- Configure Profile Manager in macOS Server
- Использование профилей конфигурации для стандартизации настроек Mac
- Установка профилей конфигурации
- Просмотр установленного профиля конфигурации
- Удаление профиля конфигурации с компьютера Mac
- Intro to Profile Manager
- Manage settings and policies
- Distribute configuration profiles
- Remotely lock or wipe a lost device
- Components of Profile Manager
- loderunner / 01-mac-profiling.md
- This comment has been minimized.
- CecileBF commented Aug 16, 2016
- This comment has been minimized.
- ShubhGar commented Nov 11, 2020
Configure Profile Manager in macOS Server
Profile Manager lets you specify how apps and books are distributed, how clients are configured, how to administer devices, and how to deliver the configurations to users and devices.
Before you can use Profile Manager, click the On button in the Server app’s Profile Manager pane, then do any of the following:
To get to the administration portal, follow the Profile Manager link in the Server app’s Profile Manager pane.
The administration portal is a website where you manage app assignments, configure settings for devices, manage enrolled devices and device groups, manage users and user groups, and execute or monitor tasks on enrolled devices.
To specify settings and assign them to users, devices, and groups, and to manage enrolled devices, click Open in Safari next to Profile Manager in the bottom of the window.
When Profile Manager opens in your web browser, sign in with your administrator name and password.
To enable remote device configuration, click Configure under of the following, then make sure the devices are enrolled:
Apple School Manager
Apple Business Manager
Device Enrollment Program (you must have an existing account)
After a device is enrolled, you can update its configuration over the network without user interaction and perform other tasks. For information about how users interact with Profile Manager, click Open Profile Manager, then choose Help from the User menu.
To assign apps and books purchased through Apple School Manager, Apple Business Manager, or Volume Purchasing, click Configure under “Volume Purchase for Apps and Books.”
For information about how to assign apps and books purchased through Apple School Manager, Apple Business Manager, or Volume Purchasing to devices, users, or groups, click Open Profile Manager, then choose Help from the User menu.
To use the Apple Push Notification service (APNs), click Configure under “Device communication push notification certificate,” then sign in with your Apple ID and password.
To sign profiles using a certificate, select “Sign configuration profiles,” then choose a certificate from the Certificates pop-up menu.
If the certificate isn’t available in the menu, choose Import from the Certificates pop-up menu and import a certificate.
Источник
Использование профилей конфигурации для стандартизации настроек Mac
Профили конфигурации позволяют стандартизировать настройки компьютеров Mac. Например, администратор может создать профили для настройки компьютеров Mac для взаимодействия с серверами в школьной или рабочей сети.
Профиль конфигурации может включать в себя настройки учетной записи пользователя в приложении «Почта», параметры Wi-Fi, параметры VPN и другие настройки. Профили конфигурации можно использовать на Mac, устройствах iOS, iPadOS, Apple Watch и Apple TV.
Ваш сетевой администратор может попросить Вас установить один или несколько профилей, или может предложить Вам установить профиль, который позволит администратору устанавливать дополнительные профили конфигурации.
Если у Вас компьютер Mac с процессором Apple и Вы получили профиль регистрации, рекомендуется обратиться к сетевому администратору для получения инструкций по установке профиля. Сведения для сетевых администраторов по настройке управляемых компьютеров и установке профилей регистрации см. в Справочнике по развертыванию Mac.
О политике конфиденциальности Apple см. на странице Политика конфиденциальности Apple.
Установка профилей конфигурации
Чтобы открыть профиль на панели «Профили» для просмотра информации о нем на Mac, выполните одно из следующих действий:
Если профиль вложен в почтовое сообщение, откройте вложение.
Если профиль размещен на веб-сайте, загрузите профиль и откройте его.
Нажмите на профиль, чтобы установить его на Ваш Mac.
Возможно, во время установки потребуется ввести пароль или другую информацию.
Если на Вашем Mac была установлена более ранняя версия профиля, настройки из обновленной версии профиля перезапишут предыдущие настройки.
Просмотр установленного профиля конфигурации
На Mac выберите меню Apple
> «Системные настройки», затем нажмите «Профили».
Если Вы еще не устанавливали профили конфигурации, панель «Профили» будет недоступна.
Выберите профиль в списке «Профили», чтобы просмотреть информацию о нем.
Удаление профиля конфигурации с компьютера Mac
На Mac выберите меню Apple
> «Системные настройки», затем нажмите «Профили».
Если Вы еще не устанавливали профили конфигурации, панель «Профили» будет недоступна.
