- Установка Oracle 12c (12.1.0.2.0) на Windows 2012 R2
- Oracle Database 12c Release 1 RAC On Windows 2012 Using VirtualBox
- Introduction
- Download Software
- VirtualBox Installation
- Virtual Machine Setup
- Guest Operating System Installation
- Oracle Installation Prerequisites
- Create Shared Disks
- Clone the Virtual Machine
- Install the Grid Infrastructure
- Install the Database Software
- Create a Database
- Check the Status of the RAC
Установка Oracle 12c (12.1.0.2.0) на Windows 2012 R2
ВНИМАНИЕ: Установку нужно проводить от лица пользователя ОС имя которого пишется латинскими буквами. Т.е. если ваш пользователь — Администратор, переименуйте его в Administrator. (Почему лучше использовать англоязычное системное программное обеспечение)
— Берем два первых диска дистрибутива. Для данной версии это p17694377_121020_MSWIN-x86-64_1of8.zip и p17694377_121020_MSWIN-x86-64_2of8.zip. Разархивируем оба в одну и ту же папку на диске. Запускаем setup.exe.
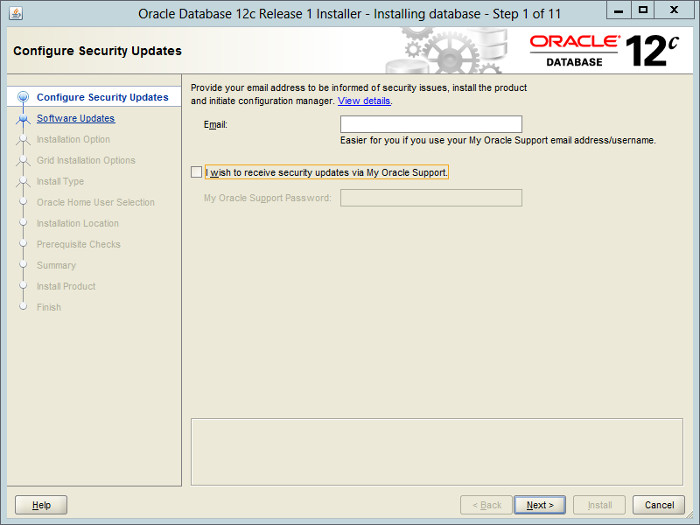
— На первом экране предлагается ввести адрес электронной почты или учетную запись My Oracle Support (MOS). Cнимаем галочку «I wish to receive security updates via My Oracle Support» — «Я хочу получать обновления безопасности с помощью My Oracle Support».
— Подтверждаем что будем оставаться в неведении по поводу важнейших вопросов безопасности в нашей конфигурации?
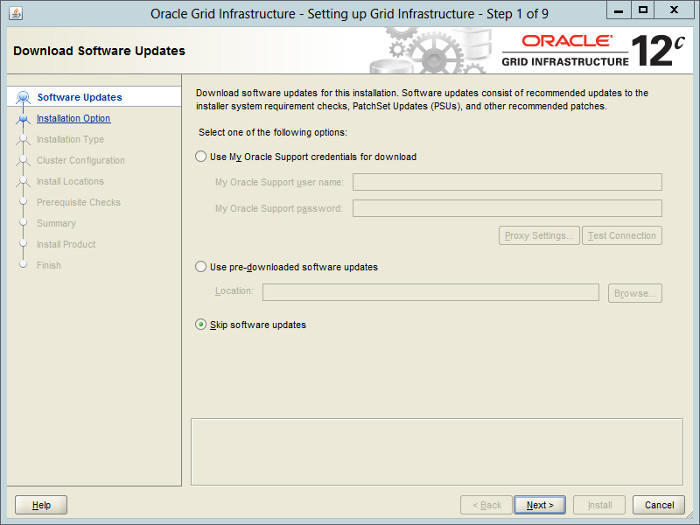
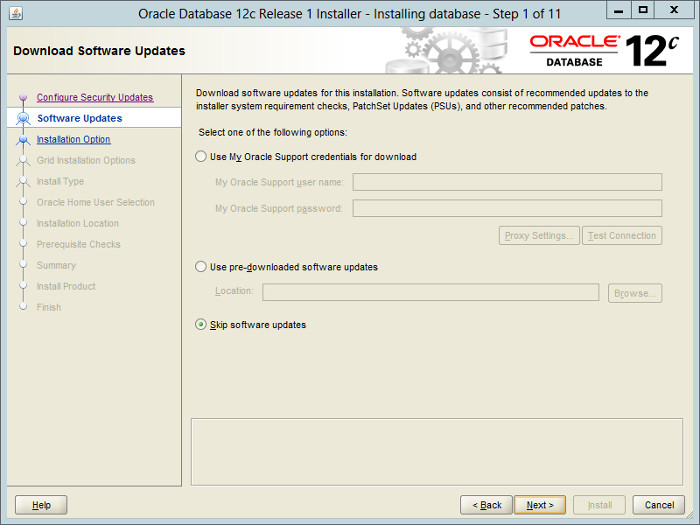
— (Этого экрана может и не быть). Здесь предлагается скачать (если есть учетная запись MOS) или указать на уже скачанное обновление, которое будет применено в процессе установки Oracle. Отказываемся от этого, выбираем «Skip software updates» — «Пропустить обновление ПО».
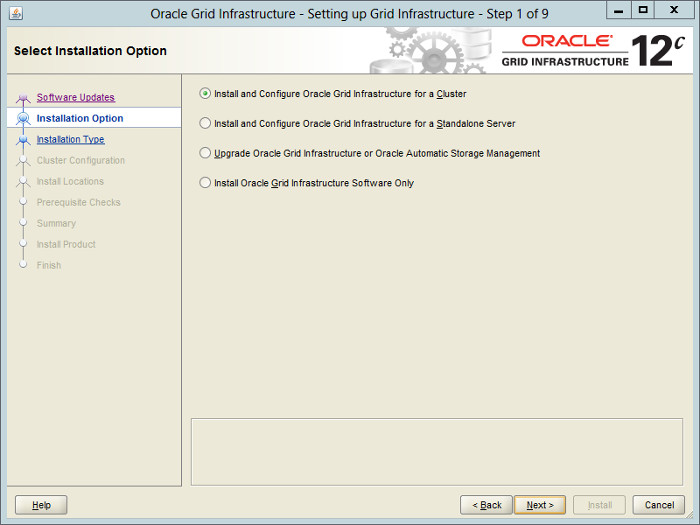
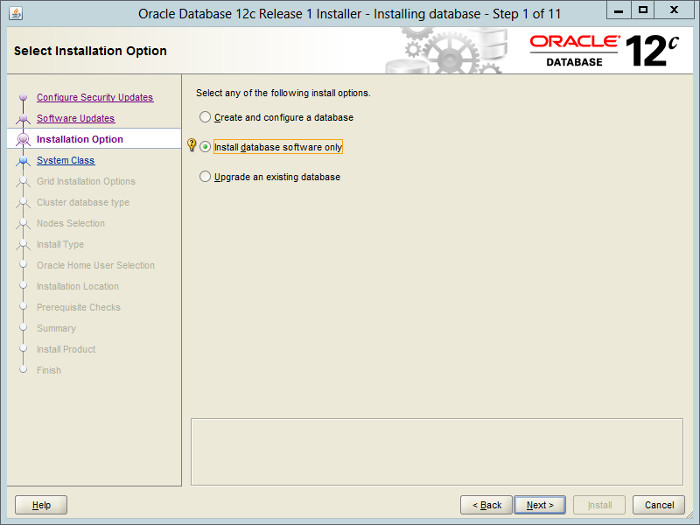
— Предлагается три варианта:
1) Во время установки создать и сконфигурировать БД — «Create and configure a database«;
2) Только установить Oracle и больше ничего — «Install database software only«;
3) Во время установки обновить существующую базу (это если вы обновляетесь с одной версии Oracle на другую) — «Upgrade an existing database«.
