- 1.5 Введение — Установка Git
- Установка Git
- Установка в Linux
- Установка на Mac
- Установка в Windows
- Установка из исходников
- How to install GitExtensions in Ubuntu
- Installing GitExtensions
- Troubleshooting
- (2017-01-19) Mono runtime errors about settings
- (2019-01-12) Failed to load plugin GitExtensions/Plugins/Bitbucket.dll
- Summary
- Getting Started¶
- Installation¶
- Portable¶
- Settings¶
- Dashboard¶
- Create new repository¶
- Open repository¶
- Clone repository¶
- Clone Github repository¶
- Getting Started¶
- Installation¶
- Installation (Linux) (2.5x only)¶
- Installation (macOS) (2.5x only)¶
- Troubleshooting Mac Installation¶
- Settings¶
- Start Page¶
- Clone repository¶
- Clone SVN repository¶
- Clone Github repository¶
- Create new repository¶
1.5 Введение — Установка Git
Установка Git
Прежде чем использовать Git, вы должны установить его на своём компьютере. Даже если он уже установлен, наверное, это хороший повод, чтобы обновиться до последней версии. Вы можете установить Git из собранного пакета или другого установщика, либо скачать исходный код и скомпилировать его самостоятельно.
В этой книге используется Git версии 2.8.0. Хотя большинство используемых нами команд должны работать даже в старых версиях Git, некоторые из них могут не работать или действовать немного иначе, если вы используете старую версию. Поскольку Git отлично справляется с сохранением обратной совместимости, любая версия после 2.8 должна работать нормально.
Установка в Linux
Если вы хотите установить Git под Linux как бинарный пакет, это можно сделать, используя обычный менеджер пакетов вашего дистрибутива. Если у вас Fedora (или другой похожий дистрибутив, такой как RHEL или CentOS), можно воспользоваться dnf :
Если же у вас дистрибутив, основанный на Debian, например, Ubuntu, попробуйте apt :
Чтобы воспользоваться дополнительными возможностями, посмотрите инструкцию по установке для нескольких различных разновидностей Unix на сайте Git https://git-scm.com/download/linux.
Установка на Mac
Существует несколько способов установки Git на Mac. Самый простой — установить Xcode Command Line Tools. В версии Mavericks (10.9) и выше вы можете добиться этого просто первый раз выполнив ‘git’ в терминале.
Если Git не установлен, вам будет предложено его установить.
Если Вы хотите получить более актуальную версию, то можете воспользоваться бинарным установщиком. Установщик Git для OS X доступен для скачивания с сайта Git https://git-scm.com/download/mac.
Установка в Windows
Для установки Git в Windows также имеется несколько способов. Официальная сборка доступна для скачивания на официальном сайте Git. Просто перейдите на страницу https://git-scm.com/download/win, и загрузка запустится автоматически. Обратите внимание, что это отдельный проект, называемый Git для Windows; для получения дополнительной информации о нём перейдите на https://gitforwindows.org.
Для автоматической установки вы можете использовать пакет Git Chocolatey. Обратите внимание, что пакет Chocolatey поддерживается сообществом.
Установка из исходников
Многие предпочитают устанавливать Git из исходников, поскольку такой способ позволяет получить самую свежую версию. Обновление бинарных инсталляторов, как правило, немного отстаёт, хотя в последнее время разница не столь существенна.
Если вы действительно хотите установить Git из исходников, у вас должны быть установлены следующие библиотеки, от которых он зависит: autotools, curl, zlib, openssl, expat, and libiconv. Например, если в вашей системе используется dnf (Fedora) или apt-get (системы на базе Debian), вы можете использовать одну из следующих команд для установки всех зависимостей, используемых для сборки и установки бинарных файлов Git:
Для того, чтобы собрать документацию в различных форматах (doc, html, info), понадобится установить дополнительные зависимости:
Пользователи RHEL и производных от неё (таких как CentOS или Scientific Linux) должны подключить репозиторий EPEL для корректной установки пакета docbook2X
Если вы используете систему на базе Debian (Debian/Ubuntu/Ubuntu-производные), вам так же понадобится установить пакет install-info :
Если вы используете систему на базе RPM (Fedora/RHEL/RHEL-производные), вам так же понадобится установить пакет getopt , который уже установлен в системах на базе Debian:
К тому же из-за различий имён бинарных файлов вам понадобится сделать следующее:
Когда все необходимые зависимости установлены, вы можете пойти дальше и скачать самый свежий архив с исходниками из следующих мест: с сайта Kernel.org https://www.kernel.org/pub/software/scm/git, или зеркала на сайте GitHub https://github.com/git/git/releases. Конечно, немного проще скачать последнюю версию с сайта GitHub, но на странице kernel.org релизы имеют подписи, если вы хотите проверить, что скачиваете.
