- Начало работы с SVN на Linux
- Subversion
- Содержание
- Subversion
- Установка
- Настройка сервера
- Создание хранилища Subversion
- Импортирование файлов
- Методы доступа
- Прямой доступ к хранилищу (file://)
- Доступ через протокол WebDAV (http://)
- Доступ по протоколу WebDAV с шифрованием SSL (https://)
- Доступ через собственный протокол (svn://)
- Доступ по собственному протоколу с SSL шифрованием (svn+ssh://)
- How to Install SVN Server on Ubuntu 18.04 & 16.04 LTS
- Step 1 – Install Apache
- Step 2 – Install SVN Server
- Step 3 – Create First SVN Repository
- Step 4 – Create Users for Subversion
- Step 5 – Configure Apache with Subversion
- Step 6 – Access Repository in Browser
- linux-notes.org
- Установка SVN сервера в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
- Установка SVN сервера в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
- Настройка SVN в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
- Ubuntu Documentation
- Assumptions
- Scope of this document
- Installation
- Server Configuration
- Create SVN Repository
- Access Methods
- Direct repository access (file://)
- Access via WebDAV protocol (http://)
- Access via WebDAV protocol with SSL encryption (https://)
- Access via custom protocol (svn://)
- Start svnserve at bootup
- Start svnserve at bootup using upstart
- Start svnserve at bootup using xinetd
- Access via custom protocol with SSH encryption (svn+ssh://)
Начало работы с SVN на Linux
Во- первых, установим SVN на Linux
Для того чтобы установить SVN, необходимо подключиться к Linux VPS через SSH.
Если вы используете Ubuntu, обновите пакеты ОС и установите SVN на сервере, используя следующие команды:
Если вы используете CentOS, вы можете использовать следующую команду для обновления пакетов ОС и установки SVN:
Чтобы проверить версию SVN, установленной на вашем сервере, используйте следующую команду:
Создайте учетную запись пользователя системы и переключитесь на этого пользователя:
Замените ‘someuser’ на действительное имя пользователя.
Создайте новый каталог для ваших файлов проекта/приложений/веб-сайта:
Создайте хранилище SVN с помощью следующей команды:
Установите соответствующие права доступа к файлам. Распределения на основе Debian, выполните следующую команду:
О распределении RPM на основе (при использовании Apache в качестве веб-сервера), выполните следующую команду:
Создайте файл ‘passwd’ в каталоге /home/someuser/svn/myapp/conf/passwd на сервере, который содержит информацию о аутентификации пользователя:
Если вы хотите добавить пользователей, используйте ту же команду, но без переключателя ‘-c‘, чтобы избежать перезаписи файла passwd.
Назначение разрешений для пользователей SVN с помощью файла authz (/home/someuser/svn/myapp/conf/authz):
Создание концептуальных групп, которые вам нужны, а затем добавить к нему пользователей:
Выберите уровень доступа с обоих разрешений и уровня проекта:
Чтобы дать разрешения для чтения и записи “allaccess” для пользователей, добавьте:
Для того, чтобы дать доступ только для чтения к “someaccess” пользователям к некоторому проекту нижнего уровня, добавьте:
Для того, чтобы скопировать неверсионное дерево вашего проекта/файлов веб-сайта и начать отслеживать в вашем хранилище SVN и создать промежуточные каталоги, введите следующие команды:
Вы можете создать единое хранилище для каждого проекта/сайта на каком – то центральном месте, где вся история.
Чтобы создать рабочую копию в другой локальный каталог, используйте:
Для того, чтобы отправить изменения из рабочей копии в хранилище, используйте:
Используйте команду ‘svn add /path/file’, чтобы добавить файл из рабочей копии в хранилище). Файл будет добавлен в хранилище, когда вы делаете commit SVN.
Чтобы удалить файл из рабочей копии (или хранилище), используйте:
и файл будет удален из хранилища после команды svn commit.
Чтобы обновить изменения из хранилища в рабочую копию, используйте:
При наличии нескольких авторов, работающих над проектом/веб-сайтом, они имеют локальные рабочие копии на нескольких машинах, всегда запускайте команду ‘svn update’ перед внесением изменений в файлы, доступные в вашей рабочей копии. После этого, вносите изменения в файлы, а затем зафиксируйте изменения в хранилище после того, как только файлы будут изменены.
