- How to List Open Ports on Linux?
- Ports on Linux
- List Open Ports
- List protocols and open ports from /etc/services
- List open ports using netstat
- List open ports using ss
- List open ports using lsof
- List open ports using nmap
- List open ports using netcat
- Final Thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
- How to check open ports in Linux using the CLI
- What the hell are a TCP and UDP ports?
- Port numbers
- Check open ports in Linux
- Using netstat to list open ports
- Use ss to list open ports
- Listening ports and applications using lsof command
- nmap command
- The open port doesn’t mean anyone from outside can access those ports
- Conclusion
- How to check if port is in use on Linux or Unix
- How to check if port is in use in
- Option #1: lsof command
- Option #2: netstat command
- Linux netstat syntax
- FreeBSD/MacOS X netstat syntax
- OpenBSD netstat syntax
- Option #3: nmap command
- A note about Windows users
- Conclusion
How to List Open Ports on Linux?
In networking, a port is an interesting feature. It’s a way for network traffic to identify the destination app or service. Each process/service gets its unique port. A port will always be associated with the IP address of the host along with the protocol.
This is a favorite metaphor of mine to describe what a port is. Imagine a ship loaded with cargo, which will travel to a distant land. What information is needed to reach the destination properly? For the sake of simplicity, let’s say it needs the country (the IP address) and the port the ship will dock.
In this guide, check out how to list open ports on Linux.
Ports on Linux
Ports act as an endpoint of communication. It’s a 16-bit number (0 to 65535 in decimal). While the range is large, for ease of use, ports are categorized into three categories. Each category is labeled as the range of port value:
- 0 to 1023: These are the “Well-known” ports, also known as the “System” ports, which are reserved for system processes that offer a wide variety of network services. To bind with a “Well-known” port, a process must have superuser privilege.