Выбираем вариант 2.
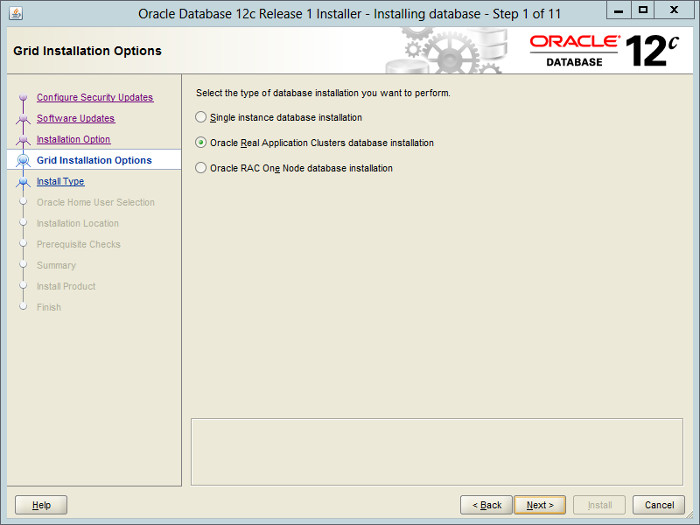
— Выбираем тип установки:
1) Одиночный экземпляр «Single instance database installation«;
2) Oracle RAC (кластер) «Oracle Real Application Clusters database installation«;
3) Oracle RAC One Node (кластер из одного узла) «Oracle RAC One Node database installation«;
Выбираю вариант 1.
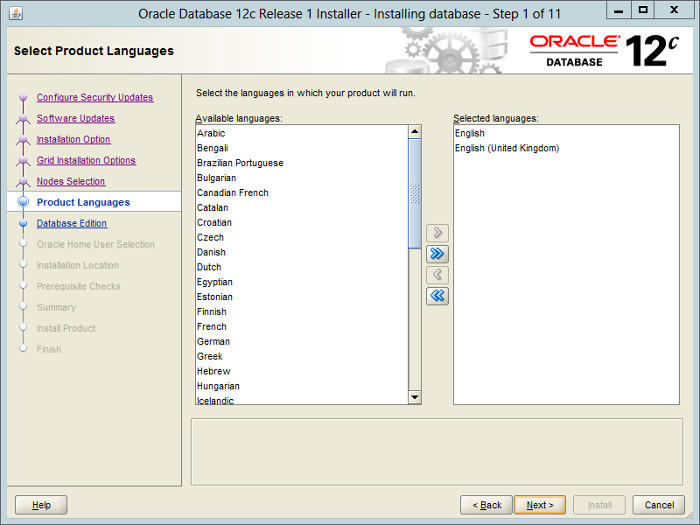
— Выбираем язык. Здесь обязательно нужно добавить русский язык «Russian«.
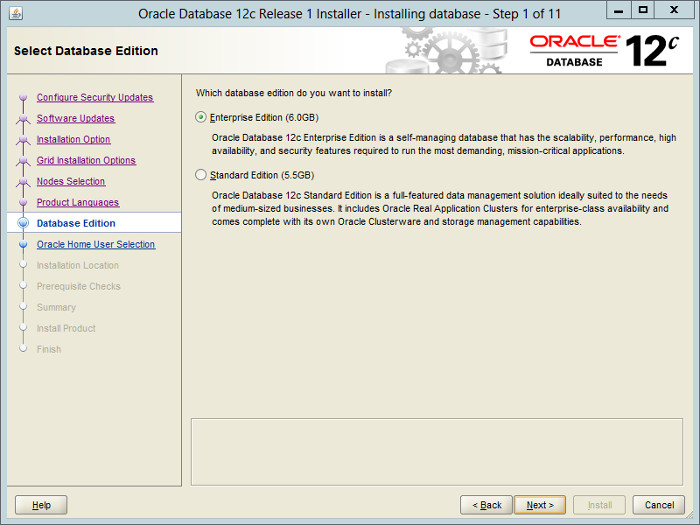
— Выбираем вариант установки. Я выбираю Enterprise Edition.
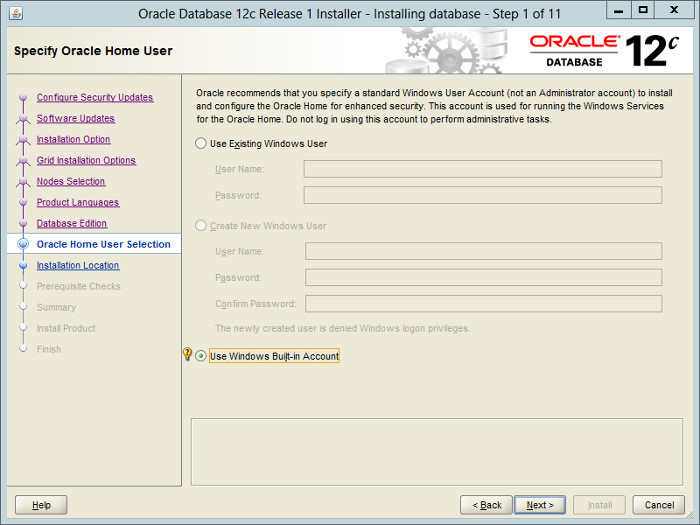
— Для повышения безопастности можно создать или указать уже созданного пользователя ОС от лица которого будут запускаться службы Oracle и назначены права на файлы в Oracle Home. Создаем нового пользователя — oracle.
