- Microsoft Windows
- Contents
- History
- 16-bit Windows
- Windows 9x
- Windows NT
- Look and feel
- Source code
- A History of Microsoft Windows – Timeline
- History of Windows
- MS-DOS
- Windows 1.0 – 2.0 (1985-1992)
- Windows 3.0 – 3.1 (1990–1994)
- Windows 95 (August 1995)
- Windows 98 (June 1998)
- Windows ME – Millennium Edition (September 2000)
- Windows NT 3.1 – 4.0 (1993-1996)
- Windows 2000 (February 2000)
- Windows XP (October 2001)
- Windows Vista (November 2006)
- Windows 7 (October 2009)
- Windows 8
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 10
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a desktop operating system developed by Microsoft since 1983. The latest released version as of April 2021 is Windows 10 October 2020 Update.
The first versions of Windows were an operating environment and graphical shell for MS-DOS. Windows 95 and later used MS-DOS for booting and kernel initialization. NT-based versions of Windows use a redesigned kernel and do not rely on MS-DOS.
Contents
History
16-bit Windows
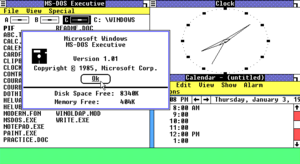
Microsoft Windows debuted to the world during the Fall COMDEX 1983 computer expo as an operating environment running on top MS-DOS. The final version of the product with the version number of 1.01 was later released on 20 November 1985 and did not gain much popularity. Windows 1.0 was a cooperative multitasking desktop environment with a tiling window manager. The first versions of Windows used the MS-DOS Executive, which was a simple file manager, as a shell, which is generally the first application ran on startup providing the user experience. Other applications included in the first version of Windows included Calculator, Cardfile, Clipboard Viewer, Clock, Control Panel, Notepad, Paint, Reversi, Spooler, Terminal, and Write. Three minor updates were released in the two following years adding support for more hardware.
A major update called Windows 2.0 was released in 1987 adding features such as overlapping windows. This version also introduced support for the Video Graphics Array and PS/2 mouse (though the IBM OEM of Windows 1.04 includes these features). A separate edition called Windows/386 was introduced that took advantage of the virtual 8086 mode of the then-new 386 processor to multitask MS-DOS applications under Windows; this would later become known as the 386 Enhanced Mode and become the cornerstone of Windows 9x. In later revisions of the Windows 2.0 environment, the original edition was renamed Windows/286.
Windows 3.0 was released in 1990 and became the first widely successful version of Windows. The new features included a revamped user experience consisting of the Program Manager, which allowed easy management of installed applications. A new File Manager was also included to replace the former shell, which was now deprecated. Under the hood, the new Standard Mode was introduced, which took advantage of the protected mode of the 286 and 386 processors. The previously separate 286 and 386 editions of Windows were unified into one version. This version of Windows was able to operate in three modes: Real mode intended for computers with the original 8088/8086 processor, Standard mode using the protected mode feature of the 286 processor, and 386 Enhanced mode combining the improved protected mode of the 386 with its ability to create and manage virtual 8086 machines for MS-DOS applications.
A major update dubbed Windows 3.1 followed in 1992 with the brand new red-green-blue-yellow Windows logo resembling a flag. The user interface was refreshed in this release, including new colorful icons. This version of Windows removed the real mode of operation and the MS-DOS Executive application. It was accompanied with a variant called Windows for Workgroups (WfW) 3.1 with an integrated networking capability, which later received a larger update bringing its version number up to 3.11, introducing 32-bit disk access and also removing the Standard mode of operation. The regular variant of Windows also received the 3.11 update, which was essentially the kernel of Windows for Workgroups 3.11 backported to Windows 3.1.
A 32-bit TCP/IP stack was ported from an early version of Windows 95 and released in 1994 as a downloadable plugin for Windows for Workgroups 3.11, providing early testing for the 16/32-bit compatibility features of the next version of Windows.
Windows 9x
On 24 August 1995, Microsoft released Windows 95, previously known under its codename «Chicago», with a brand new user interface with a Start menu, taskbar, and the desktop, as provided by the new Windows Explorer. Its hybrid 16/32-bit architecture made it possible to make and run 32-bit Windows applications and drivers while keeping a great degree of compatibility with already existing 16-bit ones. Among other improvements in this version was the support for long filenames through an extension to the FAT16 file system.
