- Red Hat сделала бесплатным свой дистрибутив RHEL
- Программа Red Hat Developer расширена
- Почему условия изменились?
- Поиск альтернатив
- Что дает обновленная программа от Red Hat?
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives
- Contents
- History
- Motivations
- Features
- Legal aspects
- Notable Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives
- See also
- Related Research Articles
Red Hat сделала бесплатным свой дистрибутив RHEL
Отличные новости, %username%! Компания Red Hat сделала бесплатным свой корпоративный дистрибутив RHEL. Правда, есть ряд правил, выполнив которые, этим дистрибутивом можно пользоваться безвозмездно, то есть даром (вы тоже читаете это голосом Совы из мультика про Винни-Пуха?).
Раньше RHEL тоже можно было использовать бесплатно, но существовало очень много ограничений. Сейчас же часть их сняли, а часть — расширили. О новых возможностях — под катом.
Программа Red Hat Developer расширена
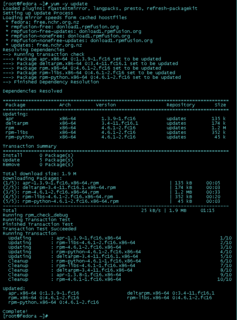
Раньше в рамках программы Red Hat Developer дистрибутивом можно было пользоваться бесплатно, но лишь при условии установки на одну виртуальную машину или один компьютер. Использовать дистрибутив разрешалось исключительно для разработки и отладки программного обеспечения. Установка дистрибутива для рабочих внедрений, сборки финальных продуктов, тестирования с участием нескольких участников или для обеспечения систем непрерывной интеграции предприятия требовала платной подписки.
Сейчас правила кардинально изменились. Так, участвовать в программе теперь могут целые команды разработчиков, а не один человек. Кроме того, дистрибутив можно разворачивать не только на ПК, но и на серверах и даже в «облаках».
Самое приятное в этом всем то, что бесплатная версия вообще ничем не отличается от платной. Если вы думаете, что у платной и бесплатной версий разные условия получения обновлений, то и это не так, все абсолютно одинаковое.
Единственные ограничения — количество копий RHEL, которые может установить одна команда разработчиков. Этот показатель не должен превышать цифру 16, и способов увеличить лимит нет. Кроме того, техническая поддержка компании доступна лишь клиентам Red Hat, которые платят.
Как стать участником программы? Нужно лишь получить учетную запись на портале Red Hat. Причем не обязательно проходить регистрацию — достаточно просто авторизоваться через профиль на Facebook, Twitter и GitHub. Все очень просто и, наверное, приятно.
Ранее регистрация подразумевала выполнение всех формальностей, включая указание ФИО, работодателя, email, номера телефона и адреса.
Почему условия изменились?
Все началось после того, как компания отказалась от развития дистрибутива CentOS 8, о чем было объявлено в конце прошлого года. Плюс ко всему, разработчики сократили срок поддержки дистрибутива. Изначально это был 2029 год, сейчас — 31 декабря 2021 года. Другими словами, меньше чем через год апдейты закончатся.
В целом, не все так плохо, поскольку вместо CentOS 8 предложена CentOS Stream. Если прежний дистрибутив получал обновления достаточно редко, то со Stream — совсем другая история. Апдейты для него выходят гораздо чаще, но здесь патчи тестируют сами разработчики, так что стабильность CentOS Stream Red Hat под вопросом.
Понятно, что многие пользователи оказались недовольны такими действиями компании. Почти сразу после объявления компании об отказе от дистрибутива в социальных сетях и мессенджерах поднялась целая волна протестов. Понять пользователей можно, ведь речь не о нескольких машинах, которые стоят дома под управлением дистрибутива. Многие бизнесы установили и настроили сетевую инфраструктуру на основе CentOS 8, рассчитывая на многолетнюю поддержку.
И когда все это превратилось в тыкву, то клиенты компании воспротивились такому подходу. Stream не устраивал пользователей по той же причине: CentOS как стабильная система использовалась во многих компаниях для обеспечения производственных процессов. Stream в качестве альтернативы здесь не подходит, поскольку стабильная работа всей компьютерной инфраструктуры — залог беспрерывности этих процессов.
Поиск альтернатив
Ряд корпоративных и обычных пользователей сразу же заявили о планах по переходу на альтернативные решения. И они не замедлили появиться. Грег Курцер, основатель CentOS, в начале года сообщил, что планирует создать форк RHEL с названием Rocky Linux. Релиз запланирован на второй квартал 2021 года. Для сборочных процессов планируют использовать Koji, Mock и MBS из Fedora Linux.