Затем скомпилируйте и установите:
После этого вы можете получать обновления Git посредством самого Git:
Источник
How to install GitExtensions in Ubuntu
For now I have Ubuntu 15.10 system with mono installed. To run and use GitExtensions on linux I have installed mono runtime (that’s more important, at least libmono-system-windows-forms library needed).
Installing GitExtensions
To install GitExtensions actually a few steps needed:
download GitExtensions zip archive for mono from sourceforge. No matter what tool you use. I used the browser for that.
extract archive content to /opt/GitExtensions directory. You can select arbitrary directory you want, but it’s seems more appropriate place for user installed software in linux.
edit gitext.sh file. This file already contains correct command, just supply GitExtensions.exe with full path. File should contains:
add execution rights to gitext.sh :
make symbolic link to /usr/local/bin directory:
Now I could type gitext from arbitrary directories where I want to run GitExtensions from.
Troubleshooting
(2017-01-19) Mono runtime errors about settings
If you got errors from mono runtime, you could use following gitext.sh :
Some versions of mono runtime has had some bugs and therefore GitExtensions can serialize window position in wrong format. rm command will delete wrong settings completely and you will be able to run GitExtensions.
But it seems like this mono bug has fixed now.
(2019-01-12) Failed to load plugin GitExtensions/Plugins/Bitbucket.dll
I’ve just updated to latest Mono v5.18.0.225 and got fatal error:
I’ve tried to update GitExtensions to latest version GitExtensions-2.51.05-Mono.zip but this didn’t helps.
To troubleshoot this issue I’ve just deleted Plugins/Bitbucket.dll file and error gone. Personally I don’t use Bitbucket plugin functionality therefore it’s fine fore me.
Summary
Now I have wonderful tool in my linux toolbox to work with git. Yes, it’s still important to me to be able to work with git through command line, but sometimes real GUI may be more convenient. I prefer it for viewing commits history, for example.

Источник
Getting Started¶
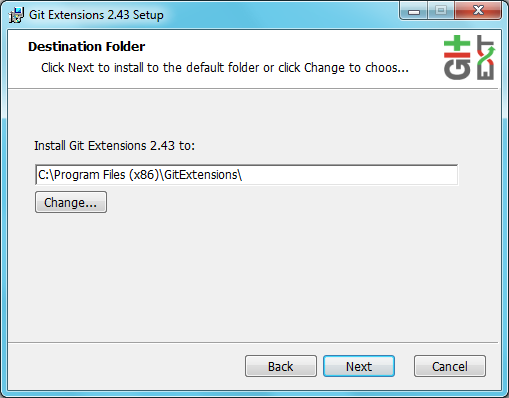
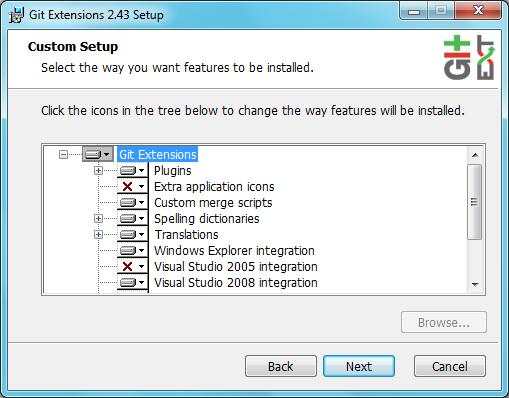
Installation¶
This section only covers Git Extensions installation, you will need to have Git for Windows installed: https://git-scm.com/download/win
The Git Extensions installer can be found on GitHub.
