- 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System
- Linux shutdown / reboot command
- 1. «shutdown» command
- 2. «reboot» command
- 3. «halt» command
- 4. «poweroff» command
- 5. REISUB — R E I S U B key strokes
- 10 thoughts on “ 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System ”
- 🇮🇷 Как использовать команды Linux Shutdown, PowerOff и Reboot
- Как использовать команду shutdown
- Расписание выключения системы
- Отправить широковещательное сообщение при выключение
- Перезагрузить систему
- Отменить запланированное отключение
- Как использовать команду Poweroff
- Команда выключения питания
- Перезагрузить систему
- Принудительного отключение
- Как использовать команду Reboot
- Перезагрузить систему
- Выключения системы
- Принудительная перезагрузка системы
- Заключение
- Reboot Linux System Command
- Linux system restart
- Reboot Linux system command
- How do I reboot remote Linux server?
- A note about systemctl command when using systemd
- Conclusion
- Can I restart systemd without rebooting?
- 2 Answers 2
5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System
Linux shutdown / reboot command
On Linux, like all tasks, the shutdown and restart operations can also be done from the command line.
The commands are shutdown, halt, poweroff, reboot and REISUB keystrokes.
In this post I am going to show you how to shutdown or restart a linux system using these commands.
The commands are useful specially when you have to reboot a remote linux server, where only shell access is available and no gui.
Servers often need a restart when upgrades are installed or need to shutdown for other maintainance tasks.
The commands are available on any linux system like centos, ubuntu, debian, fedora or suse and do not require the installation of any extra packages.
1. «shutdown» command
The first command is the shutdown command and it can be used to shutdown a system or restart it. It is commonly used to shutdown or reboot both local and remote machines.
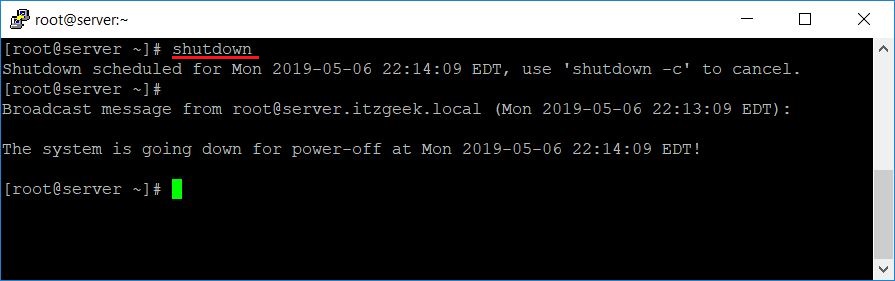
To shutdown a machine call the shutdown command like this
The h option is for halt which means to stop. The second parameter is the time parameter. «now» means that shutdown the system right away.
The time parameter can be specified in minutes or hours also. For example
The above command shall flash the message to all other logged in users and give them 5 minutes before the system goes for shutdown.
The shutdown command can be used to restart a system with the r option instead of the h option. Usage is same as before. Just replace the h option with r option.
All other logged in users will see a broadcast message in their terminal like this
At this point a shutdown can be cancelled by calling shutdown with «c» option.
2. «reboot» command
Next command is the reboot command. It can be used to shutdown or reboot linux.
The following command will shutdown linux.
The «p» options stands for poweroff.
To reboot linux just call the reboot command directly without any options.
This will perform a graceful shutdown and restart of the machine. This is what happens when you click restart from your menu.
Reboot linux forcibly
The following command will forcefully reboot the machine. This is similar to pressing the power button of the CPU. No shutdown takes place. The system will reset instantly.
The man page explains it as follows
3. «halt» command
The next command is the halt command. This can shutdown a system
The halt command also has a force option, but you do not want to use it. It is supposed to shutdown the system instantly. But its behaviour may not be consistent. Desktops might hang on running this command.
4. «poweroff» command
There is another command exactly same as the halt command. It does the same things and takes the same options.
5. REISUB — R E I S U B key strokes
The above shown commands can be used when you are in control of your system. What if the system has hanged and is not responding at all. And you do not want to press the power button on the CPU which might lead to data corruption. To save from such a situation, comes the magic sysRQ keys.
A special combination of key presses that will allow you to reboot your linux system, no matter how much it is hanged. Check the wikipedia article. for more information.
Warning : Pressing the following keys would instantly reboot your system. Its similar to pressing the power button of your CPU or executing the reboot -f command.
Now in place of the B key we have to use R E I S U letters first. Each key does a task as mentioned below
1. Hold down the Alt and SysRq (Print Screen) keys.
2. While holding those down, type the following keys in order, several seconds apart: R E I S U B
3. Computer should reboot.
Make sure to have some time gap between each of keys R E I S U B.
The sysrq feature can be controlled by changing the value of /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq. To check if sysrq is enabled on the system or not, echo the value. It should be non zero.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
10 thoughts on “ 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System ”
It worked on SUSE SLES 11
Now systemctl utility replaces a number of power management commands and even the shutdown command will call systemctl utility to perform the shutdown tasks.