- 1024 to 49151: These are the “Registered” ports, also known as the “User” ports, that are designated by IANA for specific services. Upon request, a process may have access to them. In the case of most systems, it doesn’t require any superuser privilege to use these ports.
- 49152 to 65535: These are the “Dynamic” ports, also known as the “Private” ports. These ports can’t be registered with IANA. These ports are open to using for private or customized services and may also be automatically allocated as ephemeral ports (short-lived ports used by IP).
In Linux, there are multiple ways of checking the open ports. By default, any port will remain closed unless an app is using it. If a port is open, then it must be assigned to a service/process.
List Open Ports
It’s easier to identify which ports are in use rather than which ports are open. That’s why the following section will feature methods to list all the ports that are currently in use. In Linux, there are multiple tools available for the task. Most of them come built-in in any Linux distro.
Learning which ports are currently open can be useful in various scenarios. It’s possible to configure a dedicated port for a certain application. An open port may also be a strong indication of intrusion in the network.
The following methods are demonstrated on Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS.
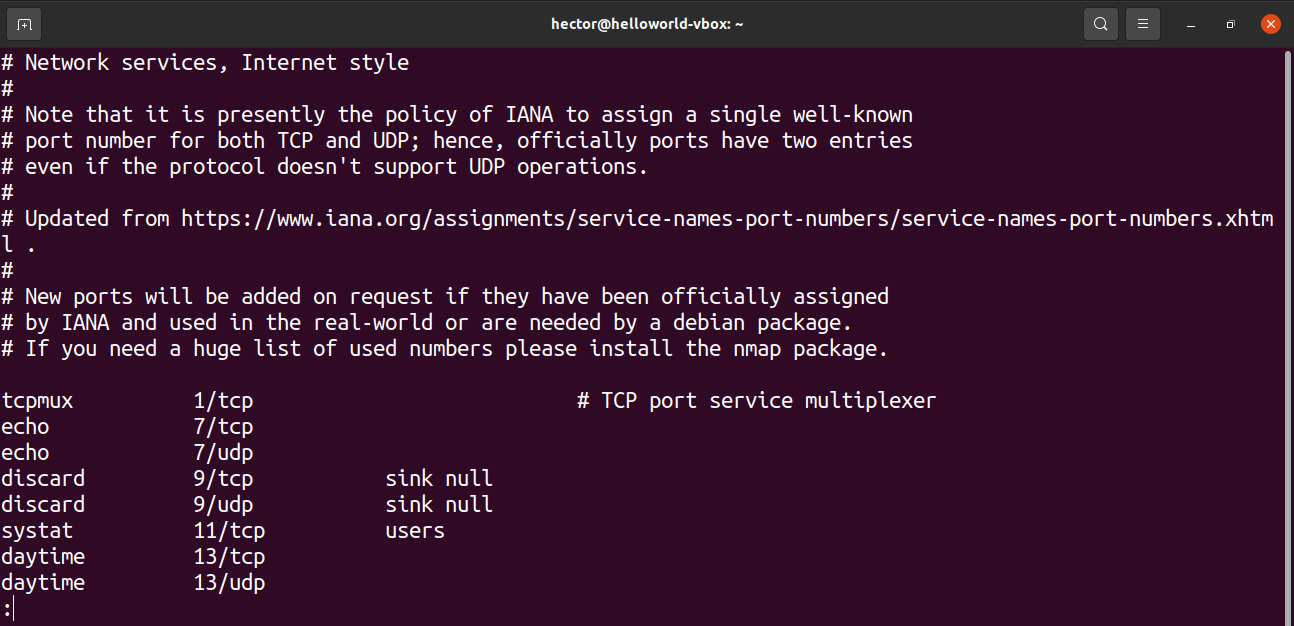
List protocols and open ports from /etc/services
The /etc/services file contains information about the currently running services. It’s a big file, so ready to get overwhelmed.
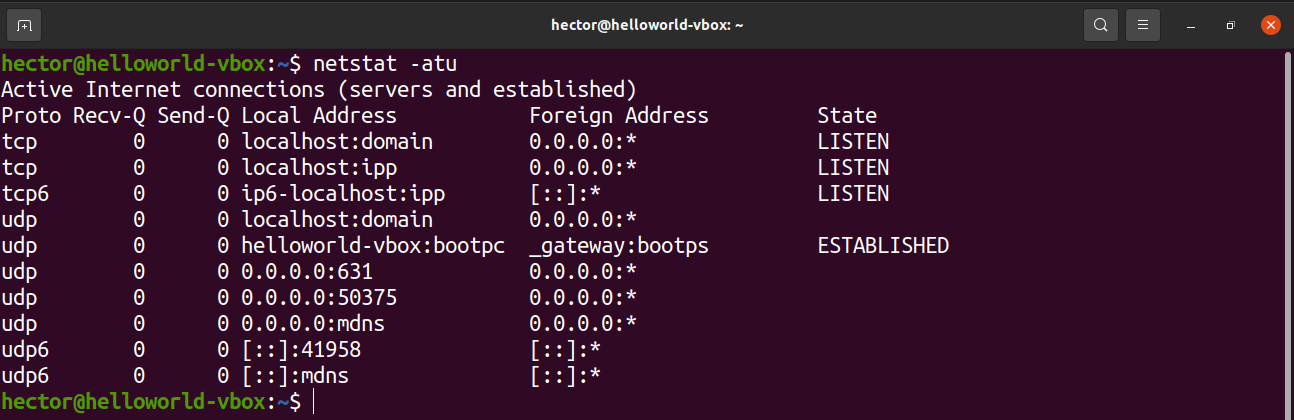
List open ports using netstat
The netstat tool is a utility for displaying network connections for TCP, routing tables, and various network interfaces. It also offers network protocol statistics. By using netstat, we can list all the open ports of the system.
Run the following netstat command:
Let’s have a quick breakdown of all the flags we used in this command.