О похожих планах рассказала и компания Cloudlinux, которая предлагает собственную альтернативу. В нее компания готова вкладывать по $1 млн в год. Называется этот дистрибутив Almalinux, и появиться он должен уже в первом квартале этого года. Характеристики дистрибутива:
- Основа — пакетная база Red Hat Enterprise.
- Полная бинарная совместимость с RHEL.
- Простая и прозрачная миграция с CentOS 8.
- Поддерживаемые обновления до 2029 года.
- Free-модель для пользователей.
- Функции принятия решений делегируют сообществу по аналогии с платформой Fedora.
Есть еще Oracle Linux. Компания Oracle 14 лет разрабатывает собственный клон RHEL. Его преимущества:
- 100% совместим с RHEL на бинарном уровне;
- разработан для гибридного облака;
- автоматическое обновление Linux без перезагрузки;
- оптимизирован для работы программного обеспечения Oracle.
Что дает обновленная программа от Red Hat?
Она позволяет закрыть потребности пользователей CentOS, а именно — в стабильном бесплатном дистрибутиве, который просто работает, получая техническую поддержку.
Сейчас CentOS Stream позиционируется как «upstream» для RHEL, т.е. в нем будет проходить тестовая обкатка пакетов перед включением в релизы RHEL. Это, в свою очередь, позволит любому участнику сообщества помогать в разработке дистрибутива. Более того, станет возможным контролировать изменения, которые разработчики готовят ввести в дистрибутив.
Источник
Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives
Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives are Linux distributions that are based on the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
Contents
History
Red Hat Linux was one of the first and most popular Linux distributions. This was largely because, while a paid-for supported version was available, a freely downloadable version was also available. Since the only difference between the paid-for option and the free option was support, a great number of people chose to use the free version.
Red Hat made the decision to split its Red Hat Linux product into two: Red Hat Enterprise Linux for customers who were willing to pay for it, and Fedora that was made available free of charge but gets updates for every release for approximately 13 months.
Fedora has its own beta cycle and has some issues fixed by contributors who include Red Hat staff. However, its quick and nonconservative release cycle means it might not be suitable for some users. Fedora is somewhat a test-bed for Red Hat,
Motivations
Red Hat does not make a compiled version of its Enterprise Linux product available for free download. However, as the license terms on which it is mostly based explicitly stipulate, Red Hat has made the entire source code available in RPM format via their network of servers. The availability of the complete source code of the distribution in RPM format makes it relatively easy to recompile the entire distribution. Several distributions were created that took Red Hat’s source code, recompiled it, and released it.
Features
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives generally include the union set
[ (July 2010)»>]]>»>clarification needed ] , which is included in the different versions of RHEL. The version numbers are typically identical to the ones featured in RHEL; as such, the free versions maintain binary compatibility with the paid-for version, which means software intended for RHEL typically runs just as well on a free version. Relatively few changes need to be made to the distributions. However, RHEL used to use Red Hat’s own Up2date technology for providing updates. For convenience, several of the free alternatives ship with yum replacing up2date, something that makes providing mirrors for upgrades significantly easier. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 and above releases use yum as their native system for providing updates, with up2date being just its front end.
Legal aspects
Free redistributions are expressly permitted by the GNU General Public License upon which Red Hat’s distributions are based. [1] However, to avoid misrepresentation of Red Hat’s trademark, material in the original distribution covered by the trademark must be stripped off or removed from the redistribution.
Where distributions (e.g., CentOS) have not been deemed sufficiently thorough in removing references to Red Hat, they have received warnings from Red Hat’s legal counsel. CentOS received such a notice seeking to have it remove all mention of Red Hat’s asserted trademarks from their website and their distribution. [2] CentOS previously referred to Red Hat as the «Upstream Vendor», or more formally as a «Prominent North American Enterprise Linux vendor». [3]
Notable Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives
- AlmaLinux – Only 100% community owned and governed, open source, forever free production enterprise distribution, successor to CentOS [4]
- Bull’s XBAS or bullx – (for high-performance computing) [5][6]
- CentOS – (version 7 gets maintenance updates until 2024-06-30)
- ClearOS
- ClefOS – [7] a port of CentOS for System z by Sine Nomine Associates.
- EulerOS – certified to The Open Group’s UNIX 03 standard. [8]
- Inspur K-UX – certified to The Open Group’s UNIX 03 standard. [9]
- Oracle Linux – Free to download, distribute and use with public access to the latest errata and patches from the Oracle Linux yum server. Optional paid support subscriptions are available from Oracle. [10]
- Rocky Linux – intended to be a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system (in response to the termination of CentOS)
- Scientific Linux – (version 7 gets maintenance updates until 2024-06-30)
- SME Server – made by the Koozali Foundation (version 10 based on CentOS 7 gets maintenance updates until 2024-06-30)
- Springdale Linux – [11] formerly PUIAS Linux is a complete operating system for desktops and servers, built by compiling the source packages for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- VzLinux – [12] made by Virtuozzo and optimized to run in containers, virtual machines or on bare-metal servers.