Выберите профиль в списке «Профили» и нажмите кнопку «Удалить» 
При удалении профиля удаляются все его настройки и информация о нем. Например, если Вы настроили учетную запись электронной почты с помощью профиля, при удалении профиля с Вашего Mac также удаляется информация об учетной записи.
Если Вы не можете удалить профиль конфигурации, обратитесь за помощью к тому, кто предоставил Вам этот профиль.
Если Вы разрабатываете приложения для компьютеров Mac и Вам нужны сведения о профилях обеспечения, см. раздел справки, посвященный созданию профиля обеспечения разработчика.
Источник
Intro to Profile Manager
You use Profile Manager to configure and distribute settings to iPhone, iPad, and Apple TV devices and Mac computers in your organization. You can also use Profile Manager to quickly configure large numbers of devices with the settings, apps, and books your organization requires.
Note: Although Profile Manager will work with earlier versions of iOS, iPadOS, tvOS, and macOS, some features are available only for the latest versions of each OS.
Manage settings and policies
Profile Manager creates and distributes configuration profiles. You install them on a device to configure the settings. To learn more about configuration profiles, see the Profile Manager User Guide. When the profile is installed on a user’s device, the settings it defines are applied. If the settings are applied to a user, those settings apply to any device associated with that user. If the settings are applied to a device, those settings are enforced regardless of who uses the device.
Each user, user group, device, and device group can have configuration profiles to provide a base level of settings. Then you can assign additional configuration profiles to customize the settings to meet your needs.
In addition to general configuration settings, Profile Manager lets you enforce organization policies. For example, you can specify password policies, define the types of networks devices can connect to, and enforce restrictions such as preventing the use of cameras on iOS and iPadOS devices and disabling specific system preferences in macOS. If you’re managing the devices remotely, you can install updated policies without user action or notification.
Distribute configuration profiles
After you define the settings for users and their devices, you can distribute the configuration profiles in the following ways:
Distributed upon activation: Settings can be automatically configured after the device has been activated over the Internet.
Remote device management: You can enable the Profile Manager mobile device management service, which lets you remotely install, remove, and update configuration profiles on enrolled devices.
User self-service: Users can download and install the settings from the Profile Manager built-in user portal. The user portal ensures that users receive the configuration profiles you assign to them or their group.
Manual distribution: You can download configuration profiles (.mobileconfig files) from the Profile Manager administration portal and then send them to your users via a mail message or post them to a website you create. When users receive or download the files, they can install them on their device.
Remotely lock or wipe a lost device
You can remotely lock devices that you manage using Profile Manager. For a Mac, locking shuts down the Mac and installs an EFI passcode so it can’t be started up without providing the passcode. On iOS and iPadOS devices, locking invokes the Lock screen and enforces the passcode, if any, installed on the device.
Wiping a Mac removes all user data. Wiping an iOS and iPadOS device restores it to factory defaults.
For iOS and iPadOS devices, you can also reset a user’s passcode when the user has forgotten it. This temporarily removes the device passcode (for 60 minutes). To unlock the device, the user is immediately required to enter a new passcode that meets the criteria specified by the configuration profiles installed on the device.
Components of Profile Manager
Profile Manager consists of three main parts that work together to let you specify when and how devices are enrolled and configured, and apps and books are distributed.
Mobile device management (MDM) service: A mobile device management service lets you remotely manage enrolled devices. After a device is enrolled, you can update a configuration over the network and perform other tasks without user interaction. MDM is supported on:
iPhone and iPod touch ( iOS 5 or later)
iPad ( iOS 5 or later or iPadOS 13.1 or later)
Mac computers ( OS X 10.7 or later)
Apple TV ( tvOS 9 or later)
Wireless configuration of Apple devices: This lets you streamline the configuration of organization-owned devices. To get users up and running quickly, enroll devices in MDM during activation and skip basic setup steps.
App and book distribution: Distribute apps and books purchased through Apple School Manager or Apple Business Manager and enterprise apps and books.
