- Start / Stop and Restart Apache 2 Web Server Command
- Debian/Ubuntu Linux Specific Commands to Start/Stop/Restart Apache
- Restart Apache 2 web server, enter:
- To stop Apache 2 web server, enter:
- To start Apache 2 web server, enter:
- A note about Debian/Ubuntu Linux systemd users
- CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat) Linux version 4.x/5.x/6.x or older specific commands
- CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat) Linux version 7.x or newer specific commands
- Alpine Linux start / stop / restart Apache 2 using openrc
- FreeBSD Unix users
- Generic method to start/stop/restart Apache on a Linux/Unix
- Summing up
- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как запустить, остановить и перезапустить сервисы в Linux
- Базовый синтаксис команды systemctl
- Как проверить, работает ли служба в Linux
- Как перезапустить сервис
- Как перезагрузить конфигурационные файлы сервиса
- Как запустить сервис
- Как остановить сервис
- Как включить сервис при загрузке
- Как отключить сервис при загрузке
- Полезно?
- Почему?
- How to Start, Stop & Restart Services in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions
- Method 1: Managing services in Linux with systemd
- 1. List all services
- 2. Start a service
- 3. Stop a service
- 4. Restart a service
- 5. Check the status of a service
- Method 2: Managing services in Linux with init
- 1. List all services
- 2. Start a service
- 3. Stop a service
- 4. Restart a service
- 5. Check the status of a service
- Ubuntu Linux: Start / Restart / Stop Apache Web Server
- Method #1: systemctl command examples
- Method #2: /etc/init.d/apache2 command examples
- Task: Start Apache 2 Server
- Task: Restart Apache 2 Server
- Task: Stop Apache 2 Server
- Method #3: service command examples
- Method #4: upstart command examples
- Method #5: apache2ctl command examples
Start / Stop and Restart Apache 2 Web Server Command
H ow do I restart an Apache 2 Web Server under a Debian / Ubuntu / CentOS / RHEL / Fedora Linux or UNIX-like operating systems? Can you tell me command to start or stop Apache 2 web server running on Linux?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Apache 2 on Linux / Unix |
| Est. reading time | 3 mintues |
Apache is primarily used to serve both static content and dynamic Web pages on the World Wide Web. Many web applications are designed expecting the environment and features that Apache provides. Apache can be started or restarted using any one of the following methods on Linux or Unix-like systems.

First, login to your web-server using ssh client, if server is not in your local data center:
ssh root@your.server.com
Once logged in type the following commands as per your Linux or Unix variant.
Debian/Ubuntu Linux Specific Commands to Start/Stop/Restart Apache
You can either use service or /etc/init.d/ command as follows on Debian Linux version 7.x or Ubuntu Linux version Ubuntu 14.10 or older:
Restart Apache 2 web server, enter:
# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
OR
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
OR
$ sudo service apache2 restart
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
To stop Apache 2 web server, enter:
# /etc/init.d/apache2 stop
OR
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 stop
OR
$ sudo service apache2 stop
To start Apache 2 web server, enter:
# /etc/init.d/apache2 start
OR
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
OR
$ sudo service apache2 start
A note about Debian/Ubuntu Linux systemd users
Use the following systemctl command on Debian Linux version 8.x+ or Ubuntu Linux version Ubuntu 15.04+ or above:
## Start command ##
systemctl start apache2.service
## Stop command ##
systemctl stop apache2.service
## Restart command ##
systemctl restart apache2.service
We can view status using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl status apache2.service
CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat) Linux version 4.x/5.x/6.x or older specific commands
## Start ##
service httpd start
## Stop ##
service httpd stop
## Restart ##
service httpd restart
CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat) Linux version 7.x or newer specific commands
Most modern distro now using systemd, so you need to use the following systemctl command:
## Start command ##
systemctl start httpd.service
## Stop command ##
systemctl stop httpd.service
## Restart command ##
systemctl restart httpd.service
Alpine Linux start / stop / restart Apache 2 using openrc
We need to use the service command as root user:
# service apache2 start
# service apache2 stop
# service apache2 status
# service apache2 restart
Session:
FreeBSD Unix users
FreeBSD user can restart Apache as follows:
# /usr/local/etc/rc.d/apache22 restart
# service restart apache22
# service stop apache22
# service start apache22
Generic method to start/stop/restart Apache on a Linux/Unix
The syntax is as follows (must be run as root user):
## stop it ##
apachectl -k stop
## restart it ##
apachectl -k restart
## graceful restart it ##
apachectl -k graceful
## Start it ##
apachectl -f /path/to/your/httpd.conf
apachectl -f /usr/local/apache2/conf/httpd.conf
Summing up
You learned how to start, stop or restart the Apache 2 web server using command-line over ssh-based session.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как запустить, остановить и перезапустить сервисы в Linux
Start — Stop — Restart — Reload
3 минуты чтения
Linux обеспечивает детальный контроль над системными службами через systemd с помощью команды systemctl. Службы могут быть включены, выключены, перезапущены, перезагружены или даже включены или отключены при загрузке. Если вы используете Debian, CentOSили Ubuntu, ваша система, вероятно, использует systemd.
