- Как смонтировать сетевую папку Windows/Samba в Linux
- Настройка автоматического монтирования сетевой папки в Linux
- How to Mount a Windows Share Folder on Linux
- Share Your Windows Folder
- Install CIFS-utils
- Mount Windows SMB Share on Linux
- Sharing Files Between Linux and Windows in Dual Boot
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Why do I get a syntax error when trying to mount a folder in Linux?
- 2. Can I mount a shared folder if I use VirtualBox?
- 3. Can I mount guest, network, or password protected folders?
- 4. Why do I only have read access for the shared folder?
- 5. Why aren’t folder changes showing up?
- Wrapping Up
- One comment
- Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Popular Posts
Как смонтировать сетевую папку Windows/Samba в Linux
Сетевая папка Windows может быть доступна в файловых менеджерах Linux как любая другая локальная папка. Для этого её нужно смонтировать. После монтирования не придётся использовать консоль для просмотра списка файлов и скачивания или закачивания файлов.
Начните с установки пакета cifs-utils.
В Debian, Linux Mint, Ubuntu, Kali Linux и производных выполните:
В Arch Linux, BlackArch и производных выполните:
Предыдущие команды smbtree и smbclient понимали имена компьютеров Windows, такие имена как HACKWARE-MIAL. Монтирование выполняется с помощью команды mount, которая такие имена не умеет обрабатывать без помощи преобразования имён DNS. Поэтому при монтировании можно либо:
- Использовать вместо имён компьютеров IP адрес. В этом случае у компьютера с сетевой папкой должен быть постоянный (статичный) IP адрес
- Либо настроить преобразование имён для компьютеров Windows. Это можно сделать, например, с помощью файла /etc/hosts. Кстати, в этом случае у компьютера с общей папкой также должен быть постоянный IP адрес (смотрите Как настроить локальный DNS используя файл /etc/hosts в Linux)
В общем, в любом случае настройте в роутере или в самой Windows постоянный локальный IP.
Если вы хотите настроить преобразование имён с помощью файла /etc/hosts, то откройте его:
И добавьте туда запись вида
Например, у меня IP_АДРЕС это 192.168.0.101, а именем компьютера является HACKWARE-MIAL, тогда я добавляю следующую запись:
Пингуем по имени компьютера Windows, чтобы убедиться, что всё сработало:
Теперь нам нужно создать точку монтирования — папку, где появятся файлы из шары. Я создаю папку /mnt/share:
Чтобы не возникало проблем с правами доступа, папка, куда монтируется шара (например, /mnt/share/), должна принадлежать текущему пользователю Linux — если вы создавали папку без sudo, то она уже принадлежит обычному пользователю. Но если вы создавали папку с sudo (например, иначе это невозможно сделать в /mnt/), то вам нужно поменять её владельца командой вида::