Choose the options to install.
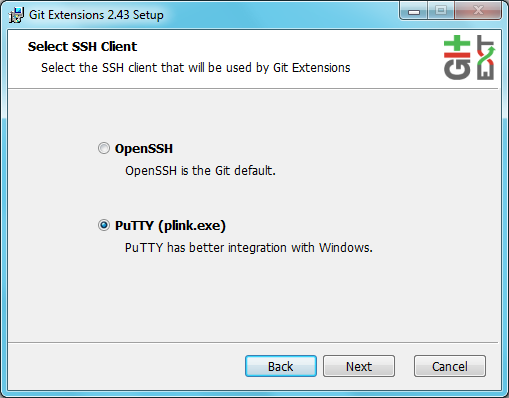
Choose the SSH client to use. PuTTY is the default because it has better Windows integration, but Pageant must be running.
Portable¶
Git Extensions is also distributed as a portable .zip file, that only require unpacking. Some features like Windows shell integration and Visual Studio integration is not available with this package.
Settings¶
Git must be installed prior to starting Git Extensions:
First selection is language (depends on the installed languages):
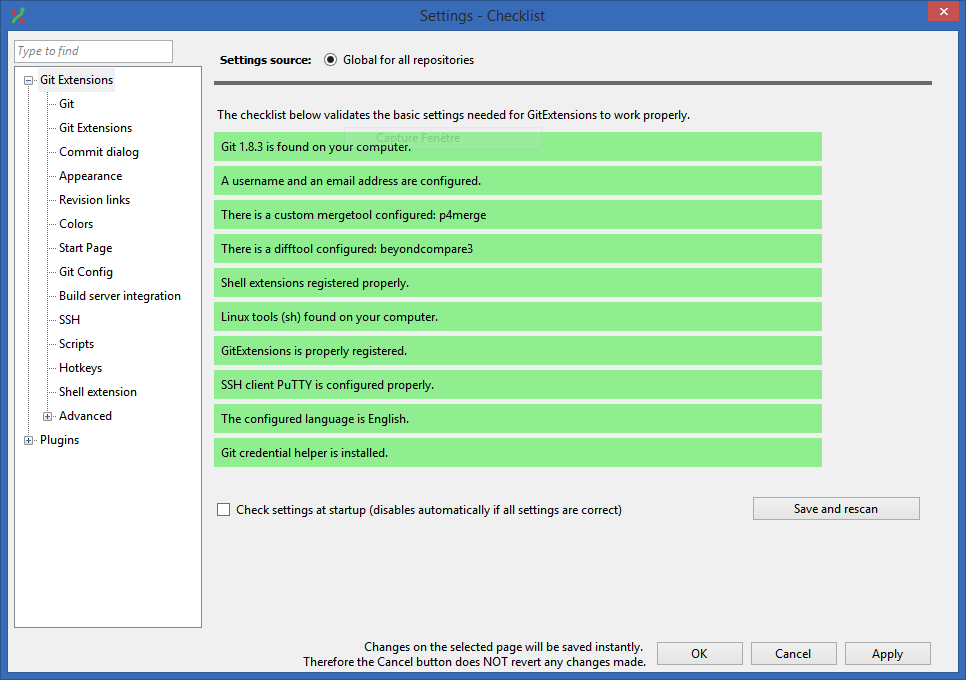
All settings will be verified when Git Extensions is started for the first time. If Git Extensions requires any settings to be changed, the Settings dialog will be shown. All incorrect settings will be marked in red (for instance if the Git version is unsupported) and orange for not recommended setting (like that Git version is older than recommended). You can ask Git Extensions to try to fix the setting for you by clicking on it. When installing Git Extensions for the first time, you will normally be required to configure your username and email address.
The settings dialog can be invoked at any time by selecting Settings from the Tools menu option.
For further information see Settings .