Источник
loderunner / 01-mac-profiling.md
Profiling an application in Mac OS X
Finding which process to profile
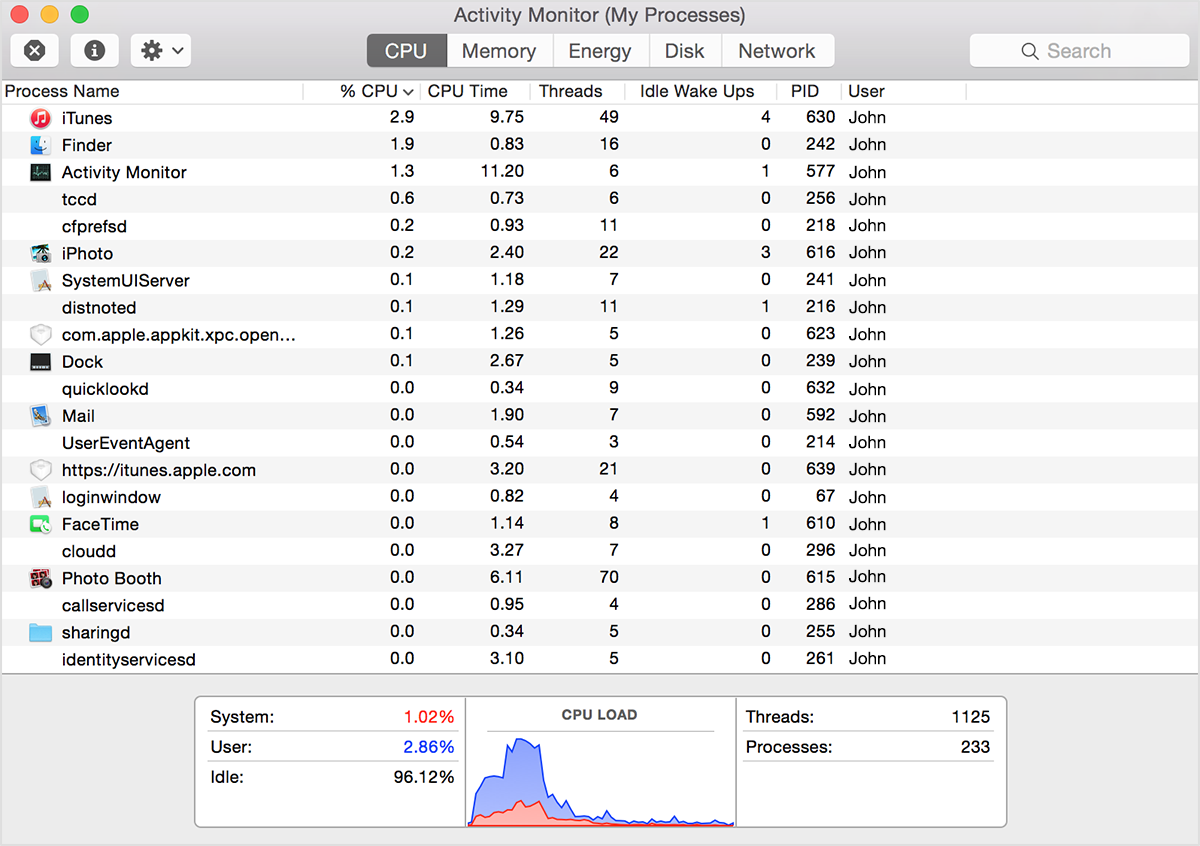
If your system is running slowly, perhaps a process is using too much CPU time and won’t let other processes run smoothly. To find out which processes are taking up a lot of CPU time, you can use Apple’s Activity Monitor.
The CPU pane shows how processes are affecting CPU (processor) activity:
Click the top of the “% CPU” column to sort by the percentage of CPU capability used by each process. If one of the top processes displays a large number (80-100% or more!) then this process may be hogging the CPU and preventing the other processes from doing their tasks. This can result in slow response times, beachballing and even some applications freezing.
A process with a high «% CPU» value is worth profiling.
A process that often freezes or beachballs, even though all other applications run smoothly and «% CPU» is very low, is also worth profiling.
Xcode Command-Line Tools
Profiling is much better with the Xcode tools installed. Instruments has a command-line interface to provide detailed profiling that can be opened in the Instruments application for investigation.
To check if Xcode Command-Line Tools are installed, open a Terminal and type:
to print the path of the current developer directory. If the command-line tools are installed, the output should be a path like the following:
If not, an error message is output:
To install Xcode Command-Line Tools, type:
Profiling with Instruments
If Xcode Command-Line Tools are installed, it is best to use Instruments to profile your application. If Xcode Command-Line Tools are not installed and you would rather not install them, skip to the next section for profiling with sample . In this example, we will show how to profile ecore .
First, we need to find the process ID (PID) of ecore . Open a Terminal and type:
and you should see something like this:
The first entry is the currently running instance of ecore . (We’ll ignore the second entry as it is only an artifact of the actual search). The second column is our PID., in this case 5773 .
Now that we know the PID, it’s time to create a time profile for ecore . Type the following in the Terminal:
After 30s (30’000ms), instruments will save the profile to the Desktop and exit with a message indicating the name of the latest profile file. This file can be opened in Instruments or forwarded to a developer to understand what performance issues have arisen in ecore on your computer.