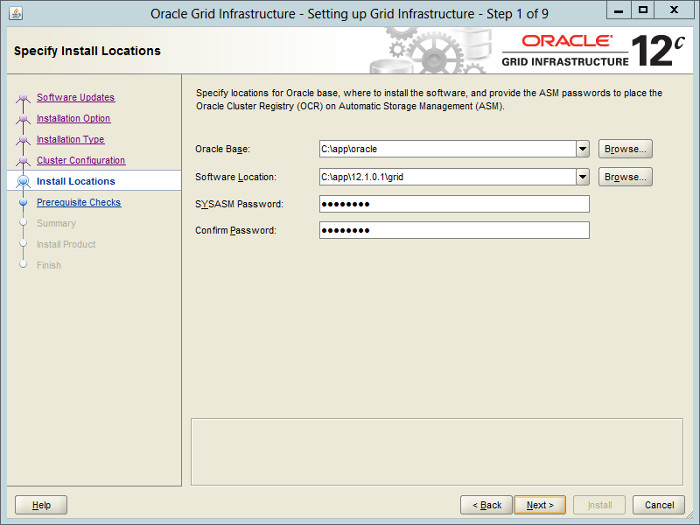
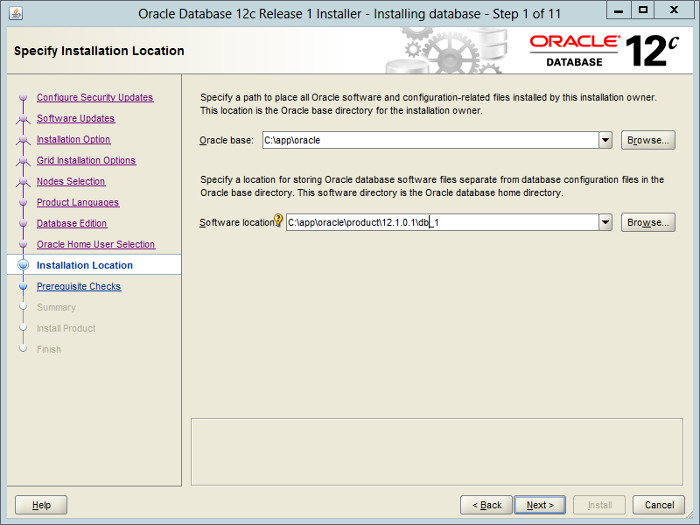
— Выбираем папки для установки.
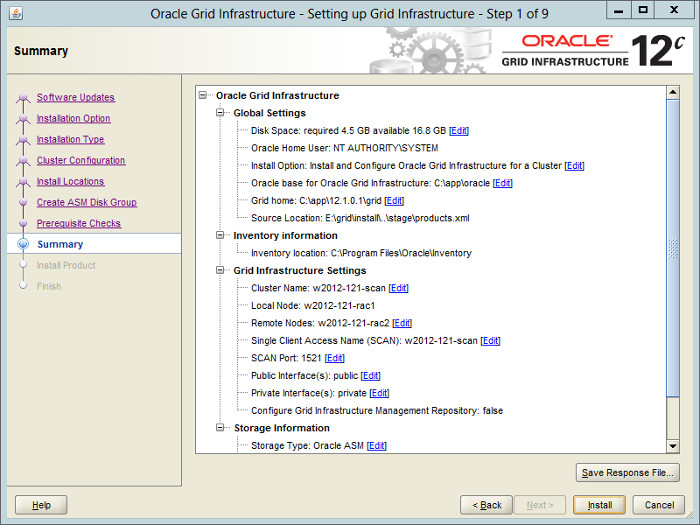
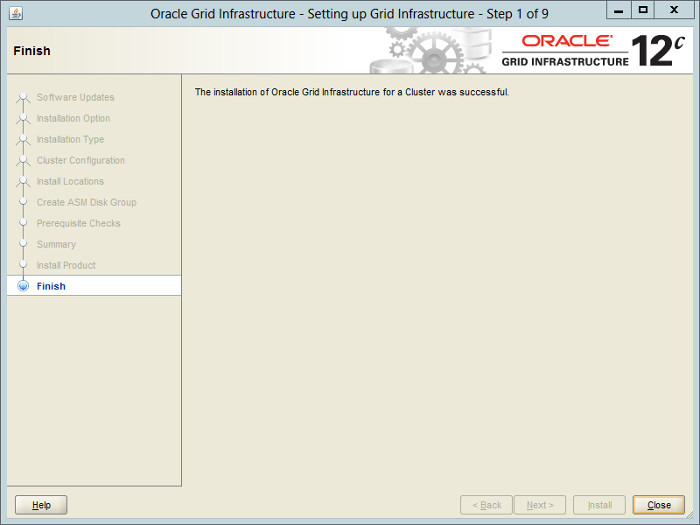
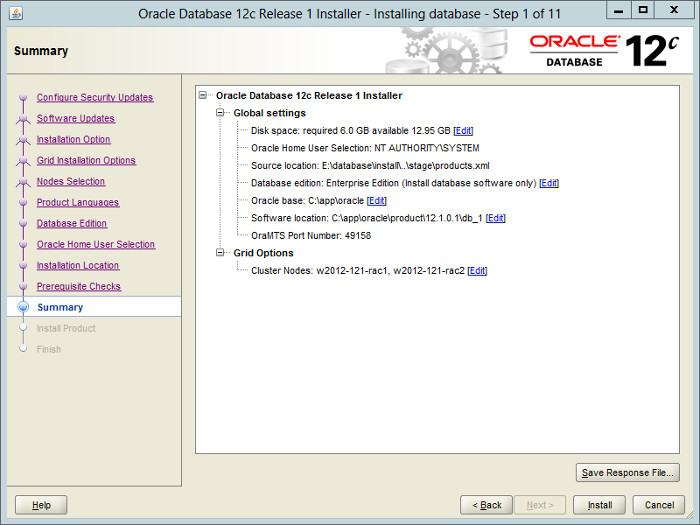
— Здесь проверка минимальных требований. Если она успешна, то увидим этот экран. Это суммарная информация по установке и последний шанс что-то еще поменять.
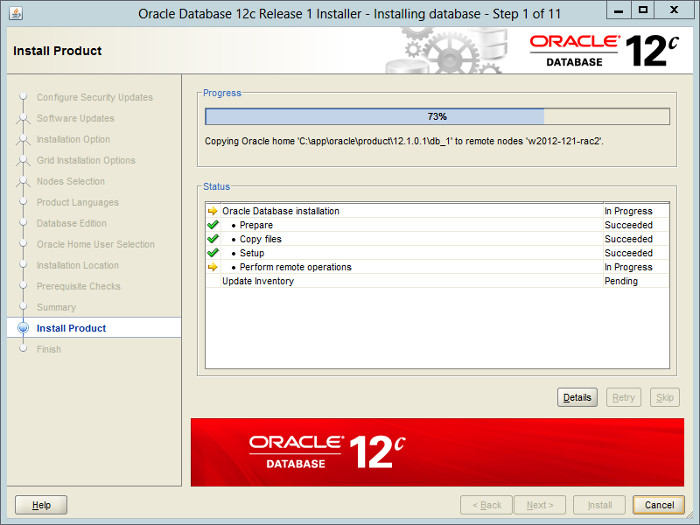
— Установка запущена, идет копирование файлов.
Oracle Database 12c Release 1 RAC On Windows 2012 Using VirtualBox
This article describes the installation of Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1) RAC on Windows 2012 Server Standard Edition using VirtualBox with no additional shared disk devices.