Для того чтобы применить различия между двумя источниками на пути в рабочей копии, используйте:
Для того, чтобы увидеть различия между этими двумя конкретными версиями файла, используйте:
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Источник
Subversion
Содержание
Subversion
Subversion — это система контроля версий с открытым кодом. Используя Subversion вы можете записывать историю исходных файлов и документов. Она управляет файлами и каталогами во времени. Дерево файлов располагается в центральном хранилище. Хранилище больше похоже на обычный файл-сервер, за исключением того, что он помнит каждое изменение когда-либо сделанное в файлах или каталогах.
Установка
Для доступа к хранилищу Subversion с помощью протокола HTTP вы должны установить и настроить web сервер. Apache2 гарантированно работает с Subversion. Пожалуйста, обратитесь к разделу Apache2 для установки и настройки Apache2. Для доступа к хранилищу Subversion по протоколу HTTPS вам потребуется установить и настроить цифровой сертификат для вашего Apache2 сервера. Пожалуйста, обратитесь к подразделу HTTPS в разделе по Apache2 для установки и настройки цифрового сертификата.
Для установки Subversion выполните следующую команду в терминале:
Настройка сервера
Этот шаг подразумевает, что вы уже установили упоминавшиеся выше пакеты на вашей системе. В этом разделе описывается как создать хранилище Subversion и получить доступ к проекту.
Создание хранилища Subversion
Хранилище Subversion может быть создано с помощью следующей команды в терминале:
Импортирование файлов
После того, как вы установили хранилище, вы можете импортировать в него файлы. Для импорта каталога, ведите следующее в терминале:
Методы доступа
Хранилище Subversion может быть доступно множеством различных способов — на локальном диске или через различные сетевые протоколы. Однако, размещение хранилища — это всегда url адрес. Таблица описывает как различные URL схемы связаны с возможными методами доступа.
Методы доступа
| Схема | Метод доступа |
|---|---|
| file:// | Прямо доступ к хранилищу (на локальном диске) |
| http:// | Доступ через протокол WebDAV к web-серверу Apache2, настроенному на Subversion |
| https:// | То же самое, что и http://, но с использованием шифрования SSL |
| svn:// | Доступ через собственный протокол к серверу svnserve |
| svn+ssh:// | То же самое, что svn://, но через туннель SSH |
В этом разделе мы рассмотрим как настроить Subversion для всех этих методов доступа. Здесь мы рассмотрим основное. Для более продвинутого использования, обратитесь к книге svn book.
Прямой доступ к хранилищу (file://)
Это самый простой из всех методов доступа. Он не требует запуска какого-либо сервера Subversion. Этот метод используется для доступа к Subversion на этой же машине. Синтаксис команды, вводимой в терминале, аналогичен следующему:
Права доступа к хранилищу определяются правами файловой системы. Если пользователь имеет право на чтение/запись, он может получить содержимое хранилища и внести изменения.
Доступ через протокол WebDAV (http://)
Для доступа к хранилищу Subversion через протокол WebDAV вам потребуется настроить сервер Apache2. Добавьте следующий фрагмент между элементами и в /etc/apache2/sites-available/default или иной VirtualHost файл:
Далее вы должны создать файл /etc/subversion/passwd, который будет содержать подробности аутентификации пользователей. Для создания файла используйте следующую команду в командной строке (которая создаст файл и добавит первого пользователя):
Чтобы добавить дополнительных пользователей, опустите опцию «-c», поскольку она заменяет старый файл. Вместо этого используйте такой вариант:
Эта команда запросит у вас ввод пароля. Как только вы введете пароль, пользователь будет добавлен. Теперь для доступа к хранилищу вы можете выполнить следующую команду:
Доступ по протоколу WebDAV с шифрованием SSL (https://)
Вы можете установить цифровой сертификат, выпущенный центром сертификации. В качестве альтернативы можно использовать самоподписанный сертификат.
Эта часть подразумевает, что вы установили и настроили цифровой сертификат в вашем сервере Apache2. Теперь чтобы получить доступ к хранилищу Subversion смотрите предыдущий раздел. Метод доступа практически тот же самый, за исключением протокола. Вы должны использовать https:// для доступа к хранилищу Subversion.