Profiling with sample
sample is a much simpler tool than Instruments. However, its simplicity is also why it is included in a standard Mac OS X installation. To profile ecore using sample , first find ecore ‘s PID (see above). For this example, I will assume that the PID is still 5773 . Open a Terminal and type:
This will sample process 5773 for 30s and write the profile to the given path. This file can be opened as text or forwarded to a developer to understand what performance issues have arisen in ecore on your computer.
Improving your sample
Under the hood, sampling checks your process every 1 ms and reports what your process was doing at the time. The data might not always be pertinent.
For example, if your process sleep s a lot or is never scheduled to run by the operating system, then no sample is taken. Luckily, you can always tell the kernel that your process is important and should be scheduled more often than others. Use renice for that. For example:
This will set the scheduling priority of your process to the maximum.
If you are using profiling to diagnose a specific operation in your process like drawing a view or listing files, you need to make sure the specific code is triggered as often as possible (by refreshing the view a lot, or performing a lot of ls ) during the sampling period.
If none of these options yield better results, or do not apply to your case, it is always possible to extend the sampling duration. 30 seconds seems a bare minimum and you will always get more data if you sample longer.
Getting a complete system diagnostics in Mac OS X
In order to understand a problem on Mac, it is sometimes useful to get a full system diagnostics. Apple provides an interface to generate extensive diagnostics about many system services and features. To generate a full system diagnosis, follow these instructions.
- Launch the troublesome app.
- Open Applications > Utilities
- Launch Activity Monitor
- In the toolbar, click the “options” button, and select “Run System Diagnostics…” from the drop-down menu
- Read the warning, and press OK
- Enter your password
- Wait for system diagnostics to finish
- When the system diagnostics are finished, a Finder window will open
- Choose the file with name similar to sysdiagnose_2015.11.18_14-36-34+0100.tar.gz and send it to customer care.
Finding crash reports in Console
- Open the Console app from Applications > Utilities
- Select User diagnostic reports from the Sidebar
- Look a file starting with the name of the app/executable that crashed. In this example, ecore has crashed, the file is named ecore_2016-05-09-170911_iChrales.crash
- Copy the entire text or just drag-and-drop the filename to the Finder
- Send the crash report attached to your issue report
Searching system log messages in Console
- Open the Console app from Applications > Utilities
- Select All messages from the Sidebar
- Type the name of the app/executable in the search field in the upper-right corner. In this example, we type ecore in the search field.
- Select the filtered lines and copy them to the clipboard (cmd-C)
- Paste (cmd-V) the log lines and save them to a text file and send the file attached to your issue report
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
CecileBF commented Aug 16, 2016
[French] non-tech (sample) version : profiler une application.
- Ouvrez votre moniteur d’activité sur votre Mac. Le pannel CPU montre comment les processus en cours affectent l’activité de votre processeur :
- Cliquez en haut sur la colonne «% CPU» pour ranger les processus par pourcentage de capacité CPU. Si celui qui arrive en haut montre un grand nombre (80-100% ou plus), cela peut surcharger le processeur et empêcher les autres processus de fonctionner. Cela peut avoir comme résulttat un ralentissement général de votre système avec des temps de réponse longs, des roues de chargement (
) récurrentes voire des applications qui bloquent.
Il est intéressant de profiler un processus qui a une grande valeur de «% CPU». - Trouvez ensuite l’identification du processus (PID) de ecore. Ouvrez un terminal et tapez :
ps aux | grep ecore
Et vous devriez trouver quelque chose comme
user 5773 0.0 0.0 3183424 9088 ?? S 2:47PM 0:09.00 /Applications/Lima.app/Contents/MacOS/ecore [. arguments. ] user 6543 0.0 0.0 2432772 648 s006 S+ 4:32PM 0:00.00 grep ecore
La première réponse est l’exécution en cours de ecore , et la deuxième colonne de cette entrée est votre PID, ici «5773».
Ouvrez un terminal et tapez en remplaçant «5773» par votre PID.
sample 5773 30 -file
/Desktop/ecore.sample.txt
Cela va échantilloner le processus 5773 pendant 30 secondes et écrire le profil du chemin d’accès vers le fichier souhaiter. Ce fichier peut petre ouvert comme texte si vous le souhaitez, mais surtout : pouvez-vous nous le transférer en pièce jointe à ce mail s’il vous plaît ?
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
ShubhGar commented Nov 11, 2020
Can we profile iOS App (iPhone connected via USB) from instrument Command line.
Источник