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
Это руководство покажет вам, как использовать основные команды для запуска, остановки и перезапуска служб в Linux.
Базовый синтаксис команды systemctl
Основной синтаксис для использования команды systemctl:
Как правило, вам нужно запускать это как суперпользователь поэтому команды будут начинаться с sudo.
Как проверить, работает ли служба в Linux
Чтобы проверить, активна ли служба или нет, выполните следующую команду:
Замените SERVICE_NAME на нужный сервис.
В нашем случае мы будем брать за пример веб-сервер Apache.
Интересный факт: в Ubuntu и других дистрибутивах на основе Debian служба Apache называется apache2. В CentOS и других дистрибутивах RedHat служба Apache называется httpd или httpd.service
Так мы проверили состояние Apache. Выходные данные показывают, что служба активна (работает), как на рисунке ниже:

Как перезапустить сервис
Чтобы остановить и перезапустить службу в Linux, используйте команду:
Где SERVICE_NAME — имя вашего сервиса.
После выполнения команды ваш сервис должен снова заработать. Вы можете проверить состояние с помощью команды status
Для перезапуска нашего сервера Apache используем:
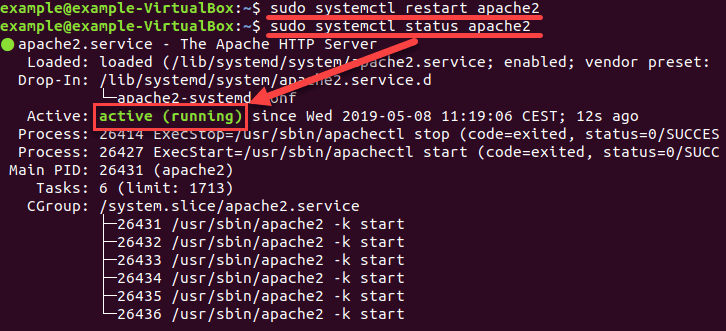
Как перезагрузить конфигурационные файлы сервиса
Чтобы служба перезагрузила свои файлы конфигурации, введите в терминале следующую команду:
После перезагрузки проверьте ее состояние командой status для подтверждения.
В нашем примере мы перезагрузили Apache, используя:

Как запустить сервис
Чтобы запустить службу в Linux вручную, введите в терминале следующее:
Например, команда для запуска службы Apache:
Как остановить сервис
Чтобы остановить активную службу в Linux, используйте следующую команду:
Для нашего апача используем команду
Проверьте, остановился ли сервис с помощью команды status . Вывод должен показать, что сервис неактивен — inactive (dead)
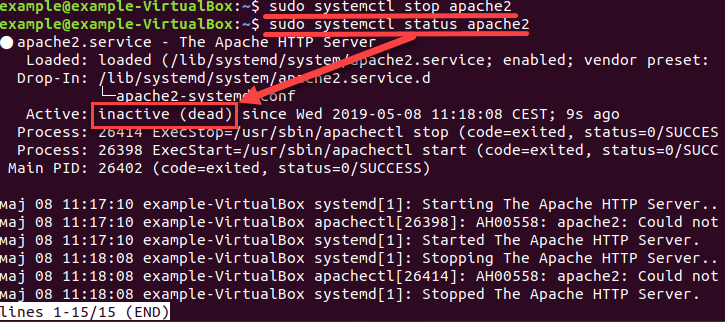
Как включить сервис при загрузке
Чтобы настроить службу для запуска при загрузке системы, используйте команду:
Чтобы включить Apache при загрузке системы, выполните команду:

Как отключить сервис при загрузке
Вы можете запретить запуск службы при загрузке с помощью команды:
Онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят тебе начать карьеру администратора Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг к DevOps
Полезно?
Почему?
😪 Мы тщательно прорабатываем каждый фидбек и отвечаем по итогам анализа. Напишите, пожалуйста, как мы сможем улучшить эту статью.