Appliance-oriented derivatives based on RHEL:
- Amazon.comAmazon Linux AMI – RHEL7 userland with a linux-xen-kernel
- Google Search Appliance – derived from CentOS
- VMware ESX’s Service Console software
Distributions which have ceased production or outdated:
- CAOS Linux – (multiple lineage)
- Fermi Linux – a.k.a. Fermi Scientific Linux, derived from Scientific Linux with additional software specific for the Fermilab research facilities
- Rocks Cluster Distribution – derived from RHEL (earlier versions) and CentOS (recent releases)
- ROSA Enterprise Linux Server
- StartCom Enterprise Linux
- White Box Enterprise Linux – No formal announcement but no longer actively developed
- Yellow Dog Linux
See also
- Free and open-source software portal
Related Research Articles
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that is based upon the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.
Red Hat, Inc. is an American multinational software company that provides open source software products to enterprises. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina, with other offices worldwide. It became a subsidiary of IBM on July 9, 2019.
The Yellowdog Updater, Modified (YUM) is a free and open-source command-line package-management utility for computers running the Linux operating system using the RPM Package Manager. Though YUM has a command-line interface, several other tools provide graphical user interfaces to YUM functionality.
Red Hat Network is a family of systems-management services operated by Red Hat. RHN makes updates, patches, and bug fixes of packages included within Red Hat Linux and Red Hat Enterprise Linux available to subscribers. Other available features include the deployment of custom content to, and the provisioning, configuration, reporting, monitoring of client systems.
up2date, also known as the Red Hat Update Agent, is a tool used by older versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS and Fedora Core that downloads and installs new software and upgrades the operating system. It functions as a front-end to the RPM Package Manager and adds advanced features such as automatic dependency resolution. The file /etc/sysconfig/rhn/sources specifies where up2date will search for packages.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a Linux distribution developed by Red Hat for the commercial market. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. All of Red Hat’s official support and training, together with the Red Hat Certification Program, focuses on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform.
CentOS is a discontinued Linux distribution that provides a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board.
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organisational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, including how quickly security upgrades are available; ease of package management; and number of packages available.
Scientific Linux (SL) is a Linux distribution produced by Fermilab, CERN, DESY and by ETH Zurich. It is a free and open-source operating system based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
The 389 Directory Server is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server developed by Red Hat as part of the community-supported Fedora Project. The name «389» derives from the port number used by LDAP.
Fermi Linux is the generic name for Linux distributions that are created and used at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab). These releases have gone through different names: Fermi Linux, Fermi Linux LTS, LTS, Fermi Linux STS, STS, Scientific Linux Fermi, SLF. For the purposes of this entry they can be used interchangeably to designate a version of Linux specific to Fermilab.
Oracle Linux is a Linux distribution packaged and freely distributed by Oracle, available partially under the GNU General Public License since late 2006. It is compiled from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) source code, replacing Red Hat branding with Oracle’s. It is also used by Oracle Cloud and Oracle Engineered Systems such as Oracle Exadata and others.
OpenJDK is a free and open-source implementation of the Java Platform, Standard Edition. It is the result of an effort Sun Microsystems began in 2006. The implementation is licensed under the GPL-2.0-only with a linking exception. Were it not for the GPL linking exception, components that linked to the Java class library would be subject to the terms of the GPL license. OpenJDK is the official reference implementation of Java SE since version 7.
Fedora is a Linux distribution developed by the community-supported Fedora Project which is sponsored primarily by Red Hat, a subsidiary of IBM, with additional support from other companies. Fedora contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of free technologies. Fedora is the upstream source of the commercial Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution and for CentOS.
Spacewalk is open-source systems management software for system provisioning, patching and configuration licensed under the GNU GPLv2.
Ksplice is an open-source extension of the Linux kernel that allows security patches to be applied to a running kernel without the need for reboots, avoiding downtimes and improving availability. Ksplice supports only the patches that do not make significant semantic changes to kernel’s data structures.
RPM Package Manager (RPM) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to .rpm file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base.
RedSleeve is a free operating system distribution based on the Linux kernel. It is derived from the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) distribution, ported to the ARM architecture.
AlmaLinux is a free and open source Linux distribution, created originally by CloudLinux to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system that is binary-compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The first stable release of AlmaLinux was published on March 30, 2021.
Источник