Например, чтобы поменять владельца папки /mnt/share/ на текущего пользователя:
Теперь для монтирования сетевой шары Windows нужно запустить команду вида:
В этой команде вы должны вставить свои значения для
- //ИМЯ-КОМПЬЮТЕРА/Папка
- /точка/монтирования
Значение других элементов команды:
- sudo — монтировать шару можно и без прав суперпользователя, но использовать опцию -o, после которой указываются опции для монтирования, можно только с правами root
- -t cifs выбор файловой системы для монтирования
- -o означает, что после этой опции будут перечислены опции для монтирования:
- username=guest,password= — произвольное имя пользователя без пароля — используется для подключение к общей папки, для которой не требуется вход. Вместо этой конструкции можно указать просто guest, но в этом случае на некоторых системах всё равно запрашивается пароль. По моим наблюдениям, пароль запрашивается когда имя текущего пользователя на Linux совпадает с именем пользователя на Windows
- uid=1000 — в качестве владельцев всех файлов в шаре будет указан текущий пользователь Linux
- iocharset=utf8 — эта кодировка позволяет работать с именами файлов, в которых используются не только латинские буквы
К примеру, путь до сетевой шары у меня //HACKWARE-MIAL/Share, её я хочу смотрировать в папку /mnt/share, тогда команда будет следующей:
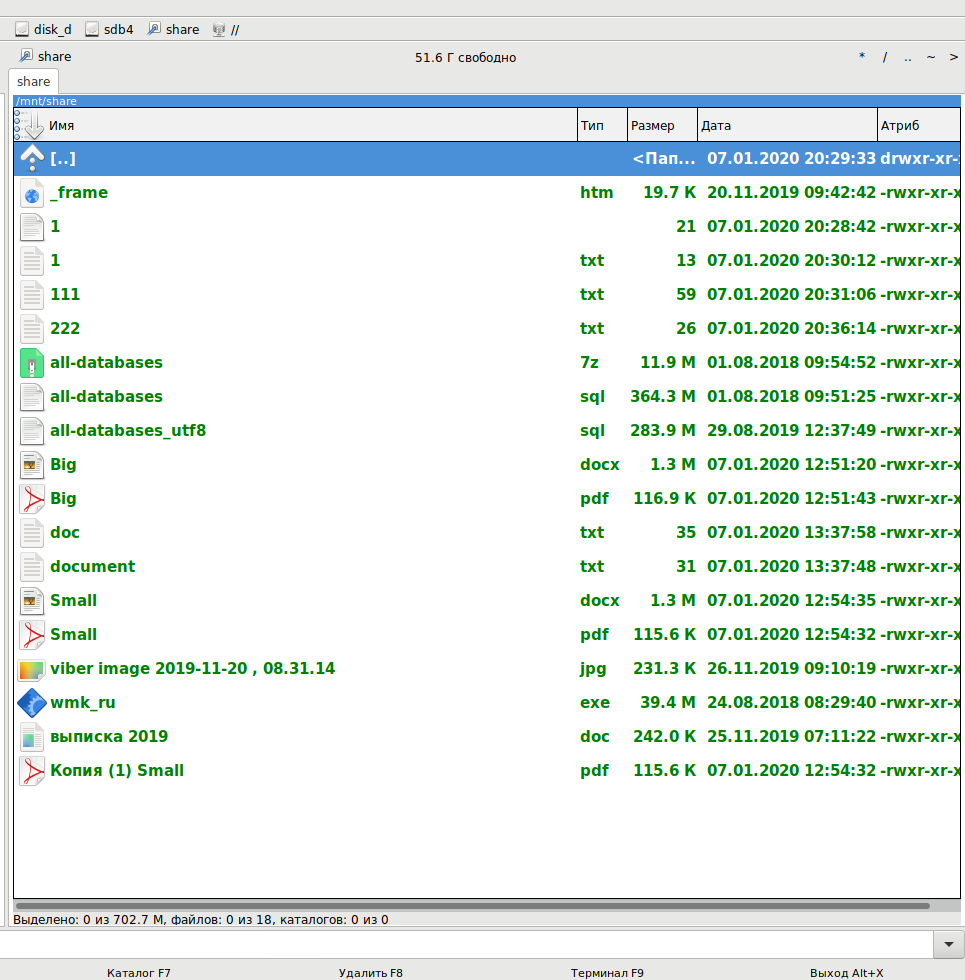
Вид сетевой папки Windows в Double Commander:
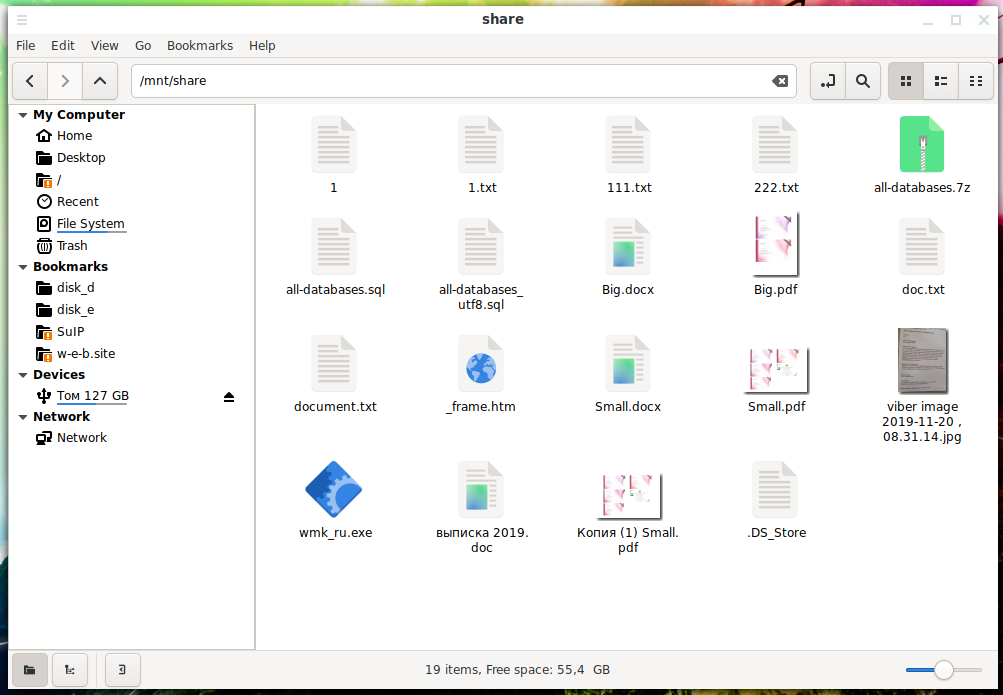
Вид сетевой папки в стандартном проводнике Linux:
Для размонтирования нужно запустить следующую команду (укажите либо точку монтирования, либо ресурсы, который был смонтирован):
Напомню, что в предыдущей части я не только настроил папку для входа без пароля, но на том же самом компьютере и настроил вторую папку с именем ShareRestricted. У этой папки владелец ShareOverlord, а пароль для входа 1234. Для подключения папки, доступ к которой возможен только по паролю, используется та же самая команда, но нужно указать реальные учётные данные:
Чуть дальше очень похожий набор опций, в том числе пароль в открытом виде, мы будем использовать в файле /etc/fstab для настройки автоматического монтирования сетевой папки. Файл /etc/fstab доступен для чтения всем а, следовательно, также доступен всем ваш пароль от Windows в нём. Чтобы обойти эту проблему, можно использовать файл с учётными данными. Это файл содержит только имя пользователя и пароль.