😍 Полезные IT – статьи от экспертов раз в неделю у вас в почте. Укажите свою дату рождения и мы не забудем поздравить вас.
Источник
How to Start, Stop & Restart Services in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions
Last updated October 29, 2020 By Sergiu 9 Comments
Services are essential background processes that are usually run while booting up and shut down with the OS.
If you are a sysadmin, you’ll deal with the service regularly.
If you are a normal desktop user, you may come across the need to restart a service like setting up Barrier for sharing mouse and keyboard between computers. or when you are using ufw to setup firewall.
Today I will show you two different ways you can manage services. You’ll learn to start, stop and restart services in Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
systemd vs init
Ubuntu and many other distributions these days use systemd instead of the good old init.
In systemd, you manage sevices with systemctl command.
In init, you manage service with service command.
You’ll notice that even though your Linux system uses systemd, it is still able to use the service command (intended to be used with init system). This is because service command is actually redirect to systemctl. It’s sort of backward compatibility introduced by systemd because sysadmins were habitual of using the service command.
I’ll show both systemctl and service command in this tutorial.
I am Ubuntu 18.04 here, but the process (no pun intended) is the same for other versions.
Method 1: Managing services in Linux with systemd
I am starting with systemd because of the obvious reason of its widespread adoption.
1. List all services
In order to manage the services, you first need to know what services are available on your system.
You can use the systemd command to list all the services on your Linux system:
This command will output the state of all services. The value of a service’s state can be enabled, disabled, masked (inactive until mask is unset), static and generated.
Combine it with the grep command and you can display just the running services:
Now that you know how to reference all different services, you can start actively managing them.
Note: in the commands should be replaced by the name of the service you wish to manage (e.g. network-manager, ufw etc.).
2. Start a service
To start a service in Linux, you just need to use its name like this:
3. Stop a service
To stop a systemd service, you can use the stop option of systemctl command:
4. Restart a service
To restart a service in Linux with systemd, you can use:
5. Check the status of a service
You can confirm that you have successfully executed a certain action by printing the service status:
This will output information in the following manner:
That was systemd. Let’s switch to init now.
Method 2: Managing services in Linux with init
The commands in init are also as simple as system.
1. List all services
To list all the Linux services, use
The services preceded by [ – ] are disabled and those with [ + ] are enabled.
2. Start a service
To start a service in Ubuntu and other distributions, use this command:
3. Stop a service
Stopping a service is equally easy.
4. Restart a service
If you want to restart a service, the command is:
5. Check the status of a service
Furthermore, to check if your intended result was achieved, you can output the service status:
This will output information in the following manner:
This will, most importantly, tell you if a certain service is active (running) or not.
Wrapping Up
Today I detailed two very simple methods of managing services on Ubuntu or any other Linux system. I hope this article was helpful to you.
Which method do you prefer? Let us know in the comment section below!
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
Ubuntu Linux: Start / Restart / Stop Apache Web Server
H ow do I start, restart, or stop Apache 2.x web server on Ubuntu Linux operating systems using command line options?
You can use any one of the following method to restart / start / stop your Apache (httpd) sever on Ubuntu:
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Shell |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
- systemctl command – Only works on systemd based Ubuntu like version 16.04 LTS and above.
- /etc/init.d/apache2 – A sys v init style script to start / stop / restart the Apache2 service under Debian or Ubuntu Linux.
- service command – This command work in most Linux distributions including Debian and Ubuntu.
- upstart command – Only works on certain version of Ubuntu.
- apache2ctl command – This method should work on all Linux and Unix like operating systems.
Method #1: systemctl command examples
To start Apache 2 on Ubuntu Linux LTS 16.04 LTS or the latest systemd based Ubuntu Linux, type:
$ sudo systemctl start apache2.service
To stop Apache 2 on Ubuntu Linux LTS 16.04 LTS or the latest systemd based Ubuntu Linux, type:
$ sudo systemctl stop apache2.service
To restart Apache 2 on Ubuntu Linux LTS 16.04 LTS or the latest systemd based Ubuntu Linux, type:
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2.service
To status of start/restart/stop operation, enter:
$ journalctl -u apache2
To find out whether Apache 2 running or not, enter:
$ sudo systemctl status apache2.service
Sample session:
Fig.01: Ubuntu Linux systemctl start/stop/restart Apache server (systemd)
Method #2: /etc/init.d/apache2 command examples
You need to login as root user or use the sudo command to control Apache web-server.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Task: Start Apache 2 Server
# /etc/init.d/apache2 start
or
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
Task: Restart Apache 2 Server
# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
or
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Task: Stop Apache 2 Server
# /etc/init.d/apache2 stop
or
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 stop
Method #3: service command examples
To restart Apache 2, enter:
$ sudo service apache2 restart
To stop Apache 2, enter:
$ sudo service apache2 stop
To start Apache 2, enter:
$ sudo service apache2 start
To gracefully reload Apache 2, enter:
$ sudo service apache2 reload
Method #4: upstart command examples
The following commands only works with certian version of Ubuntu such as Ubuntu Linux LTS 12.04 and 14.04. To start Apache 2 on Ubuntu, run:
$ sudo start apache2
To stop Apache 2 on Ubuntu, run:
$ sudo stop apache2
To restart Apache 2 on Ubuntu, run:
$ sudo restart apache2
To gracefully reload Apache 2 on Ubuntu, run:
$ sudo restart apache2
Method #5: apache2ctl command examples
apache2ctl is Apache HTTP server control interface command, which can be used to stop or start web server under any Linux distribution or UNIX.