Доступ через собственный протокол (svn://)
Как только создано хранилище Subversion, вы можете настроить контроль доступа. Вы можете отредактировать файл /path/to/repos/project/conf/svnserve.conf для изменения контроля доступа. Например, для установки авторизации вы можете раскомментировать следующие строки в файле конфигурации:
После снятия знака комментария (#) с этих строк, вы можете поддерживать список пользователей в файле passwd. И так, редактируйте файл passwd в этом же каталоге и добавляйте новых пользователей. Синтаксис должен быть таким:
Более подробно смотрите комментарии в самом файле.
Теперь, чтобы подключиться к Subversion через собственный протокол svn://, с этой же машины или другой, вы можете запустить svnserver с помощью команды svnserve. Синтаксис следующий:
Как только вы выполните указанную команду, Subversion запустится на порту по умолчанию (3690). Для доступа к хранилищу проектов вам потребуется выполнить следующую команду из терминала:
Основываясь на конфигурации сервера, у вас будет запрошен пароль. После аутентификации будет проверен код из хранилища Subversion. Для синхронизации проекта из хранилища с локальной копией вам потребуется выполнить подкоманду update. Синтаксис команды, вводимой в терминале следующий:
Для подробной информации о каждой подкоманде Subversion вы можете обратиться к встроенному руководству. Например, чтобы узнать больше о команде co (checkout) выполните следующую команду в терминале:
Доступ по собственному протоколу с SSL шифрованием (svn+ssh://)
Настройка и работа сервера такая же, как при svn:// методе. Детали описаны в предыдущей части.Этот шаг предполагает, что вы следовали инструкциям предыдущей части и запустили сервер Subversion с помощью команды svnserve.
Также предполагается, что у вас на машине запущен сервер ssh и он разрешает входящие соединения. Для проверки, пожалуйста, попробуйте войти на машину с использованием ssh. Если вам удалось соединиться, все замечательно. Если соединиться не получилось, обратитесь к данной проблеме, прежде чем следовать дальше.
Основываясь на настройках сервера, будет запрошен пароль. Вы должны будете ввести пароль, который используете при доступе через ssh. После аутентификации команда проверит код из хранилища Subversion.
© 2012 Ubuntu-ru — Русскоязычное сообщество Ubuntu Linux.
© 2012 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu и Canonical являются зарегистрированными торговыми знаками Canonical Ltd.
Источник
How to Install SVN Server on Ubuntu 18.04 & 16.04 LTS
Subversion is an open-source version control system. It helps you keep track of a collection of files and folders. Any time you change, add or delete a file or folder that you manage with Subversion, you commit these changes to your Subversion repository, which creates a new revision in your repository reflecting these changes. You can always go back, look at and get the contents of previous revisions.
This article will help you for step by step setup of Subversion (svn) server on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS & 16.04 LTS systems.
Step 1 – Install Apache
First of all, you need to install the Apache webserver to access the svn server using HTTP URLs. Skip this step if you already have Apache web server on your system.
Step 2 – Install SVN Server
Use the following command to install subversion packages and their dependencies. Also, install svn module for Apache libapache2-mod-svn packages on your system.
After installation, enable required Apache modules and restart Apache service.
Step 3 – Create First SVN Repository
Use the following commands to create your first svn repository with name myrepo. Also, set the required permissions on newly created directories.
Step 4 – Create Users for Subversion
Now create first svn user in /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd file. These users will use for authentication of svn repositories for checkout, commit processes.
To create additional users, use following commands.
Step 5 – Configure Apache with Subversion
Subversion Apache module package creates an configuration file /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dav_svn.conf. You just need to make necessary changes to it.
Save the file and restart the Apache service to apply the new configuration.