Используя текстовый редактор, создайте файл с учётными данными для входа на ваш удалённый сервер:
В этот файл введите имя пользователя и пароль от Windows:
В моём примере это:
Сохраните файл и закройте редактор.
Измените права доступа к этому файлу, чтобы предотвратить нежелательный доступ к вашим учётным данным:
Посмотрите абсолютный путь до этого файла:
В моём случае абсолютный путь:
Теперь вместо двух опций:
нужно использовать одну опцию, в качестве значения которой нужно указать абсолютный путь до файла с логином и паролем:
Моя команда стала выглядеть так:
Настройка автоматического монтирования сетевой папки в Linux
Автоматически монтируемые файловые системы прописываются в файле /etc/fstab. Откроем этот файл:
Теперь в него нужно добавить строку вида:
Мы добавили опцию nofail, чтобы ОС нормально загружалась даже если не удалось смонтировать данную файловую систему. Ещё добавьте опцию _netdev, эта опция означает, что файловая система находится на устройстве, которому требуется доступ к сети (используется для предотвращения попыток системы смонтировать эти файловые системы до тех пор, пока в системе не будет включена сеть).
Для моего примера это строка:
Сохраним и закроем этот файл. Для проверки выполним:
Если сетевая папка успешно смонтировалась, значит можно выполнить проверку перезагрузкой.
Если нужно смонтировать папку для входа в которую не требуется пароль, то используйте в качестве опции учётные данные «username=guest,password=»:
Либо можно по-прежнему использовать файл .smbcredentials, как это было показано выше:
/.smbcredentials запишите следующее:
Источник
How to Mount a Windows Share Folder on Linux
Linux and Windows systems have major differences, with different file systems and protocols in use. Sharing files between them can be difficult, especially because they use two different sharing protocols. That doesn’t mean it’s impossible to mount a Windows share folder on Linux, however. Follow along below to find out how.
Also read: 
Share Your Windows Folder
Before you do anything, you need to ensure that Windows has been correctly set up to allow for networking file sharing.
To enable this on Windows, right-click on the network icon in the notifications area of your Windows taskbar. From here, click “Open Network & Internet Settings.”
Under the “Status” category, click “Sharing options.”
In your Windows sharing options menu, make sure that “Turn on network discovery” and “Turn on file and printer sharing” are enabled.
Click the radio buttons next to both options to make sure this is the case.
Click “Save changes” to save your settings. Once this is done, open Windows File Explorer and locate the folder you’re looking to share with your Linux PC.
Right-click the folder and click “Properties.”
In your folder properties, click the “Sharing” tab, then click “Advanced Sharing.” Click to enable the “Share this folder” checkbox, then click “Permissions.”
Under the “Permissions” section, set the control rights for your folder. By default, Windows will grant read-only access to your files.
If you want to allow everyone to read or write to the folder, click “Allow” for the “Full Control” permissions set. Set these permissions to suit your own requirements.
Once you’re done, click “OK” three times to close each of the dialog boxes.
Your folder should now be shared on your network, ready for you to access from your Linux PC.
Install CIFS-utils
Depending on your Linux distribution, you may be able to mount your Windows-shared folder automatically in your distribution’s file explorer.