The command reboot does work and immediately rebooted my Bluestar Linux system 4.20.7 (based on Arch Linux).
I am so glad that you could reboot your linux system!
If I’m not mistaken, reboot by itself actually does a shutdown: https://linux.die.net/man/8/reboot . You have to do reboot -f to actually get it to reboot.
Arrrgh so sick of finding the incorrect example of shutdown everywhere. The reboot syntax shown, on Ubuntu and probably in every flavor today, will Immediately reboot your server with no delay or warning. the +5 option is either wrong or in the wrong spot.
Important note – this only applies (AFAIKT) to x86 systems. On arm – no-worky.
what? 20 – 30 mins? O.o Shouldn’t it be 20 – 30 seconds?
I rebooted my linux machine using command reboot -f, it went down. How long does it takes normally to start again?
Its depends upon hardware and file system mounted on Linux box , If it is high end hardware and have been mounted more file system then it will 20-30 mins to come online
Источник
🇮🇷 Как использовать команды Linux Shutdown, PowerOff и Reboot
Команды shutdown, poweroff и reboot являются наиболее важными командами выключения питания в Linux.
Эти команды специально используются в ситуации, когда вам нужно выключить сервер для обслуживания или перезагрузить серверы для обновления ядра или исправлений.
Здесь мы увидим, как использовать команду Linux shutdown и poweroff для выключения / выключения системы.
Также команду reboot для перезагрузки системы.
Чтобы иметь возможность завершить работу или перезагрузить систему, вы должны войти в систему как пользователь root или пользователь с привилегиями sudo.
Как использовать команду shutdown
Команда shutdown в Linux безопасно отключает систему.
Когда мы инициируем завершение работы, все вошедшие в систему пользователи получают уведомление о том, что система отключается, и новые входы в систему не разрешены, а затем все запущенные процессы останавливаются, прежде чем система, наконец, останавливается.
Команда shutdown является простой командой и доступна во всех разновидностях Linux, таких как CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian или Fedora.
- OPTIONS – параметры выключения, такие как останов (-h), перезагрузка (-r) или выключение питания (-P по умолчанию)
- TIME – указывает, когда выполнять отключение (+ m, чч: мм или сейчас)
- MESSAGE – широковещательное сообщение всем зарегистрированным пользователям.
Когда никакая опция не используется с командой shutdown , она просто выключит машину.
Процесс выключения начинается через 1 минуту (интервал по умолчанию).
Выключение системы немедленно
Используйте now в команде shutdown, чтобы немедленно привести систему в режим 0.
Система не будет отправлять широковещательные сообщения зарегистрированным пользователям.
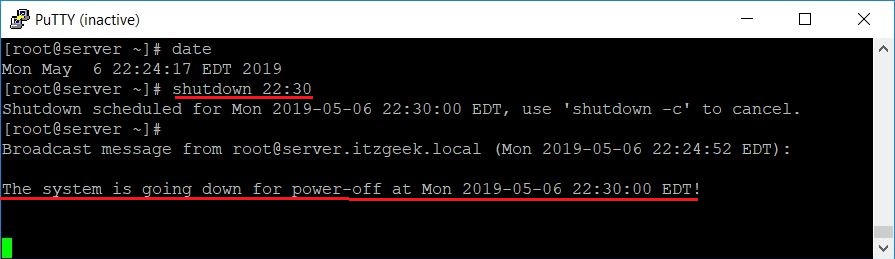
Расписание выключения системы
Вы можете запланировать отключение сервера, указав относительное время в формате чч: мм (24-часовой формат) или + m, где m – минуты, которые необходимы до процесса завершения работы.
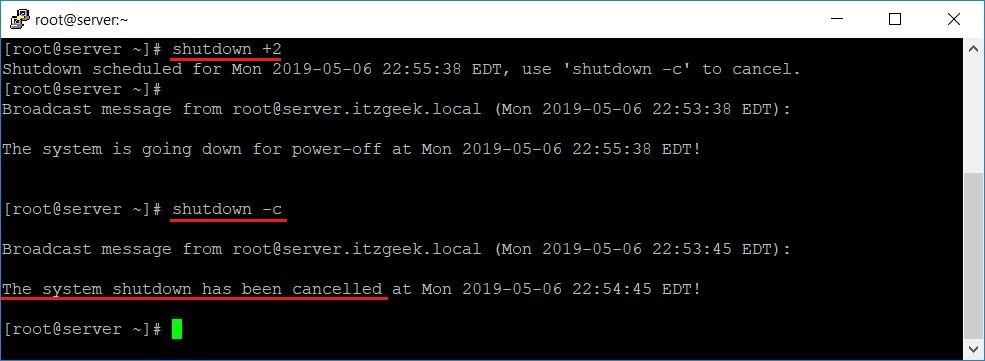
Чтобы выключить систему через 2 минуты, используйте:
Чтобы выключить систему в 22:30, используйте:
Отправить широковещательное сообщение при выключение
Вы можете отправить пользовательское сообщение всем зарегистрированным пользователям в качестве уведомления.