Step 6 – Access Repository in Browser
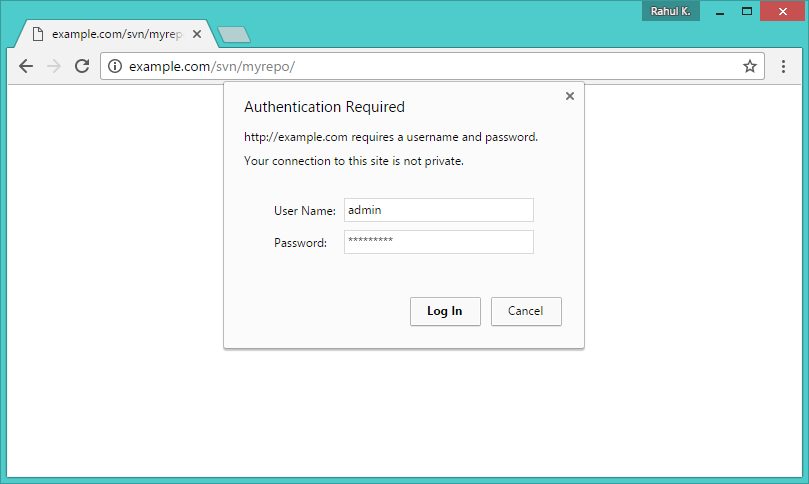
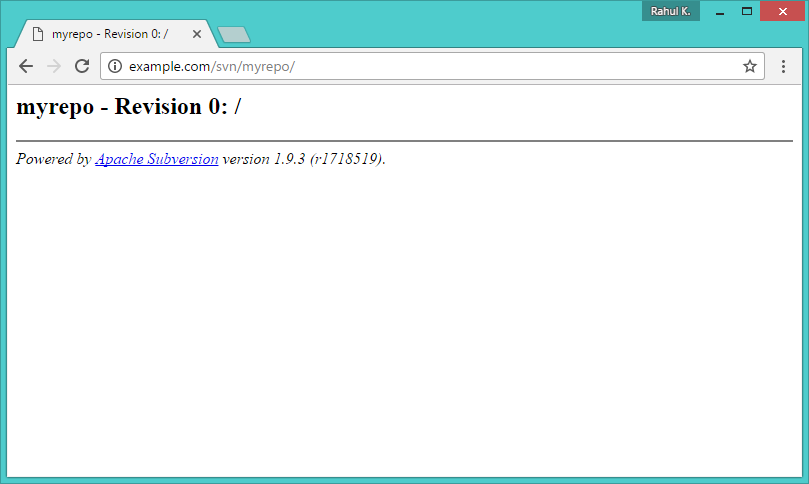
Use HTTP URLs to access your repository in the browser. It will prompt for authentication. Use login credentials created in Step 5. Change example.com with your system hostname, domain name or IP address.
Thank You for using this article. Read our next article How to Backup and Restore SVN Repository in Linux.
Источник
linux-notes.org
Установка SVN сервера в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
В этой статье «Установка SVN сервера в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint» я хотел бы рассказать как установить и настроить SVN сервер в deb ОС, на примере Debian 8.
Установка SVN сервера в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
И так, выполним установку утилиты следующей командой:
Создаю директорию для будущего репозитория:
Создаем собственно, сам репозиторий:
Создаю юзверя-владельца репы и от него же, будет запускаться сам демон:
Выставляем нужные права на директорию репы:
И даем права на запись:
Сейчас, необходимо добавить скрипт SVN сервера, выполняем команду:
Даем права всем на выполнение:
Добавлю скрипт в автозагрузку ОС:
Настройка SVN в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
В моем примере, все конфиги и различные настройки находятся в /srv/svn/repo/conf/ директории. Сейчас нужно немного видоизменить некоторые настройки в файлах.
Поправлю основной конфиг-файл:
Приводим к виду:
Пропишем доступ для пользователей и ихние пароли (пароли хранятся в открытом виде):
Добавим пользователей в группы и назначим нужные права на работу с репозиторием или на часть его:
Сейчас, выставляю права на корень и назначаю группе «group1» только для чтения. Пользователю captain даю полный доступ, а всем остальным — вообще запрещаю доступ:
Настройку завершил, осталось только — запустить демон SVN чтобы начать уже работу:
PS: Сервер SVN юзает TCP 3690 порт, по этому, при необходимости откройте его в фаерволе.
Тема «Установка SVN сервера в Debian/Ubuntu/Mint» завершена.
Источник
Ubuntu Documentation
This wiki document explains how to setup Subversion alias SVN on Ubuntu. The intended audience is experienced Linux users and system administrators.
If you are new to Subversion, this section provides a quick introduction.
Subversion is an open source version control system. Using Subversion, you can record the history of source files and documents. It manages files and directories over time. A tree of files is placed into a central repository. The repository is much like an ordinary file server, except that it remembers every change ever made to files and directories.
Assumptions
It is assumed that you are aware of how to run Linux commands, edit files, start/stop services in an Ubuntu system. It is also assumed that Ubuntu is running, you have sudo access and you want to use Subversion software.