Introduction
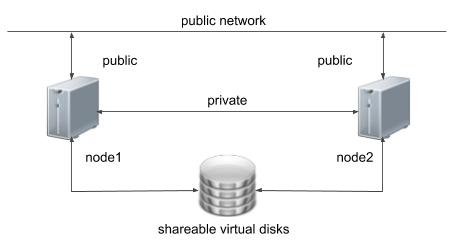
One of the biggest obstacles preventing people from setting up test RAC environments is the requirement for shared storage. In a production environment, shared storage is often provided by a SAN or high-end NAS device, but both of these options are very expensive when all you want to do is get some experience installing and using RAC. A cheaper alternative is to use a FireWire disk enclosure to allow two machines to access the same disk(s), but that still costs money and requires two servers. A third option is to use virtualization to fake the shared storage.
Using VirtualBox you can run multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) on a single server, allowing you to run both RAC nodes on a single machine. In additon, it allows you to set up shared virtual disks, overcoming the obstacle of expensive shared storage.
Before you launch into this installation, here are a few things to consider.
- The finished system includes the host operating system, two guest operating systems, two sets of Oracle Grid Infrastructure (Clusterware + ASM) and two Database instances all on a single server. As you can imagine, this requires a significant amount of disk space, CPU and memory.
- Following on from the last point, the VMs will each need at least 4G of RAM, preferably more if you don’t want the VMs to swap like crazy. Don’t assume you will be able to run this on a small PC or laptop. You won’t.
- This procedure provides a bare bones installation to get the RAC working. There is no redundancy in the Grid Infrastructure installation or the ASM installation. To add this, simply create double the amount of shared disks and select the «Normal» redundancy option when it is offered. Of course, this will take more disk space.
- During the virtual disk creation, I always choose not to preallocate the disk space. This makes virtual disk access slower during the installation, but saves on wasted disk space. The shared disks must have their space preallocated.
- This is not, and should not be considered, a production-ready system. It’s simply to allow you to get used to installing and using RAC.
- The Single Client Access Name (SCAN) should be defined in the DNS or GNS and round-robin between one of 3 addresses, which are on the same subnet as the public and virtual IPs. Prior to 11.2.0.2 it could be defined as a single IP address in the «/etc/hosts» file, which is wrong and will cause the cluster verification to fail, but it allowed you to complete the install without the presence of a DNS. This does not seem to work for 11.2.0.2 onward.
- The virtual machines can be limited to 2Gig of swap, which causes a prerequisite check failure, but doesn’t prevent the installation working. If you want to avoid this, define 3+Gig of swap.
- This article uses the 64-bit versions of Windows and Oracle 11g Release 2.
- In this article I am using a Oracle Linux as my host OS.
Download Software
Download the following software.
VirtualBox Installation
First, install the VirtualBox software. On RHEL and its clones you do this with the following command as the root user.
The package name will vary depending on the host distribution you are using. Once complete, VirtualBox is started from the menu.
Virtual Machine Setup
Now we must define the two virtual RAC nodes. We can save time by defining one VM, then cloning it when it is installed.
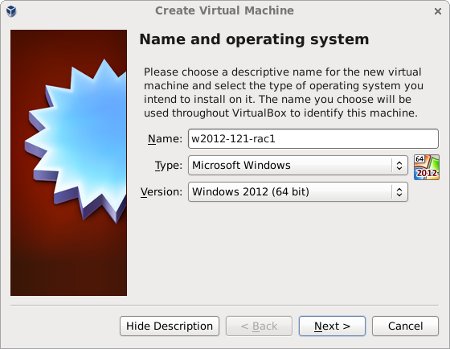
Start VirtualBox and click the «New» button on the toolbar. Enter the name «w2012-121-rac1», OS «Microsoft Windows» and Version «Windows 2012 (64 bit)», then click the «Next» button.
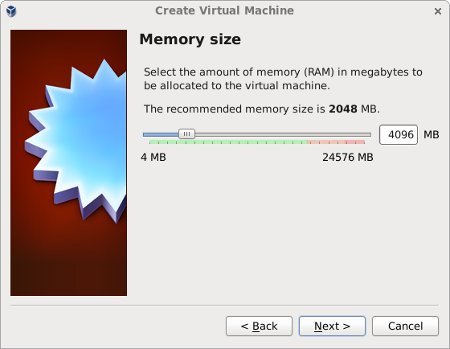
Enter «4096» as the base memory size, then click the «Next» button. Use more memory if you have enough physical memory on your machine as it will make the process much quicker!
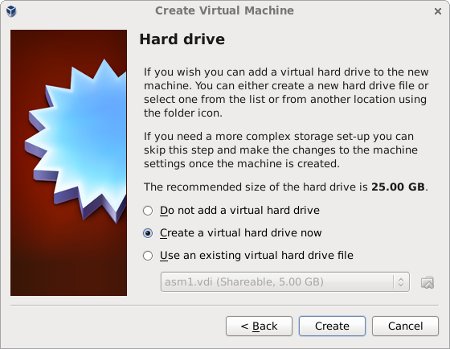
Accept the default option to create a new virtual hard disk by clicking the «Create» button.
Acccept the default hard drive file type by clicking the «Next» button.
Acccept the «Dynamically allocated» option by clicking the «Next» button.
Accept the default location and set the size to «30G», then click the «Create» button. If you can spread the virtual disks onto different physical disks, that will improve performance.
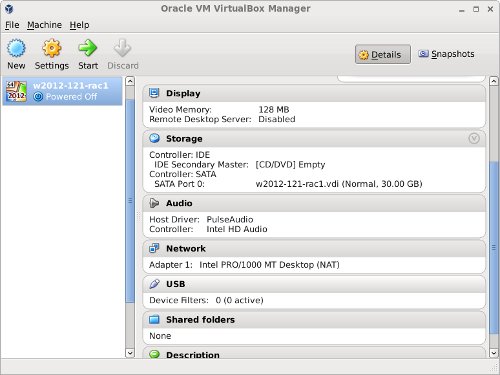
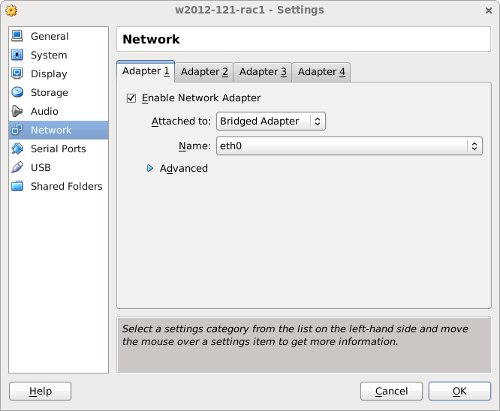
The «w2012-121-rac1» VM will appear on the left hand pane. Scroll down the details on the right and click on the «Network» link.
Make sure «Adapter 1» is enabled, set to «Bridged Adapter», then click on the «Adapter 2» tab.