Windows 95 was the first widespread release of Windows to be packed together with a specific MS-DOS version, however, the old operating system was used only as a bootloader and a compatibility layer for ancient device drivers. Most MS-DOS user applications were either extended with Windows code or entirely replaced with a Windows version, keeping only the ones that were required to run without Windows, e.g. during the OS installation, such as FDISK and FORMAT .
During its lifetime Windows 95 saw several larger updates dubbed the OEM Service Releases (OSR) that were released only to computer manufacturers, specifically OSR 1.0, OSR 2.0, OSR 2.1, and OSR 2.5. A Service Pack was also released that updated an RTM copy of Windows 95 to the OSR 1.0 level. In 1997 a USB Supplement was released for OSR 2.x that added support for the then-new Universal Serial Bus interface.
The classic Windows line received a major update on 25 June 1998 with the release of Windows 98, codenamed «Memphis». It was the first version to integrate Internet Explorer deeply into the operating system’s user interface as a part of the Windows Desktop Update. Many parts of the UI started using HTML and Internet Explorer’s rendering engine to present a web-like user interface. A feature called Active Desktop made it even possible to set a webpage as the desktop background. Under the hood Windows 98 introduced the new Windows Driver Model, which enabled the use of the same drivers on Windows 9x as well as on the radically different Windows NT based operating systems.
A year later, Windows 98 received an update which was called the Second Edition, which included a new version of Internet Explorer, added Internet Connection Sharing and improved USB support.
In 2000, Windows Me (Millennium Edition), the last release of the classic Windows line was released. It carried over the improvements made to the user interface in its NT-based counterpart, Windows 2000. Windows Me is based on Windows 98, however, access to the real mode MS-DOS was restricted in order to decrease boot time among other changes to the kernel. It was infamously known for its stability problems partially caused by the rushing of its release following the cancelation of the Neptune project. It was replaced by Windows XP in 2001, ending the era of classic Windows.
Windows NT
Windows NT (New Technology) is the current iteration of Windows. It is built on the NT hybrid kernel, which was originally intended for use in OS/2 3.0 but was adapted for a 32-bit version of Windows after the Microsoft — IBM split. The first release based on the new kernel was Windows NT 3.1, which was launched in 1993 and was equivalent to Windows 3.1 released two years earlier. All NT-based releases up until Windows 2000 were intended primarily for business use. With Windows XP, the NT series replaced the classic Windows series, creating a single operating system for consumers and businesses. Windows Phone 8 is the first Windows Phone release to be based on the NT kernel. The most recent version of Windows based on the NT kernel is Windows 10. Following the release of Windows 10, Microsoft has switched to a system of more frequent smaller updates to Windows.
Look and feel
Windows allowed customization of its user interface since its first versions. Windows 1.0 and Windows 2.x allowed the user to change the color scheme in their Control Panel, however, there was no selection of pre-made color schemes and the user only had the option to reset to the default scheme, which was provided by the installed video driver. This was improved with Windows 3.0 and its new Colors control panel, which added several color schemes for the user to choose from, however, the Windows default preset was still dependent on the type of the graphics card installed. Windows NT 3.1 and Windows NT 3.5x also featured the same Color control panel applet, however, drivers no longer had the ability to override the default color preset.
Windows 95 introduced a new 3D look inspired by NeXTSTEP which initially only made use of solid colors. This was subsequently refined in Windows 98 and Windows 2000 with the possibility to use 2-color gradients for the titlebar. Windows XP introduced a proper theming engine, allowing the use of bitmaps for various user interface elements and saw the first proper visual style, called Luna, come in to use, but users could still switch to Windows Classic if they so chose. Windows Vista introduced the hardware-accelerated Desktop Window Manager, which allowed for advanced effects such as translucent title bars used by the new Windows Aero theme. For users whose hardware couldn’t handle Aero, Windows Vista included the software rendered Windows Basic theme.
With Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, the Aero theme was revamped and the Aero Lite theme replaced the Basic theme for lower-end computers. In Windows 10, the Aero theme was revamped again, but the Aero Lite theme remained. Windows 10’s November Update saw the option to enable colors on title bar. Finally, with Windows 10 build 18282, the new Light theme was introduced.
Source code
In 2004, incomplete copies of the source code of Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 leaked to the Internet. These leaks were illegal, as the Windows source code is both a trade secret and copyrighted, and as so is protected by law. However, Microsoft has released parts of the source of the Windows Server 2003 kernel for research purposes.
In 2017, The Register and other technology journals reported about a leak of the Windows 10 Shared Source Kits, which are available to qualified customers, enterprises, governments, and partners for debugging and reference purposes, to BetaArchive. Following the controversy, BetaArchive removed all source code content from its archives, which also included the aforementioned incomplete copies of the Windows source code, and adopted a policy of not accepting any more source code material.
In 2018, the source code of the Windows NT File Manager ( winfile ) was released on GitHub under the open source MIT license. This was later followed in 2019 by the Windows 10 Calculator application.
In May 2020, a copy of the source code of Windows NT 3.5 build 782.1 leaked to the 4chan /vp/ board. It is not yet known whether the leaked source is complete. This was later followed in September by the source code of Windows XP Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003. The leaked copy is mostly complete, but misses activation components, therefore it is likely that the leak originated from a Microsoft partner who had access to the source code rather than Microsoft itself. This code base had been apparently circulating in online circles since at least 2015.
A History of Microsoft Windows – Timeline
Don’t be surprised if I say that 9 out of 10 computers run some version of the Windows operating system, today. However, no one could have predicted this outcome when the whole journey started with MS-DOS and a vision to have every computer on a desktop. Below, you will find a chronology of events that take you through highlights from the first 25 years of Windows, more preferably – A History of Windows.
In 1975, Gates and Allen formed a partnership called Microsoft. Like most start-ups, Microsoft began small but had a huge vision—a computer on every desktop and in every home. During the next years, Microsoft began to change the ways we work.
In June 1980, Gates and Allen hired Gates’ former Harvard classmate Steve Ballmer to help run the company.
IBM approached Microsoft about a project code-named “Chess.” In response, Microsoft focused on a new operating system—the software that manages, or runs, the computer hardware and also serves to bridge the gap between the computer hardware and programs, such as a word processor. It’s the foundation on which computer programs can run. They named their new operating system “MS-DOS.”
When the IBM PC is running MS-DOS shipped in 1981, it introduced a whole new language to the general public.
Microsoft worked on the first version of a new operating system. Interface Manager was the code name and was considered as the final name, but Windows prevailed because it best described the boxes or computing “windows” that were fundamental to the new system. Windows was announced in 1983, but it took a while to develop. Skeptics called it “vaporware.”
On November 20, 1985, two years after the initial announcement, Microsoft shipped Windows 1.0.
History of Windows
MS-DOS
Windows 1.0 required a minimum of 256 kilobytes (KB), two double-sided floppy disk drives, and a graphics adapter card. A hard disk and 512 KB memory was recommended for running multiple programs or when using DOS 3.0 or higher. It was originally developed by Microsoft for IBM-compatible personal computers. Although the first version of OS from Microsoft, MS-DOS was a little-used or preferred alternative to Apple’s Macintosh. Despite witnessing little success, Microsoft continued to offer support for MS-DOS till the development of Windows XP.
Q: Ever wondered, what MS-DOS stood for?
Microsoft Disk Operating System
Windows 1.0 – 2.0 (1985-1992)
Instead of typing MS-DOS commands, Windows 1.0 allowed users to point and click to access the windows.
In 1987 Microsoft released Windows 2.0, which was designed for the Intel 286 processor. This version added desktop icons, keyboard shortcuts, and improved graphics support.
Q: Why was Windows OS named so?
Microsoft Windows 1.0 was named so since the computing boxes, or Windows design represented a fundamental aspect of the operating system.
Windows 3.0 – 3.1 (1990–1994)
Microsoft released Windows 3.0 in May 1900 offering better icons, performance and advanced graphics with 16 colors designed for Intel 386 processors. Its popularity grew by manifolds following the release of SDK that helped software developers focus more on writing and less on writing device drivers. With Windows 3.0 Microsoft completely rewrote the application development environment. The OS included Program Manager, File Manager, Print Manager and games, remember Solitare, a complete time-waster??
