде. При использовании данной структуры достигается такой же эффект, как и при использовании команды echo строка | команда (но вы сможете избежать создания одного дополнительного процесса).
Для получения дополнительной информации об алгоритме base64 следует обратиться к стандарту rfc 3548.
Неоднозначное перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
Быстрая очистка содержимого файла
Практическое задание: перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
1. Активируйте параметр командной оболочки noclobber .
2. Проверьте, активирован ли параметр noclobber , повторив вызов команды вывода содержимого директории ls для директории /etc с перенаправлением данных из стандартного потока вывода в файл.
3. Какой из символов представляет параметр noclobber в списке всех параметров командной оболочки.
4. Деактивируйте параметр noclobber .
5. Убедитесь в том, что вы имеете доступ к двум командным оболочкам, открытым на одном компьютере. Создайте пустой файл tailing.txt . После этого выполните команду tail -f tailing.txt . Используйте вторую командную оболочку для добавления строки текста в этот файл. Убедитесь в том, что эта строка была выведена в первой командной оболочке.
6. Создайте файл, содержащий имена пяти людей. Используйте команду cat и механизм перенаправления потоков ввода/вывода для создания файла, а также структуру here document для завершения ввода.
Корректная процедура выполнения практического задания: перенаправление потоков ввода/вывода
1. Активируйте параметр командной оболочки noclobber .
2. Проверьте, активирован ли параметр noclobber , повторив вызов команды вывода содержимого директории ls для директории /etc с перенаправлением данных из стандартного потока вывода в файл.
3. Какой из символов представляет параметр noclobber в списке всех параметров командной оболочки.
4. Деактивируйте параметр noclobber .
5. Убедитесь в том, что вы имеете доступ к двум командным оболочкам, открытым на одном компьютере. Создайте пустой файл tailing.txt . После этого выполните команду tail -f tailing.txt . Используйте вторую командную оболочку для добавления строки текста в этот файл. Убедитесь в том, что эта строка была выведена в первой командной оболочке.
6. Создайте файл, содержащий имена пяти людей. Используйте команду cat и механизм перенаправления потоков ввода/вывода для создания файла, а также структуру here document для завершения ввода.
Источник
What are stdin, stderr and stdout in Bash
Let’s check out how stdin, stderr, and stdout works and how you can use them as well.
stdin, stdout and stderr
In computing, the term stream refers to something that can transfer data. Here, all three streams carry text as the data.
Similar to water streams, data streams also have two endpoints. There are a source and an outflow. Whatever command you’re running in the terminal will be at either point of the stream. Using the stream, you can connect two terminal windows, two different commands, and even files!
Let’s have a quick breakdown of the special streams.
- stdin: Stands for standard input. It takes text as input.
- stdout: Stands for standard output. The text output of a command is stored in the stdout stream.
- stderr: Stands for standard error. Whenever a command faces an error, the error message is stored in this stream.
In Linux, almost all the streams are treated as if they were files. Just like you can read/write a file, you can read/write data from these streams.
An easy way to access any file is by using the unique file descriptor number associated with it. In the case of these streams, there are unique values assigned to each one of them.
stdin, stdout, and stderr in action
Let’s get started by learning more about these streams through action, we will start with stdin.
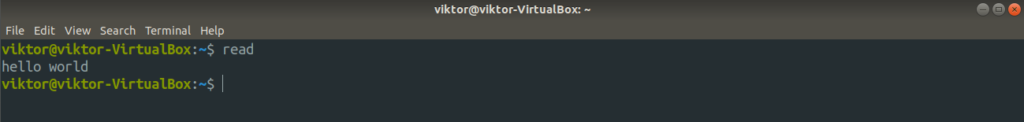
Run the following command.
The command will require input from the keyboard. Here, the read tool is getting the input from stdin. Now let’s look at stdout.
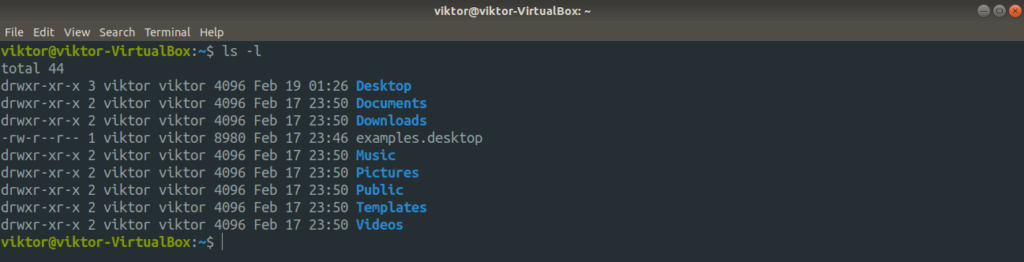
Run the command first.
Here, the ls command lists the file(s) in the current directory. The list is sent to stdout and the terminal prints it out. Let’s check stderr now.