However, this may not work correctly. The safest way to mount Windows-shared folders on Linux is to use the CIFS-utils package and mount the folder using the Linux terminal.
This allows Linux machines to access SMB file shares used by Windows PCs.
To install CIFS-utils, open a new terminal window. For Ubuntu and Debian-based distributions, type:
For Arch users, type:
Once installed, you can then mount your Windows share folder from the Linux terminal.
Mount Windows SMB Share on Linux
You’ll need to create a mount directory before you can mount your Windows SMB-shared folder on Linux. This is where Linux will mirror the contents of your shared folder.
To do that, open a terminal window and type:
Once created, type the following:
Replace “Windows” with the IP address or hostname for your Windows PC and “SharedFolder” with your shared folder name. For the username, replace “account” with your Windows username or full Microsoft account email.
You’ll be asked to provide your Windows password before the mounting process is complete. Type this in, then click Enter. If you used the correct information, your Windows folder should now be mounted and accessible in the folder you created.
Sharing Files Between Linux and Windows in Dual Boot
Sharing files between Windows and Linux works great when you mount a shared folder between the two devices, but can you still share files with a dual boot setup? Linux and Windows have separate file systems. Linux usually uses Ext4, while Windows uses NTFS and also works with FAT32. This doesn’t mean it’s impossible to see and share files, though.
You’ll need a compatible Windows system, build 20211 or higher, and a few other resources to make it work. Don’t worry. Everything is free. This guide walks you through each step in the process, including a way to read and share files between Windows and Linux.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do I get a syntax error when trying to mount a folder in Linux?
Either there’s a small error in the command in the terminal window, or you have a space in the folder name. Spaces don’t always come across correctly in the syntax. Instead of recognizing the command as the full name of the folder, the system sees two unrelated items.
Avoid this by placing the name in quotes. For instance, Shared Folder would become “Shared Folder.” Of course, you can also just rename the Windows 10 folder to place the words together or have a dash between them.
2. Can I mount a shared folder if I use VirtualBox?
Yes. The process should work the same way. You can also share devices, such as USB drives.
3. Can I mount guest, network, or password protected folders?
Yes, but since you’re not using the main Windows 10 account, you will need to adjust the syntax a bit. Plus, if you’re mounting a network folder, you’ll also need the server or machine name.
While this guide applies to Ubuntu, it should work for most major Linux distros as well. It lists the syntax for different scenarios, assuming you’ve already completed all of the steps (except the final mounting) above.
4. Why do I only have read access for the shared folder?
If you want to store files in the shared folder from Linux, make sure you have full read/write access to the folder in Windows. If the Windows user account only has read permission, this is the only permission you’ll have from Linux as well. You must change your account permissions from within Windows 10. For companies, you’ll need your IT admin to make the change for you.
5. Why aren’t folder changes showing up?
If you’ve made changes to the permissions of the folder, they may not show up immediately in Linux. You’ll need to remount the folder for changes to take effect.
Use the command above to remount any shared folders. This should ensure things work as expected. If you have any random glitches, remounting typically fixes them.
Wrapping Up
Mounting Windows and Linux shared folders gives you the freedom to access your most important files, no matter the operating system. The SMB protocol is well supported on Linux, so you shouldn’t find it difficult to continue accessing your Windows files and folders once you’ve installed the CIFS-utils package.
If you’d rather use a single system, here are five of the best Linux distros for Windows users you could use.
Crystal Crowder has spent over 15 years working in the tech industry, first as an IT technician and then as a writer. She works to help teach others how to get the most from their devices, systems, and apps. She stays on top of the latest trends and is always finding solutions to common tech problems.
One comment
I make an NTFS partition and save files to be shared on it. Linux files have ‘permissions’ which are not saved on an NTFS partition, so they become available to anyone, even a Windows pain!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Popular Posts
RedMagic 6S Pro Review: Gaming Is Serious Business.
How to Boot to Recovery Mode (Safe Mode) in Ubuntu
Ubuntu Software Center Not Working? Here Are the Fixes
How to Stress Test a Graphics Card on Linux
How to Mount Your iPhone as an External Drive in Ubuntu
How to Fix Ubuntu Freezing in VirtualBox
How to Fix «Repository Does Not Have Release File» Error
How to Combine PDF Files on Windows and Linux
How to Reset the Root Password in Linux
8 Reasons to Switch from Windows to Linux
5 of the Best Linux Distros for Developers and Programmers
Affiliate Disclosure: Make Tech Easier may earn commission on products purchased through our links, which supports the work we do for our readers.
Источник