- a: Tells netstat to show all sockets
- t: Tells netstat to list TCP ports
- u: Tells netstat to list UDP ports
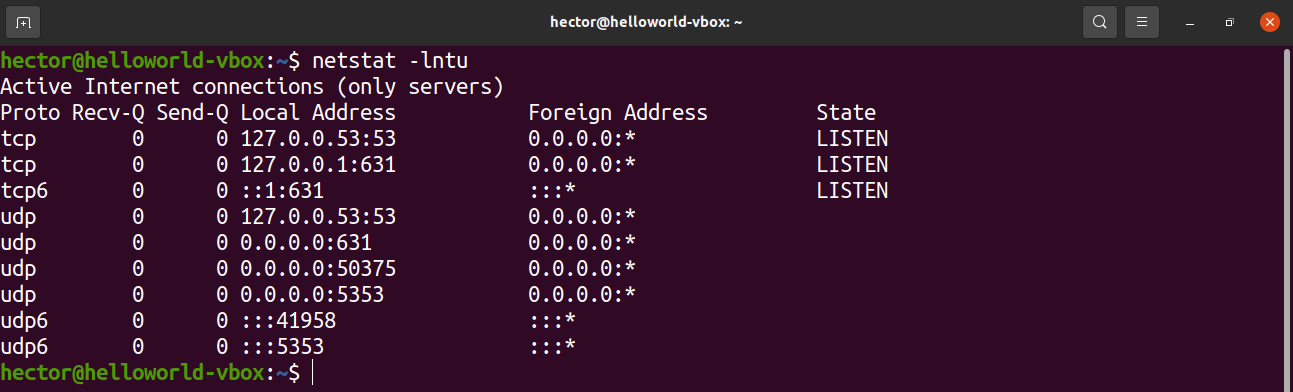
Here’s another variation of the netstat command:
There are two new flags used in the command. What do they mean?
- l: Tells netstat to print only the listening sockets
- n: Tells netstat to show the port number
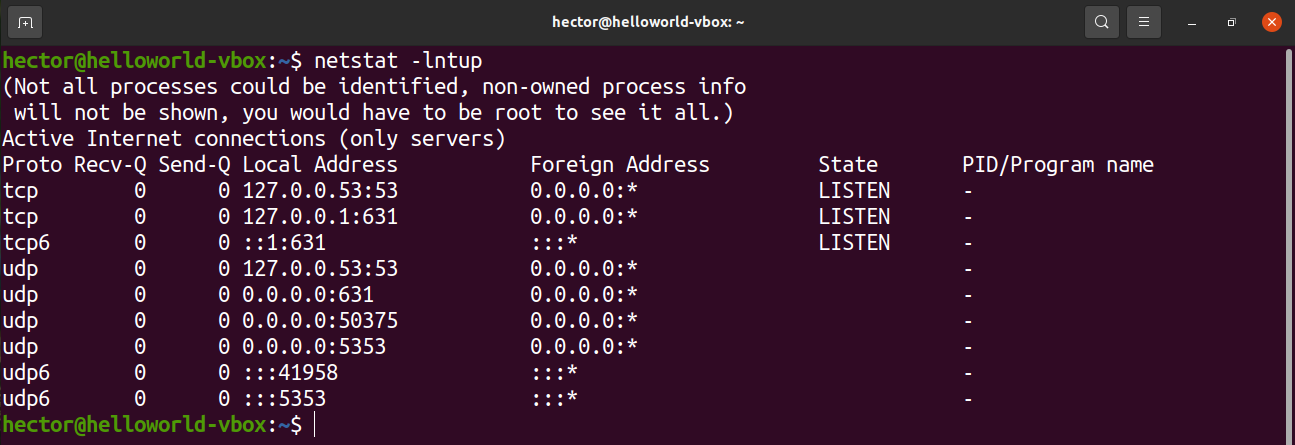
To display the PID of the process that’s using a port, use the “-p” flag:
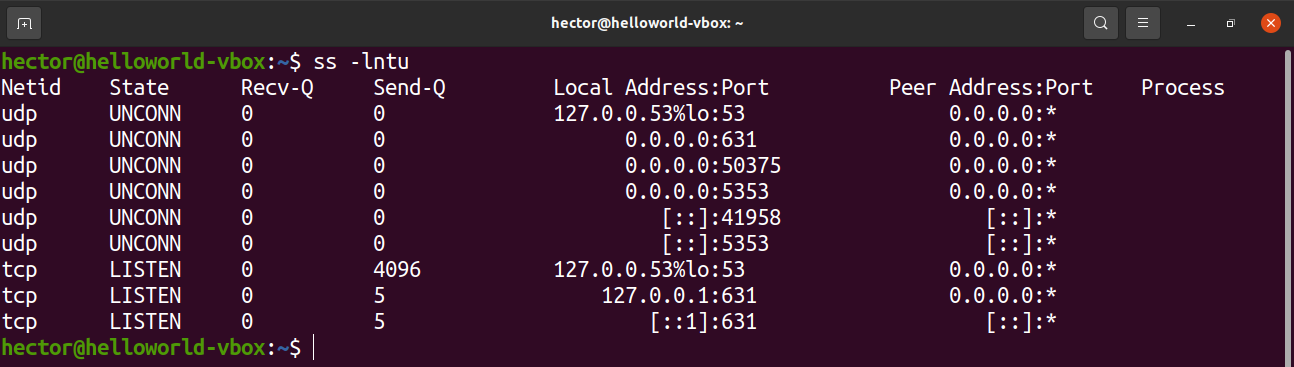
List open ports using ss
The ss tool is a utility for investigating socket. Its usage is similar to netstat.