Dashboard¶
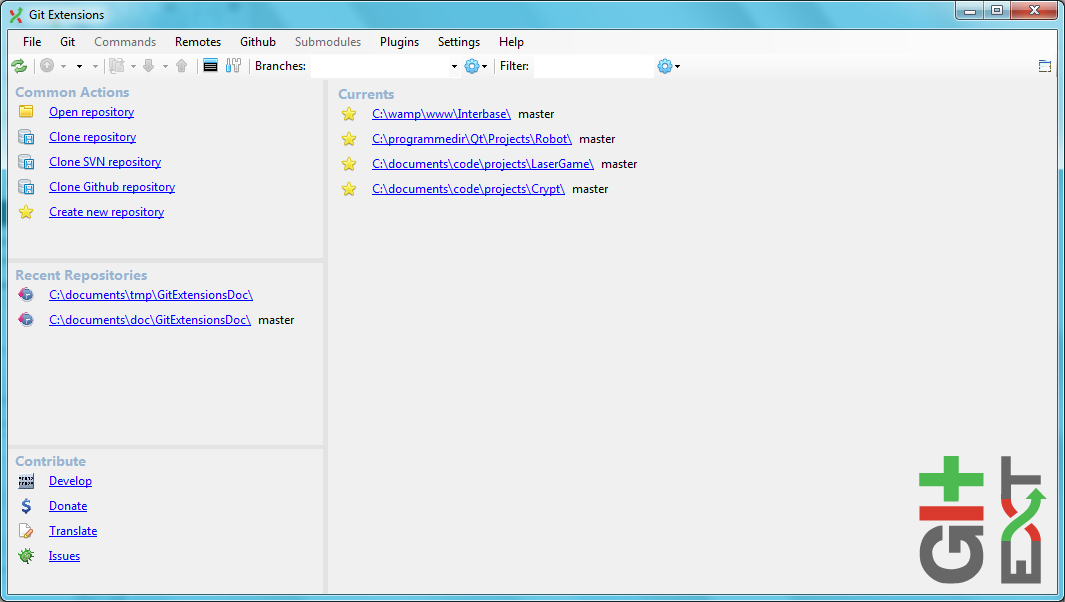
The dashboard contains the most common tasks, recently opened repositories and favourites. Favourite repositories can be added, grouped under Category headings in the right panel.
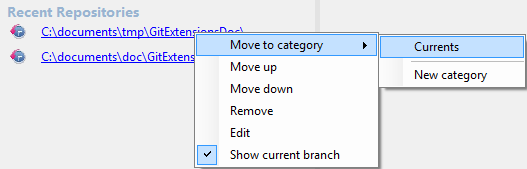
Recent Repositories can be moved to favourites using the repository context menu. Choose Categories / Add new to create a new category and add the repository to it, or you can add the repository to an existing category (e.g. вЂCurrents’ as shown below).
To open an existing repository, simply click the link to the repository, or select Open repository (from where you can select a repository to open from your local file system).
To create a new repository, one of the following options under Common Actions can be selected.
Create new repository¶
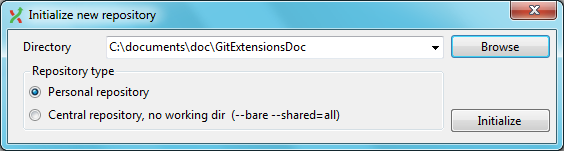
When you do not want to work on an existing project, you can create your own repository using this option.
Select a directory where the repository is to be created. You can choose to create a Personal repository or a Central repository.
A personal repository looks the same as a normal working directory but has a directory named .git at the root level containing the version history. This is the most common repository.
Central repositories only contain the version history. Because a central repository has no working directory you cannot checkout a revision in a central repository. It is also impossible to merge or pull changes in a central repository. This repository type can be used as a public repository where developers can push changes to or pull changes from.
Open repository¶
Opens a Git repo already existing on the file system.
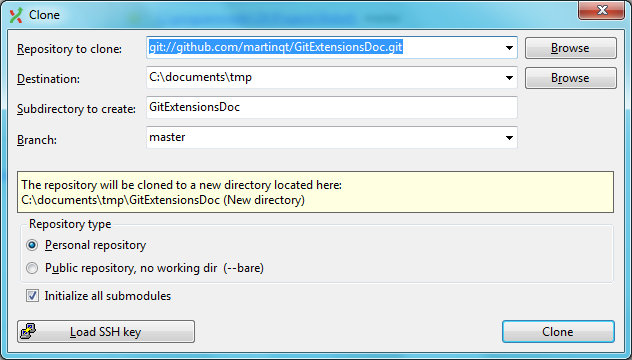
Clone repository¶
You can clone an existing repository using this option.