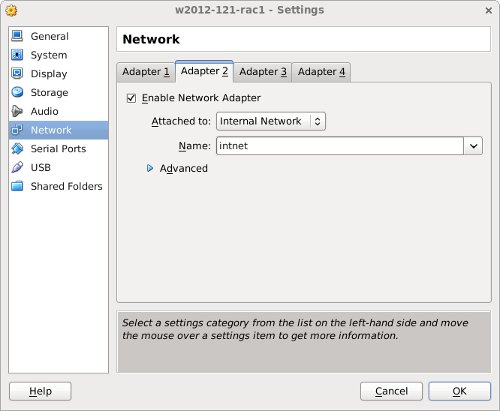
Make sure «Adapter 2» is enabled, set to «Internal Network», then click on the «System» section.
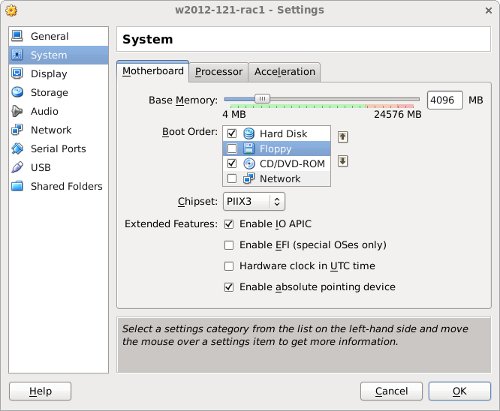
Move «Hard Disk» to the top of the boot order and uncheck the «Floppy» option, then click the «OK» button.
The virtual machine is now configured so we can start the guest operating system installation.
Guest Operating System Installation
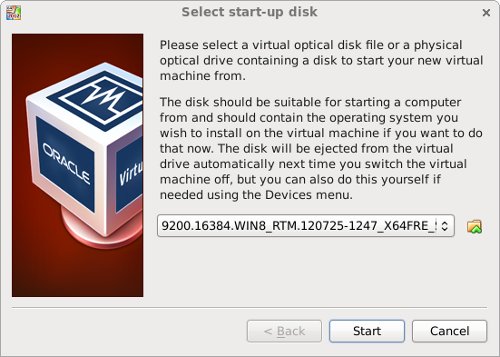
With the new VM highlighted, click the «Start» button on the toolbar. On the «Select start-up disk» screen, choose the relevant Oracle Linux ISO image and click the «Start» button.
The resulting console window will contain the Windows 2012 boot screen.
Continue through the Full Standard Edition installation as you would for a normal server. In this case I was using an evaluation version of Windows 2012, so I picked the «Windows Server 2012 Standard Evaluation (Server with a GUI)» option. Pick the custom install when doing a fresh installation.
When the installation is complete, install the VirtualBox Guest Additions on the server. This is initiated from the «Devices > Install Guest Additions. » menu. Accept all the defaults and reboot the server when requested.
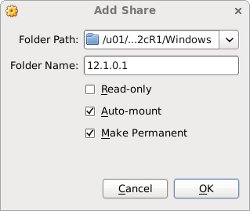
Create a shared folder (Devices > Shared Folders) on the virtual machine, pointing to the directory on the host where the Oracle software was unzipped. Check the «Auto-mount» and «Make Permanent» options before clicking the «OK» button.
The VM will need to be restarted for the guest additions to be used properly. The next section requires a shutdown so no additional restart is needed at this time. Once the VM is restarted, the shared folder will be available as the «E:\» drive.
Oracle Installation Prerequisites
Perform the following steps whilst logged into the virtual machine.
Turn off the Windows firewall «Server Manager > Local Server > Windows Firewall > Public:On > Turn Windows Firewall on or off» to prevent it from interfering with the sever communication. You can turn it on later and open up any required ports if you want to.
Amend the «C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts» file to contain the following information. Even if you are using DNS to resolve the SCAN, include the SCAN entries in the «hosts» files. Without them the installer had trouble recognising the SCAN.
Open the «Network Connections» screen (Server Manager > Local Server > Ethernet (click link next to it)). Rename the «Ethernet» to «public» and «Ethernet 2» to «private», making sure you apply the names to the appropriate connections. You can do this by right-clicking on the connection and selecting «Rename» from the pop-up menu.
Set the correct IP information for the public and private connections. Right-click on a connection and select the «Properties» menu option. Click on «Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)» option and click the «Properties. button. Enter the appropriate IP, subnet, default gateway and DNS for the networks.
- IP Address: 192.168.0.151
- Subnet: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway: 192.168.0.1
- DNS: 192.168.0.6
- IP Address: 192.168.1.151
- Subnet: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway: N/A
- DNS: N/A
Click on the «Advanced» button, followed by the «DNS» tab. Select the «Append these DNS suffixes (in order)» option and add the domain suffix, in this case «localdomain». Use the «OK» buttons to exit the dialogs.
It’s worth double-checking the MAC addresses of the network adapters in the VM against those of the network interfaces on the guest operating system. Make sure the public interface is the bridged connection. The guest OS sometimes shows the interfaces out of order.
If any of the network connections are left in a disabled state, right-click on then and select the «Diagnose» option to repair them.
Ensure the public interface is first in the bind order:
- On the «Network Connections» dialog, press «Alt+N» to show the advanced menu. Select «Advanced Settings. «.
- On the «Adapters and Bindings» tab, make sure the public interface is the first interface listed.
- Click on each network in turn and make sure the «TCP/IPv4» bindings come before the «TCP/IPv6» bindings. This should be correct by default.
- Accept any modifications by clicking on the «OK» button and exiting the «Network Connections» dialog.
Disable Windows Media Sensing for TCP/IP:
- Backup the Windows registry.
Run the Registry Editor (Regedit.exe) and find the following key.
Add the following registry value.
Open the «System Properties» dialog (Start > Control Panel > System and Security > System > Change Settings) and do the following:
- Click the «Change» button, enter the machine name «w2012-121-rac1» then click the «OK» button.
- Click on the Advanced tab and the «Environment Variables» button.
- Edit both the «TEMP» and «TMP» environment variables to be «%WINDIR%\temp», which is «C:\Windows\temp».
- Click the «OK» button and «Apply» out of the «System» dialog.
Restart the server.
Create Shared Disks
Make sure the VM is shutdown, create a directory to host the shared virtual disks on the host OS, then create the shared disks. My host is Linux, so the paths to the virtual disks are UNIX-style paths. If your host is Windows, then you will be using Windows-style paths.
Start the w2012-121-rac1 virtual machine by clicking the «Start» button on the toolbar. When the server has started, log in so you can partition the disks.
We will partition the disks using the «DiskPart» utility. To get alist of the current disks do the following.
In the diskpart utility we will perform the following commands.
Stamp the disks for use with ASM. This is done using the asmtool that comes with the Grid Infrastructure media.
The shared disks are now configured.
Clone the Virtual Machine
VirtualBox allows you to clone VMs, but these also attempt to clone the shared disks, which is not what we want. Instead we must manually clone the VM.
Shutdown the «w2012-121-rac1» VM.
Manually clone the virtual disk using the following commands on the host server.