Q: What does SDK stand for?
SDK refers to a set of tools that allows for the creation of applications for certain software.
Windows 95 (August 1995)
A major release of the Microsoft Windows operating system that caused Apple’s Market share to decline or shrink was Windows 95. Windows 95 as the name suggests was released in 1995 represented a significant advance over its precursor, Windows 3.1. By the way, this was also the time when the first version of Microsoft’s proprietary browser – Internet Explorer 1 was rolled out in August 1995 to catch up the Internet wave.
Windows 98 (June 1998)
Described as an operating system that “Works Better & Plays Better, ‘Windows 98’ offered support for a number of new technologies, including FAT32, AGP, MMX, USB, DVD, and ACPI. Also, it was the first OS to include a tool called Windows Update. The tool alerted the customers when software updates became available for their computers.
Q: Which was the last version based on MS-DOS application?
Windows 98 indeed, was the last version based on MS?DOS.
Windows ME – Millennium Edition (September 2000)
The Windows Millennium Edition, referred as “Windows Me” was an update to the Windows 98 core that included some features of the Windows 2000 operating system. The version had the “boot in DOS” option removed but included other enhancements like Windows Media player and Movie Maker for basic video editing.
Q: System Restore, a feature that rolled your PC software configuration back to a date or time before a problem occurred first appeared in which version of Windows?
Windows ME – Millennium Edition
Windows NT 3.1 – 4.0 (1993-1996)
A version of the Windows OS with 32-bit support for preemptive multitasking. Two versions of Windows NT:
- Windows NT Server – Designed to act as a server in networks
- Windows NT – Workstation for stand-alone or client workstations
Windows 2000 (February 2000)
W2K (abbreviated form) was an operating system for business desktop and laptop systems to run software applications, connect to Internet and intranet sites, and access files, printers, and network resources. Windows 2000 4 versions released by Microsoft
- Professional (for business desktop and laptop systems)
- Server (both a Web server and an office server)
- Advanced Server (for line-of-business applications)
- Datacenter Server (for high-traffic computer networks)
Windows XP (October 2001)
This version of the OS was built on Windows 2000 Kernel and was introduced in 2001 along with a redesigned look and feel. It was made available to the public in 2 versions
- Windows XP Home
- Windows XP Professional
Microsoft focused on mobility for both editions, including plug and play features for connecting to wireless networks was introduced in this version of Windows, and it proved to one of Microsoft’s best-selling products. Its use started declining with more Windows 7 deployments.
Windows Vista (November 2006)
A marketing flop! People expected too much from its WOW factor. Windows Vista released in November 2006 was widely criticized for performance related issues.
Windows 7 (October 2009)
Windows 7 made its official debut on October 22, 2009. The OS included enhancements in the form of fast start-up time, Aero Snap, Aero Shake, support for virtual hard disks, a new and improved Windows Media Center, and better security features.
Windows 8
Bill Gates’ vision of future computing was Touch and voice replacing mouse and keyboard. We already have the touch with Windows 8, a completely redesigned OS built from the ground up.
The OS replaces the more traditional Microsoft Windows OS look and feels with a new “Modern Interface” consisting of flat tiles that first debuted in the Windows Phone 7 mobile operating system.
Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1 changed a few things for the better which were found wanting in Windows 8.
Notable changes included a visible Start button, improved Start screen, Internet Explorer 11, tighter OneDrive integration, Bing-powered unified search box, the ability to land on the desktop on login instead of the Start screen.
Windows 10
Windows 10 has been described as the ‘last operating system’ from Microsoft. It is now a series of releases that receives half-yearly feature updates. They are referred to as Windows 10 v1501, Windows 10 1803 and so on..
The OS introduced Edge a new browser meant to replace Internet Explorer. It supports Universal Apps which Universal apps can be designed to run across multiple Microsoft product families like PCs, tablets, smartphones, embedded systems, Xbox One, Surface Hub and Mixed Reality. It has been well received – but its Automatic Windows Update system is one area that is disliked by some.
Date: October 16, 2018 Tags: Microsoft, Misc