The repository you want to clone could be on a network share or could be a repository that is accessed through an internet or intranet connection. Depending on the protocol (http or ssh) you might need to load a SSH key into PuTTY. You also need to specify where the cloned repository will be created and the initial branch that is checked out. If the cloned repository contains submodules, then these can be initialised using their default settings if required.
There are two different types of repositories you can create when making a clone. A personal repository contains the complete history and also contains a working copy of the source tree. A central (bare) repository is used as a public repository where developers push the changes they want to share with others to. A central repository contains the complete history but does not have a working directory like personal repositories.
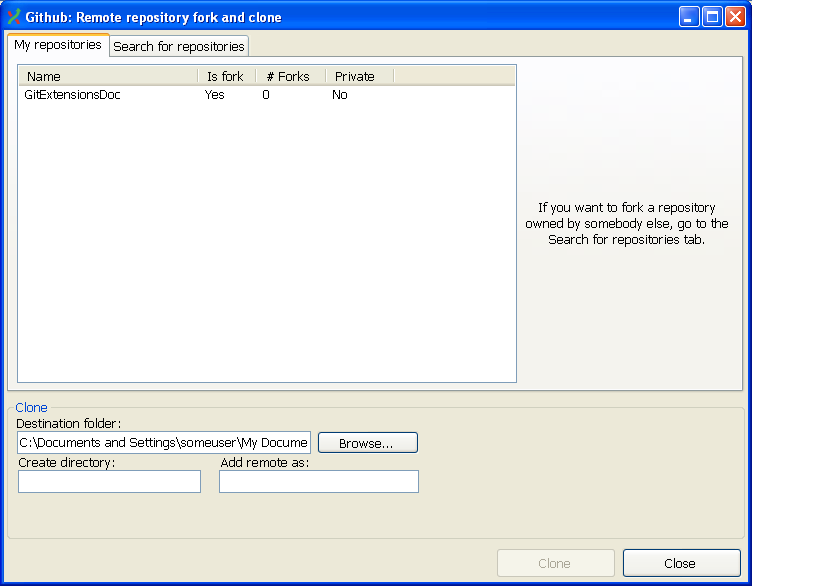
Clone Github repository¶
This option allows you to
- Fork a repository on GitHub so it is created in your personal space on GitHub.
- Clone any repositories on your personal space on GitHub so that it becomes a local repository on your machine.
You can see your own personal repositories on GitHub, and also search for repositories using the Search for repositories tab.
Источник
Getting Started¶
Installation¶
The single click Git Extensions installer can be found here.
Choose the options to install.
Choose the SSH client to use. PuTTY is the default because it has better Windows integration.
Installation (Linux) (2.5x only)¶
You can watch this video as a starting point: Install Git Extensions on Ubuntu 11.04
This section only covers mono installation, you should have git installed in your Linux at this point. Please refer to https://git-scm.com/download/linux
First, make sure you have the latest mono version on your Linux. This section will cover installation of Mono 4.6 on a Linux.
Install mono latest version. You can always check for this here: http://www.mono-project.com/download/#download-lin
If everything went okay, you should open your terminal and check mono version:
Now download Git Extensions latest version from https://github.com/gitextensions/gitextensions/releases/latest. Remember to select the appropriate package otherwise you could have problems.
Browse into the folder where you extracted the package and just run mono command, like the example below:
Installation (macOS) (2.5x only)¶
This section only covers mono installation, you should have git installed in your Mac at this point. Please refer to https://git-scm.com/download/mac
First, make sure you have the latest 32-bit mono version on your Mac. This section will cover installation of Mono 4.6 on a Mac.
Download mono latest version. You can always check for this here: http://www.mono-project.com/download/#download-mac
After you have completed the download, you will see a .dmg file. Double click it to open the package.
Inside the .dmg file you will have MonoFramework-
Follow the wizard until it’s completion.