Create the «w2012-121-rac2» virtual machine in VirtualBox in the same way as you did for «w2012-121-rac1», with the exception of using an existing «w2012-121-rac2.vdi» virtual hard drive.
Remember to add the three network adaptors as you did on the first VM. When the VM is created, attach the shared disks to this VM.
Start the «w2008-112-rac2» virtual machine.
Open the «Network Connections» screen (Server Manager > Local Server > Ethernet (click link next to it)) and amend the IP address values of each network to the appropriate values for the second node.
Open the «System Properties» dialog (Start > Control Panel > System and Security > System > Change Settings) and change the machine name by clicking the «Change» button. Click all «OK» buttons to exit the «System Properties» dialog and restart the server when prompted.
Once the RAC2 virtual machine has restarted, start the RAC1 virtual machine. When both nodes have started, check they can both ping all the public and private IP addresses using the following commands.
At this point the virtual IP addresses defined in the hosts file will not work, so don’t bother testing them.
The virtual machine setup is now complete.
Before moving forward you should probably shut down your VMs and take snapshots of them. If any failures happen beyond this point it is probably better to switch back to those snapshots, clean up the shared drives and start the grid installation again. An alternative to cleaning up the shared disks is to back them up now using zip and just replace them in the event of a failure.
Install the Grid Infrastructure
Make sure both virtual machines are started. Login to «w2012-121-rac1» and start the Oracle installer.
Select the «Skip software updates» option, then click the «Next» button.
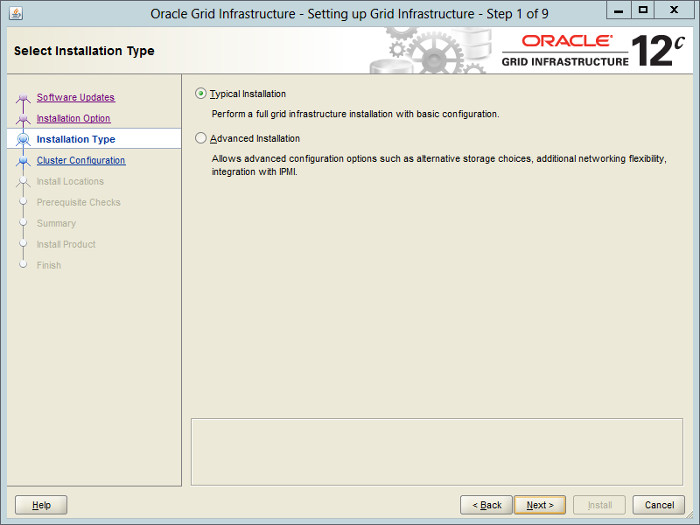
Select the «Install and Configure Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Cluster» option, then click the «Next» button.
Select the «Typical Installation» option, then click the «Next» button.
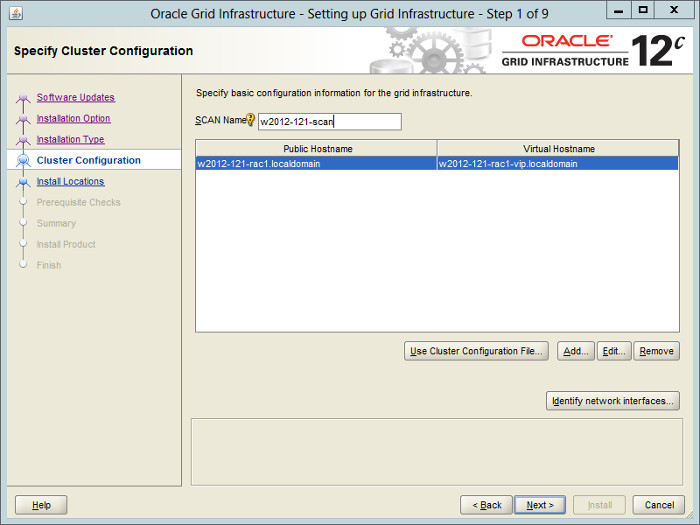
On the «Specify Cluster Configuration» screen, enter the correct SCAN Name and click the «Add» button.
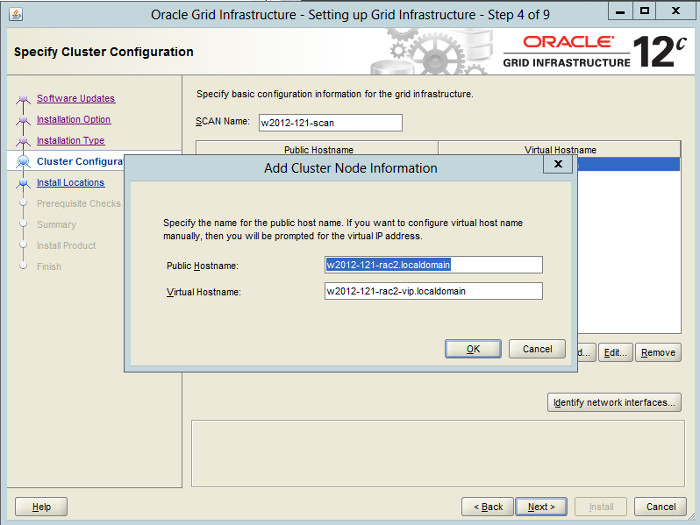
Enter the details of the second node in the cluster, then click the «OK» button.
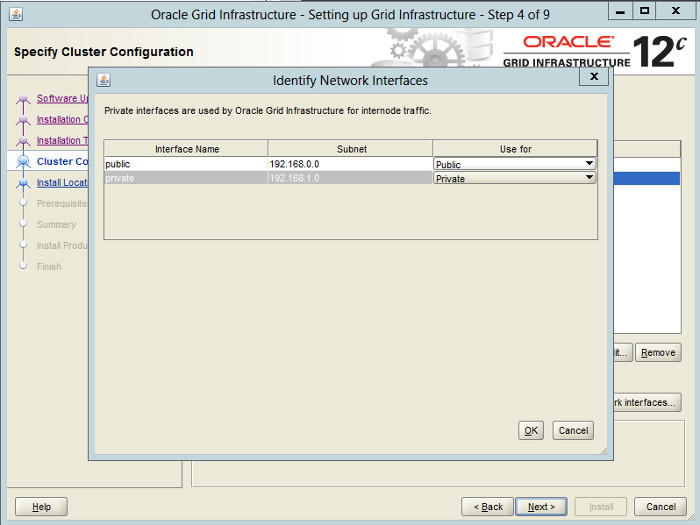
Click the «Identify network interfaces. » button and check the public and private networks are specified correctly. Remember to mark the NAT interface as «Do Not Use». Once you are happy with them, click the «OK» button and the «Next» button on the previous screen.
Enter the ORACLE_BASE of «c:\app\12.1.0.1», a software location of «c:\app\12.1.0.1\grid» and the SYSASM password. click the «Next» button.