To start Apache 2 on Ubuntu, type:
$ sudo apache2ctl start
To stop Apache 2 on Ubuntu, type:
$ sudo apache2ctl stop
To restart Apache 2 on Ubuntu, type:
$ sudo apache2ctl restart
To gracefully reload Apache 2 on Ubuntu, type:
$ sudo apache2ctl graceful
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
/.bash_profile and add:
alias apache=’sudo /etc/init.d/apache2′
Then it’s just apache start, apache restart, etc.
Thanks for the tip. It worked like a charm.
These cmd line works great.
Here is what works for me:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd (space) start
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd (space) stop
nice tutorials,
is there a way to run the apache server as services just like in xampp?
Thanks,
man
wohooooooo. good tutorial . 4 thumbs ^_^
it s not workin for me….
the result is
sudo: /etc/init.d/apache2 commad not found
pls help me guys
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 do not put that column after sudo
i has stop my apache server, but another connections still establish
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 14940 /tmp/orbit-username/
I’m from Brazil, and your tip helped me a lot, thanks!
sudo service apache2 restart
Thanks mate! nice and easy ( I like the easy ones!)
Thanks for the help.
the amount of times i forget this. sheesh. thanks gzip
Hi! this tutorial is great. things have been ok but mine didnt work at the configuration stage. i restart the server but this d response:
Restarting web server apache2 apache2: Could not reliably determine the server’s fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.1.1 for ServerName
… waiting apache2: Could not reliably determine the server’s fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.1.1 for ServerName
help me pls
Your can also use this command
sudo service apache2 restart
Does the “sudo service apache2” apply for the php cli ?
PHP Cli uses a different php.ini .
sudo service apache2 This worked for me, thanks a lot. I had an instance of apache2 running, but it was screwing up apache that was trying to run in xampp.
Nice tutorial. Help a lot 🙂
If you get “command not found” then apache2 may have been installed in a non-standard directory. For instance the bitnami installers put it in ‘stack’, so to find the ctl.sh you may need to use
sudo stack/apache2/scripts/ctl.sh restart
Whether this actually solves your problem or not, I don’t know, but it doesn’t cause the error.
Also when using bitnami the command
sudo stack/ctlscript.sh restart
restarts every service bitnami installed, including apache, in a logical order.
Final comment on this: If you are using one of the XAMPP or other stacks that installs apache as part of a larger package, you want to watch the stack-restart command (like the one I gave above for bitnami) very closely and always get the verbose log.
If you have made some change like blowing away an app directory you aren’t using to fit within tight cloud host requirements, the configuration files generated for apache may be wrong/fragile and may cause apache to just not start with no indication why. However the stack-restart command for the stack you are using will generally report that problem. For instance in bitnami the restart is fragile – unless every single line of the configuration files it is relying on is up to date, you’ll have to go edit them yourself
sudo nano /opt/bitnami/apache2/conf/bitnami/bitnami-apps-prefix.conf
PHP is however more robust and usually only generates a warning if it doesn’t find some app configuration include. The worst you will see from PHP is a line like this
WARNING: Nothing matches the include pattern ‘/opt/bitnami/apps/limesurvey/conf/php-fpm/pool.conf’ from /opt/bitnami/php/etc/php-fpm.conf at line 17.
so you can sudo nano that .conf file also, but it might be better to let all future shell users have at least a chance to notice that you blew away an app package and then manually reconfigured. I would leave the warnings in place myself. Your mileage may vary.
why we have to restart apache server in ubantu
## How To Install Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP) stack on Ubuntu 14.04
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install apache2
Источник