If everything went okay, you should open your terminal and check mono version:
Now download Git Extensions latest version from https://github.com/gitextensions/gitextensions/releases/latest. Remember to select the appropriate package otherwise you could have problems.
Browse into the folder where you extracted the package and just run mono command, like the example below:
This is the minimal setup you need in order to run Git Extensions.
Troubleshooting Mac Installation¶
- If your Git Extensions crashes with an exception that a font is missing (generic sans serif), you probably can fix this by installing Xquartz. This is a version of the X.Org X Windows System that runs on OS X. I am not sure what the side effects are. This can be installed from here: http://xquartz.macosforge.org/landing/
- If Git Extensions still crashes because it is unable to load a plugin, empty the plugins folder.
Settings¶
All settings will be verified when Git Extensions is started for the first time. If Git Extensions requires any settings to be changed, the Settings dialog will be shown. All incorrect settings will be marked in red. You can ask Git Extensions to try to fix the setting for you by clicking on it. When installing Git Extensions for the first time (and you do not have Git already installed on your system), you will normally be required to configure your username and email address.
The settings dialog can be invoked at any time by selecting Settings from the Tools menu option.
For further information see Settings .
Start Page¶
The start page contains the most common tasks, recently opened repositories and favourites. The left side of the start page (Common Actions and Recent Repositories) is static. The right side of the page is where favourite repositories can be added, grouped under Category headings.
Recent Repositories can be moved to favourites using the repository context menu. Choose Move to category / New category to create a new category and add the repository to it, or you can add the repository to an existing category (e.g. ‘Currents’ as shown below).
A context menu is available for both the category and the repositories listed underneath it.
Entries on Category context menu
| Move Up | Move the category (and any repositories under it) higher on the page. |
| Move Down | Move the category (and any repositories under it) lower on the page. |
| Remove | Remove the category (and any repositories under it) from the page. Note: Git repositories are not physically removed either locally or remotely. |
| Edit | Shows the Start Page settings window where both category and repository details can be modified. |
Entries on repository context menu
| Move to category | Move the repository to a new or existing category. |
| Move up | Move the repository higher (within the category). |
| Move down | Move the repository lower (within the category). |
| Remove | Remove the repository from the category. Note: the repository is not physically removed either locally or remotely. |
| Edit | Shows the Start Page settings window where both category and repository details can be modified. |
| Show current branch | Toggles the display of the branch name next to the repository name. This identifies the currently checked out branch for the repository. |
To open an existing repository, simply click the link to the repository under Recent Repositories or within the Categories that you have set up, or select Open repository (from where you can select a repository to open from your local file system).
To create a new repository, one of the following options under Common Actions can be selected.
Clone repository¶
You can clone an existing repository using this option. It displays the following dialog.
The repository you want to clone could be on a network share or could be a repository that is accessed through an internet or intranet connection. Depending on the protocol (http or ssh) you might need to load a SSH key into PuTTY. You also need to specify where the cloned repository will be created and the initial branch that is checked out. If the cloned repository contains submodules, then these can be initialised using their default settings if required.
There are two different types of repositories you can create when making a clone. A personal repository contains the complete history and also contains a working copy of the source tree. A central repository is used as a public repository where developers push the changes they want to share with others to. A central repository contains the complete history but does not have a working directory like personal repositories.
Clone SVN repository¶
You can clone an existing SVN repository using this option, which creates a Git repository from the SVN repository you specify. For further information refer to the Pro Git book.
Clone Github repository¶
This option allows you to
- Fork a repository on GitHub so it is created in your personal space on GitHub.
- Clone any repositories on your personal space on GitHub so that it becomes a local repository on your machine.
You can see your own personal repositories on GitHub, and also search for repositories using the Search for repositories tab.
Create new repository¶
When you do not want to work on an existing project, you can create your own repository using this option.
Select a directory where the repository is to be created. You can choose to create a Personal repository or a Central repository.
A personal repository looks the same as a normal working directory but has a directory named .git at the root level containing the version history. This is the most common repository.
Central repositories only contain the version history. Because a central repository has no working directory you cannot checkout a revision in a central repository. It is also impossible to merge or pull changes in a central repository. This repository type can be used as a public repository where developers can push changes to or pull changes from.
Источник