It is also assumed you have an internet connection.
Scope of this document
To make an SVN repository available to access using the HTTP protocol, you must install & configure web server. Apache 2 is proven to work with SVN. The installation of Apache 2 Webserver is beyond the scope of this document. (See ApacheHTTPserver.) However, the configuration of Apache 2 Webserver for SVN is covered in this document.
To access an SVN repository using HTTPS protocol, you must install & configure digital certificate in your Apache 2 web server. The installation and configuration of digital certificate is beyond the scope of this document. (See OpenSSL.)
Installation
Subversion is already in the main repository, so to install Subversion you can simply install the subversion package (see InstallingSoftware).
If it fails reporting dependencies, please locate the packages and install them. If it reports any other issues, please resolve them. If you cannot resolve the issue, please refer the mailing list archive of those packages.
Server Configuration
This step assumes you have installed above mentioned packages on your system. This section explains how to create SVN repository and access the project.
Create SVN Repository
There are several typical places to put a Subversion repository; most common places are: /srv/svn, /usr/local/svn and /home/svn. For clarity’s sake, we’ll assume we are putting the Subversion repository in /home/svn, and your project’s name is simply ‘myproject’
There are also several common ways to set permissions on your repository. However, this area is the most common source of errors in installation, so we will cover it thoroughly. Typically, you should choose to create a new group called ‘subversion’ that will own the repository directory. To do this (see AddUsersHowto for details):
Choose System > Administration > Users and Groups from your Ubuntu menu.
(Note: in order to see www-data you may need to see FixShowAllUsers)
You have to logout and login again before you are a member of the subversion group, and can do check ins.
Now issue the following commands:
The SVN repository can be created using the following command:
And use the following commands to correct file permissions:
The last command sets gid for proper permissions on all new files added to your Subversion repository.
If you want to use WebDAV as an access method described below, repeat the chmod -R g+rws myproject command again. This is because svnadmin will create directories and files without group write access. This is no problem for read only access or using the custom svn protocol but when Apache tries to commit changes to the repository linux will deny it access. Also the owner and group are set as root. This can be changed by repeating the chown and chgrp commands listed above.
Access Methods
Subversion repositories can be accessed (checkout) through many different methods-on local disk, or through various network protocols. A repository location, however, is always a URL. The table describes how different URL schemas map to the available access methods.
Schema
Access Method
direct repository access (on local disk)
Access via WebDAV protocol to Subversion-aware Apache 2 web server
Same as http://, but with SSL encryption
Access via custom protocol to an svnserve server
Same as svn://, but through an SSH tunnel
In this section, we will see how to configure SVN for all these access methods. Here, we cover the basics. For more advanced usage details, you are always recommended to refer the svn book.
Direct repository access (file://)
This is the simplest of all access methods. It does not require any SVN server process to be running. This access method is used to access SVN from the same machine. The syntax is as follows:
NOTE: Please note, if you do not specify the hostname, you must use three forward slashes (///). If you specify the hostname, you must use two forward slashes (//).
The repository permission is dependant on filesystem permission. If the user has read/write permission, he can checkout/commit the changes to the repository. If you set permissions as above, you can give new users the ability to checkout/commit by simply adding them to the Subversion group you added above.
Access via WebDAV protocol (http://)
To access the SVN repository via WebDAV protocol, you must configure your Apache 2 web server.
First install the following package libapache2-svn (see InstallingSoftware).
NOTE: If you have already tried to install the «dav» modules manually, package installation may fail. Simply remove all files beginning with «dav» from the mods-enabled directory, then remove and install the package again. Let the package put files in the correct place, then edit your configuration.
You must add the following snippet in your /etc/apache2/mods-available/dav_svn.conf file:
NOTE: The above configuration assumes that all Subversion repositories are available under /home/svn directory.
TIP: If you want the ability to browse all projects on this repository by going to the root url (http://www.serveraddress.com/svn) use the following in dav_svn.conf instead of the previous listing:
NOTE: The above configuration requires authentication with any of the users specified within the file to access the repository. If you want to allow anonymous read access to the repositories add the following and lines around the «Require valid-user» line. The previous listing would become:
NOTE: If a client tries to svn update which involves updating many files, the update request might result in an error Server sent unexpected return value (413 Request Entity Too Large) in response to REPORT request, because the size of the update request exceeds the limit allowed by the server. You can avoid this error by disabling the request size limit by adding the line LimitXMLRequestBody 0 between the and lines.