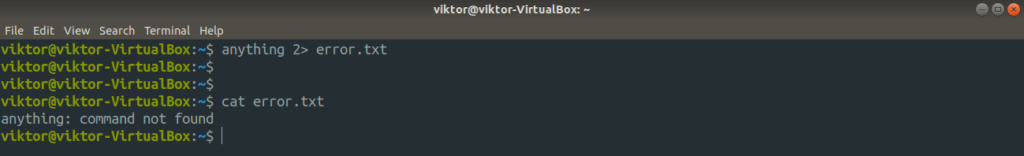
There are different ways an error may occur. For this example, sending ls an invalid argument will result in an error.
Here, there’s no file named anything. That’s why the message ls returns is sent to stderr.
Piping
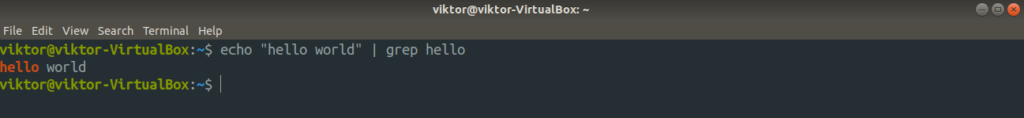
This is a common technique that takes full advantage of the stdin and stdout streams. Let’s explain it with an example.
Here, the | sign is responsible for piping. The output echo generates is written in the stdout stream. Then, the piping redirects the content of stdout to stdin for the grep command. That’s how grep knows what content to perform the operation on.
If you want to pipe both the stderr and stdout to the next command, then use the “|&” instead.
Redirecting streams
Now we know how these streams work, let’s have a look at how you can redirect them. Piping is a form of redirection. However, it only involves stdin and stdout. Bash allows specific control over all three of the streams.
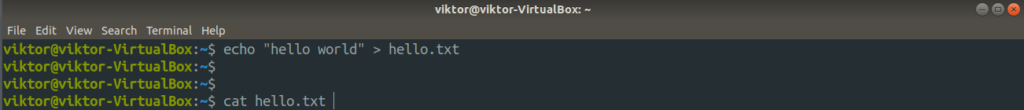
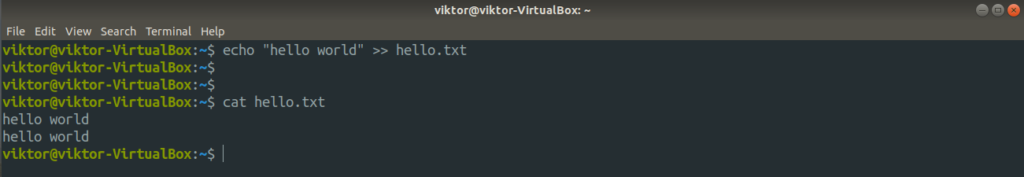
To redirect the stdout content to a file, add the “>” angle followed by the target file name.
Here, the output of the echo command will be stored in the hello.txt file.
If the file did already exists, then the command above will overwrite it. To avoid it, make sure that the file name is unique. If you don’t want to overwrite, you may want to use “>>” instead. It appends the output at the end of the target file.
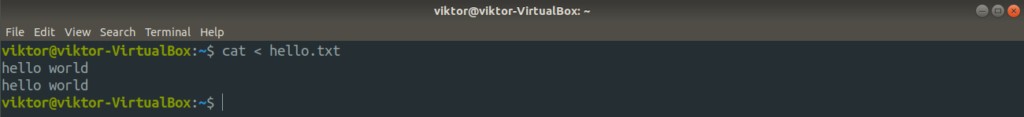
The goal of stdin is to work with input. This can also be redirected. For example, instead of typing the input from the keyboard, it can be loaded from a file.
In this command, cat will take its input directly from the hello.txt file.
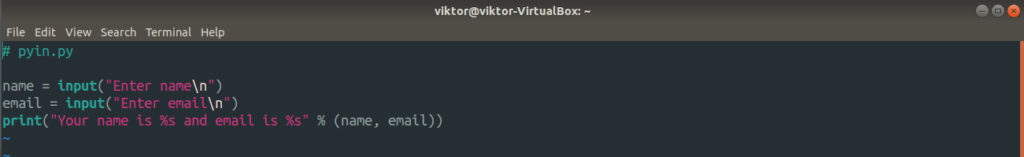
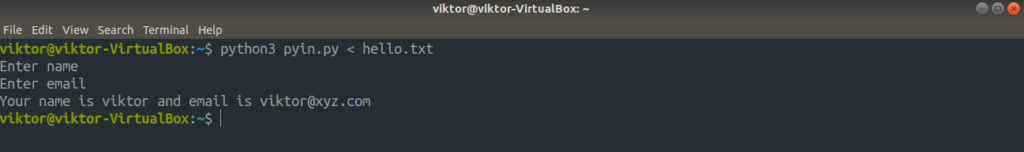
Let’s check out the redirection with a different example. This time, it’s going to involve a Python script.