Эта опция часто полезна для планового обслуживания.
Перезагрузить систему
Используйте параметр -r с командой shutdown для перезагрузки системы.
Вы также можете запланировать перезагрузку системы следующим образом.
Отменить запланированное отключение
Если по любой причине, если вы хотите отменить запланированное завершение работы, используйте параметр -c.
Как использовать команду Poweroff
Команда poweroff используется для выключения системы.
Команда выключения питания
Когда используется без параметров, система немедленно отключается.
Перезагрузить систему
Использование опции –reboot с командой poweroff перезагрузит систему вместо выключения питания
Принудительного отключение
Опция -f с командой poweroff принудительно отключает питание системы.
Система мгновенно отключается, как при отключении источника питания процессора.
Как использовать команду Reboot
Команда reboot используется для перезагрузки системы.
Перезагрузить систему
При использовании без параметров, она сразу же перезагрузит систему.
Выключения системы
Опция -p с командой reboot выключит систему вместо перезагрузки системы
Принудительная перезагрузка системы
Опция -f с командой reboot принудительно перезагрузит систему.
Система будет мгновенно перезагружена, как при нажатии кнопки сброса в CPU.
Заключение
Я надеюсь, что теперь вы хорошо понимаете, как использовать команды Linux shutdown, poweroff и reboot.
Всегда выполняйте эти команды с осторожностью и убедитесь, что вы выполняете их в правильной системе.
Источник
Reboot Linux System Command
Linux system restart
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
To reboot Linux using the command line:
- To reboot the Linux system from a terminal session, sign in or “su”/”sudo” to the “root” account.
- Then type “ sudo reboot ” to reboot the box.
- Wait for some time and the Linux server will reboot itself
Reboot Linux system command
You must login as root user to reboot the system. Open the terminal application (or login to remote box using ssh client) and type any one of the following command to reboot the system immediately:
# /sbin/reboot
OR
# /sbin/shutdown -r now
You can also use sudo command under Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora and other Linux based distros:
$ sudo reboot
It is a good idea to provide notification to all logged-in users that the system is going down and, within the last five minutes of TIME, new logins are prevented. Type the following command:
# shutdown -r +5
Sample output:
TIME may have different formats, the most common is simply the word “ now ” which will bring the system down immediately. Other valid formats are +m, where m is the number of minutes to wait until shutting down and hh:mm which specifies the time on the 24hr clock.
How do I reboot remote Linux server?
Simply login as the root user using ssh command:
$ ssh root@remote-server-com /sbin/reboot
OR
$ ssh root@remote-server-com /sbin/shutdown -r now
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Get notification using the ping command when remote-server-com comes online:
ping -a remote-server-com
It is possible to use sudo command along with normal user over ssh session too. The syntax is:
$ ssh -t vivek@remote-server-com /sbin/reboot
Without the -t you will seen an error “sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified“, hence you must pass the -t to the ssh command.
A note about systemctl command when using systemd
Are you using systemd as init on your Linux distro? Most modern Linux distro such as Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Arch, and many uses systemd, and we can use the following command to reboot the system:
sudo systemctl reboot
Conclusion
This page demonstrated how to use reboot command on Linux to reboot the server or desktop for software and kernel updates.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Can I restart systemd without rebooting?
I’m trying to restart services after a yum update on RHEL 7.4. I could restart every service using systemctl, but needs-restarting from yum utils tells me that I should also restart systemd itself:
Can I restart systemd without rebooting the server, and how?
I found a few mentions of systemctl daemon-reload , but this doesn’t make it disappear from the needs-restarting list.
2 Answers 2
To restart the daemon, run
Reexecute the systemd manager. This will serialize the manager state, reexecute the process and deserialize the state again. This command is of little use except for debugging and package upgrades. Sometimes, it might be helpful as a heavy-weight daemon-reload . While the daemon is being reexecuted, all sockets systemd listening on behalf of user configuration will stay accessible.
Unfortunately needs-restarting can’t determine that systemd has actually restarted. systemd execs itself to restart, which doesn’t reset the process’s start time; but needs-restarting compares the executable’s modification time with the process’s start time to determine whether a process needs to be restarted (among other things), and as a result it always considers that systemd needs to be restarted. To determine whether systemd really needs to be restarted, you can check the output of lsof -p1 | grep deleted : systemd uses a library, libsystemd-shared , which is shipped in the same package and is thus upgraded along with the daemon, so if systemd needs to be restarted you’ll see it using a deleted version of the library. If lsof shows no deleted files, systemd doesn’t need to be restarted. (Thanks to Jeff Schaller for the hint!)
Источник