Alternatively, you can allow svn access on a per-site basis. This is done by adding the previous snippet into the desired site configuration file located in /etc/apache2/sites-available/ directory.
Once you add the above lines, you must restart apache2 web server. To restart apache2 web server, you can run the following command:
Next, you must create /etc/subversion/passwd file. This file contains user authentication details.
If you have just installed SVN, the passwd file will not yet exist and needs to be created using the «-c» switch. Adding any users after that should be done without the «-c» switch to avoid overwriting the passwd file.
To add the first entry, ie.. to add the first user, you can run the following command:
It prompts you to enter the password. Once you enter the password, the user is added.
To add more users after that, you can run the following command:
If you are uncertain whether the passwd file exists, running the command below will tell you whether the file already exists:
Now, to access the repository you can run the following command:
It prompts you to enter the password. You must enter the password configured using htpasswd command. Once it is authenticated the project is checked out. If you encounter access denied, please remember to logout and login again for your memebership of the subversion user-group to take effect.
WARNING: The password is transmitted as plain text. If you are worried about password snooping, you are advised to use SSL encryption. For details, please refer next section.
Access via WebDAV protocol with SSL encryption (https://)
Accessing SVN repository via WebDAV protocol with SSL encryption (https://) is similar to http:// except you must install and configure the digital certificate in your Apache 2 web server.
You can install a digital certificate issued by Signing authority like Verisign. Alternatively, you can install your own self signed certificate.
This step assumes you have installed and configured digital certificate in your Apache 2 web server. Now to access SVN repository please refer the above section. You must use https:// to access the SVN repository.
Access via custom protocol (svn://)
Once the SVN repository is created, you can configure the access control. You can edit /home/svn/myproject/conf/svnserve.conf file to configure the access control.
NOTE: svnserve.conf is sensitive to whitespace, be sure not to leave any whitespace at the start of a line or it will not be able to read the file.
For example, to setup authentication you can uncomment the following lines in the configuration file:
After uncommenting the above lines, you can maintain the user list in passwd file. So, edit the file passwd in the same directory and add new user. The syntax is as follows:
For more details, please refer the file.
Now, to access SVN via svn:// custom protocol either from the same machine or different machine, you can run svnserver using svnserve command. The syntax is as follows:
Once you run this command, SVN starts listening on default port (3690). To access the project repository, you must run the following command:
Based on server configuration, it prompts for password. Once it is authenticated, it checks out the code from SVN repository.
To synchronize the project repository with the local copy, you can run update sub-command. The syntax is as follows:
For more details about using each SVN sub-command, you can refer the manual. For example, to learn more about co (checkout) command, please run:
Start svnserve at bootup
One can start the svnserve daemon at bootup using an initd script. Look at Michał Wojciechowski Blog post for instructions and a good initd script for svnserve.
Start svnserve at bootup using upstart
On recent upstart based Ubuntu versions you can place an upstart config file in /etc/init/svnserve.conf. See the example svnserve.conf; however, you will most likely need to edit it after reading the upstart documentation and the svnserve man page.
After placing the config file you can start svnserve with:
Start svnserve at bootup using xinetd
An alternative method to run svnserve at startup is to install xinetd, and then add the following line to /etc/xinetd.conf (replacing ‘svnowner’ and ‘/home/svn’ with appropriate values)
Access via custom protocol with SSH encryption (svn+ssh://)
It is not necessary to run the SVN server (svnserve) in order to access SVN repositories on a remote machine using this method. However, it is assumed that the SSH server is running in the remote machine with the repository and it is allowing incoming connections. To confirm, please try to login to that machine using ssh. If you can login, then everything is perfect. If you cannot login, please address it before continuing further.
The svn+ssh:// protocol is used for accessing SVN repositories with SSH based encryption for secure data transfer. To access a repository using this method, run the following command:
NOTE: You must use full path (/home/svn/myproject) to access an SVN repository using this method.
Based on the SSH server configuration, it prompts for password. You must enter the password you use to login via ssh. Once it is authenticated, it checks out the code from SVN repository.
You can also refer the SVN book for details about the svn+ssh:// protocol.
Источник