The input for the script is located at hello.txt.
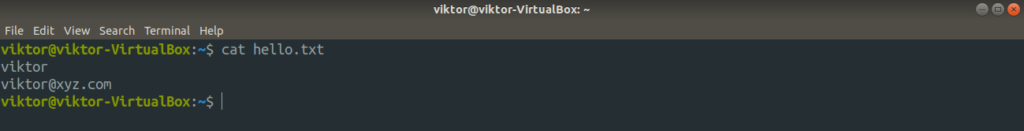
Let’s send the file as input for the script.
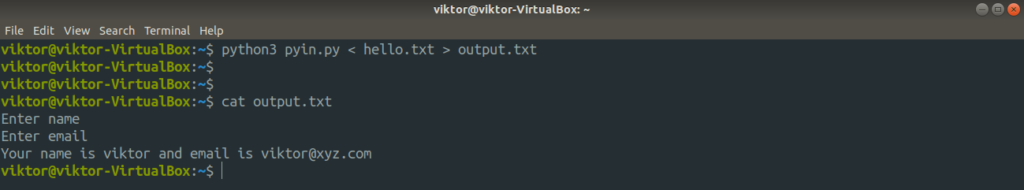
Interestingly, you can redirect both stdin and stdout in the same command line. Here, the following command will use hello.txt as stdin and send the stdout of the command to a file.
Redirecting stderr is similar to stdout. However, you need to mention the description ID 2 for indicating stderr. Otherwise, it’ll just use stdout.
Here, I’ll be redirecting the content of the stderr to a text file.
Redirecting Stdout and Stderr
Yes, it’s possible to redirect both of them simultaneously. All you need is to mention the description ID 1 and 2 before the redirection.
Final thoughts
stdin, stdout, and stderr are wonderful features bash offers by default. If you’re into bash scripting, using them can be incredibly useful in tricky situations.
Want to learn more about bash scripting? Let’s get started with this beginner’s guide to bash scripting!
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
Источник
What is Linux standard input output error and how to redirect stdout and stderr to file in Linux
This article will quickly guide you about Linux standard input output error.Also we will learning how we can redirect stdout and stderr to file in Linux.
Linux standard input output error
Every command or in-turn respective process initialized with some kind of streams.
- Standard input stream (abbreviated stdin) which is use to get the input for the associated program or process.
- Standard output (abbreviated stdout) where process or program writes the output.
- Standard error (abbreviated stderr) used to store or display error preferably on the screen.
In Linux terminology each above streams are indicated by the digits or symbol as below:
| Data Stream | symbol |
|---|---|
| standard input | 0 |
| standard output | 1 |
| standard error | 2 |
While using the above symbol you must use either “ ” depending on the condition.
How to redirect stdin
Redirecting standard input stdin in Linux is pretty simple you need to use “ How to redirect stdout and stderr to file
Redirect stdout to file
First of all we will learn how to redirect stdout to file. In order to redirect standard output to a file you need to use symbol “>” followed by the name of the file.
Syntax:
Here we are using “>” symbol as a result all the output of the command gets redirected to output.log file.
Example:
Redirect stderr to file
In some of the cases you also wanted to be redirect standard error (stderr) to file instead of displaying them on to the screen. In order to redirect standard error stderr to file you need to use “2>” symbol followed by the name of the file.
In the above example we are purposefully using wrong argument “-t” along with the command “df” because we want to generate error message. As a result error gets generated then redirected to file followed by “2>” symbol.
How to redirect standard error stderr and standard out stdout in one go
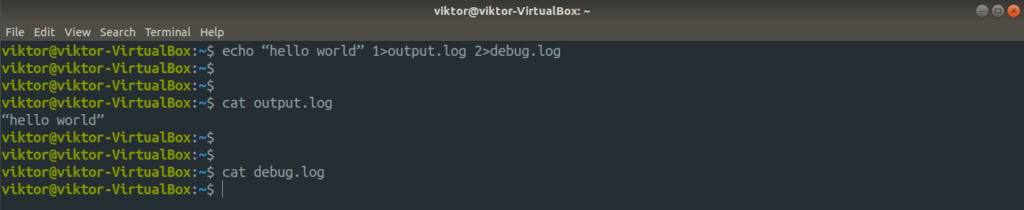
Most of the time we want stderr as well as stdout to be redirected to one single file. Hence we must use “2>&1” symbol which will redirect stderr to stdout. And then we can use “>” symbol to direct it to one single file. Yet other easy method would be use symbol “&>”.
command > file.log 2>&1
standard output example
standard error example
Now we are generating standard error stderr by listing file “.uxtecho” which does exists.
Combine redirection of both stderr and stdout to a single file as below:
Maybe you can also use below method which does almost same work.
Источник