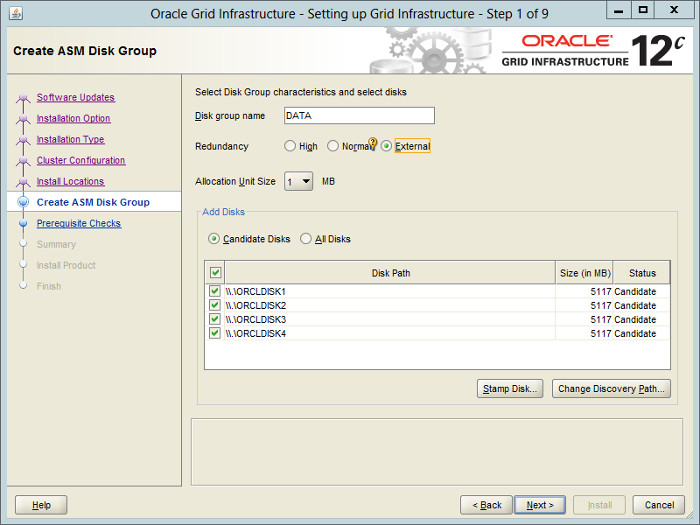
Set the redundancy to «External», select all 4 disks and click the «Next» button.
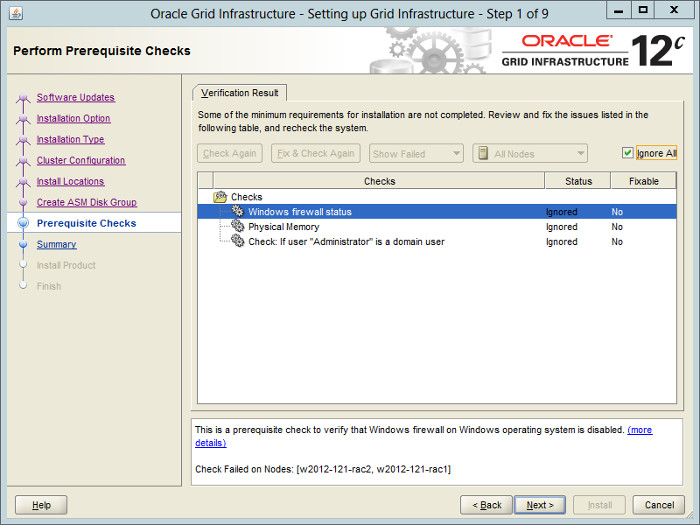
Wait while the prerequisite checks complete. If you have any issues, either fix them or check the «Ignore All» checkbox and click the «Next» button. It is likely the «Windows firewall status», «Physical Memory» and «Administrator» tests will fail for this type of installation.
If you are happy with the summary information, click the «Install» button.
Wait while the setup takes place.
Click the «Close» button to exit the installer.
The grid infrastructure installation is now complete. We can check the status of the installation using the following commands.
At this point it is probably a good idea to shutdown both VMs and take snapshots. Remember to make a fresh zip of the ASM disks on the host machine, which you will need to restore if you revert to the post-grid snapshots.
Install the Database Software
Make sure the «w2012-121-rac1» and «w2012-121-rac2» virtual machines are started, then login to «w2012-121-rac1» and start the Oracle installer.
Uncheck the security updates checkbox and click the «Next» button and «Yes» on the subsequent warning dialog.
Check the «Skip software updates» checkbox and click the «Next» button.
Select the «Install database software only» option, then click the «Next» button.
Accept the «Oracle Real Application Clusters database installation» option by clicking the «Next» button.
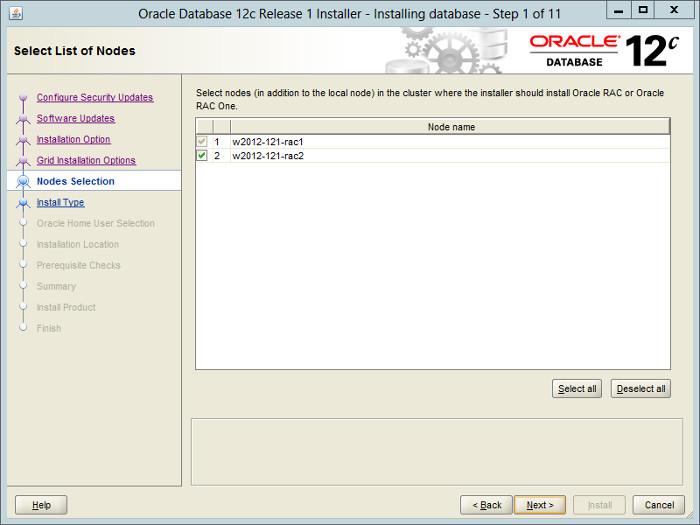
Make sure both nodes are selected, then click the «Next» button.
Select the required languages, then click the «Next» button.
Select the «Enterprise Edition» option, then click the «Next» button.
Decide the credentials for the database user, then click the «Next» button. In this case I picked the «Use Windows Built-in Account» option, which is not recommended. If you pick this option, accept the following warning dialog.
Enter «c:\app\oracle» as the Oracle base and «c:\app\oracle\product\12.1.0.1\db_1» as the software location, then click the «Next» button.
Wait for the prerequisite check to complete. If there are any problems either fix them, or check the «Ignore All» checkbox and click the «Next» button.
If you are happy with the summary information, click the «Install» button.
Wait while the installation takes place.
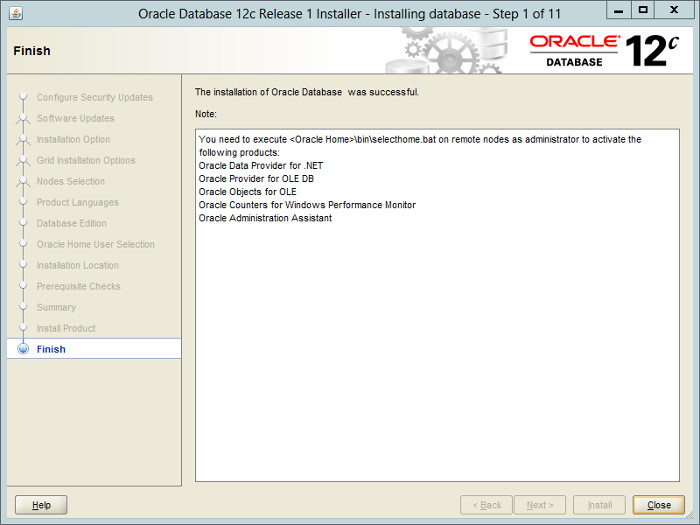
Click the «Close» button to exit the installer.
Shutdown both VMs and take snapshots. Remember to make a fresh zip of the ASM disks on the host machine, which you will need to restore if you revert to the post-db snapshots.
Create a Database
Make sure the «w2012-121-rac1» and «w2012-121-rac2» virtual machines are started, then login to «w2012-121-rac1» and start the Database Creation Asistant (DBCA).
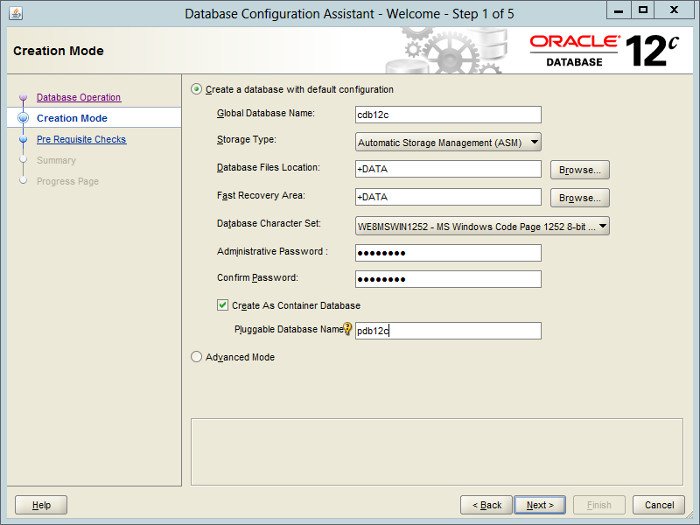
Select the «Create Database» option and click the «Next» button.
img src=»https://oracle-base.com/articles/12c/images/w2012-121-rac/50-DBCA-DatabaseOperation.jpg» alt=»DBCA — Database Operation»>
Select the «Create a database with default configuration» option. Enter the container database name (cdbrac), pluggable database name (pdbrac) and administrator password. Click the «Next» button.
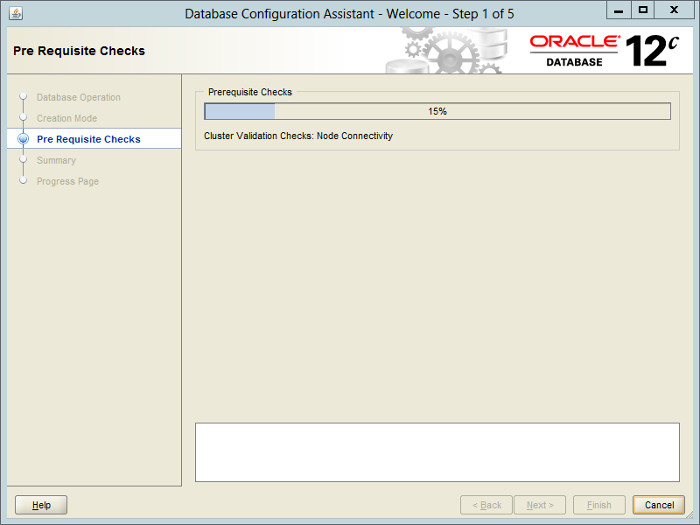
Wait for the prerequisite checks to complete. If there are any problems either fix them, or check the «Ignore All» checkbox and click the «Next» button.
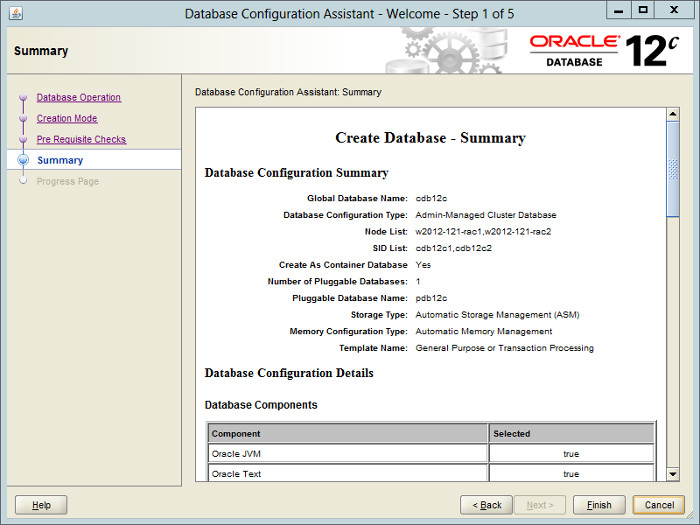
If you are happy with the summary information, click the «Finish» button.
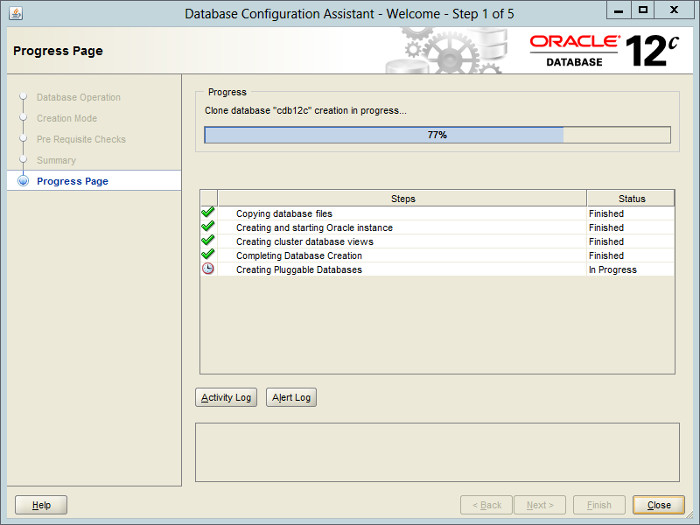
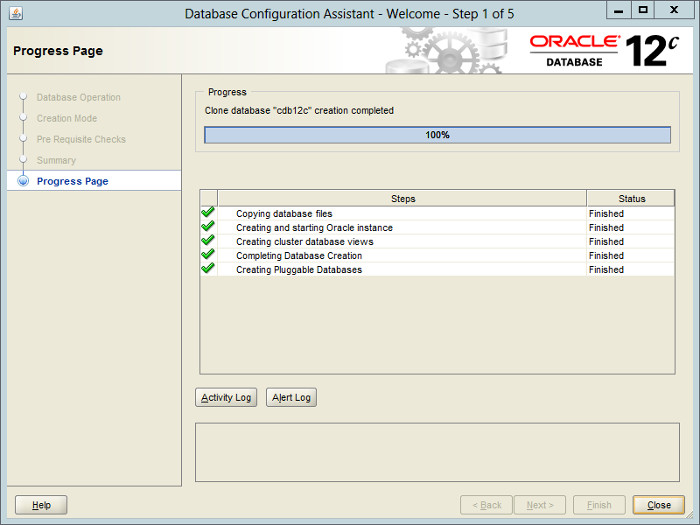
Wait while the database creation takes place.
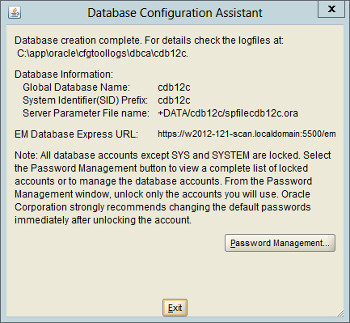
If you want to modify passwords, click the «Password Management» button. When finished, click the «Exit» button.
Click the «Close» button to exit the DBCA.
The RAC database creation is now complete.
Check the Status of the RAC
There are several ways to check the status of the RAC. The srvctl utility shows the current configuration and status of the RAC database.
The V$ACTIVE_INSTANCES view can also display the current status of the instances.