To list the open ports, run the following ss command:
The flags are similar to netstat. The functions they describe are also quite similar.
- l: Tells ss to display listening sockets
- n: Tells ss not to try to resolve service names
- t: Tells ss to display TCP sockets
- u: Tells ss to display UDP sockets
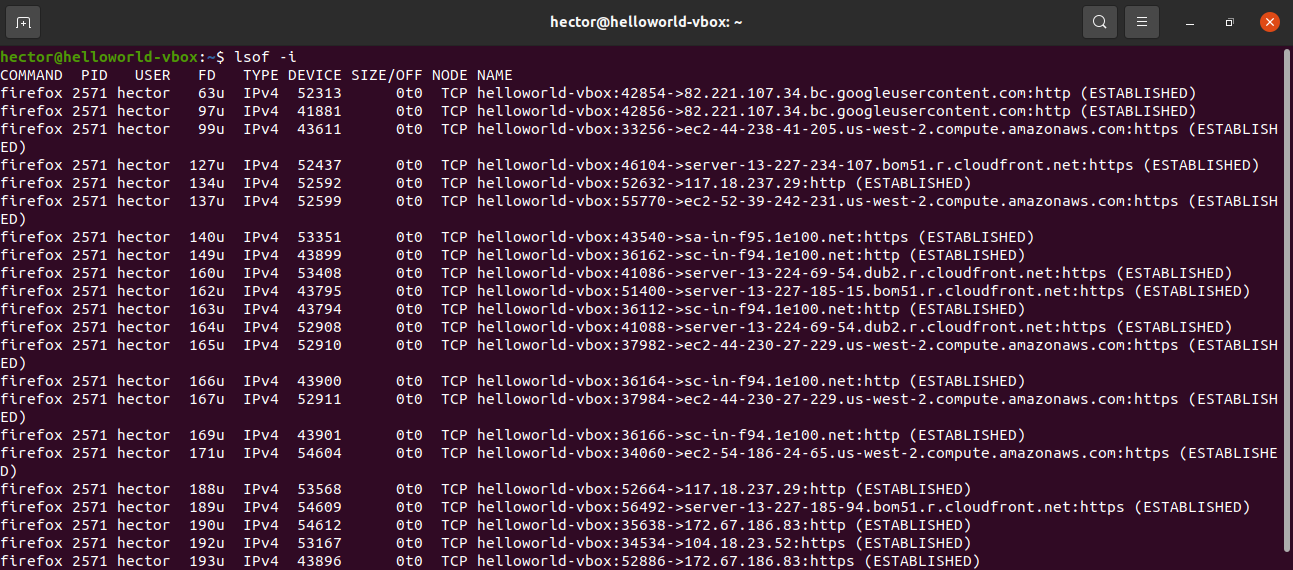
List open ports using lsof
The lsof command is to list open files. However, it can also be used for displaying the open ports.
Run the following lsof command:
To get the open ports of a specific protocol (TCP, UDP, etc.) then define it after the “-i” flag, use:
List open ports using nmap
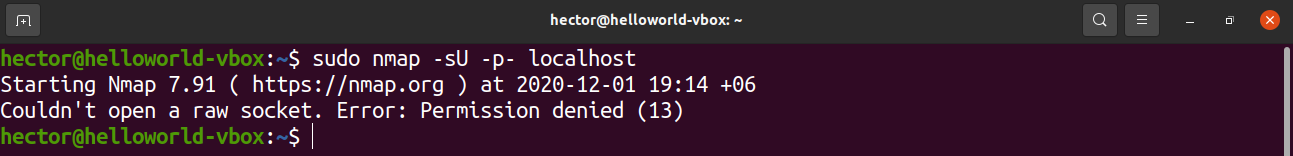
The nmap tool is a powerful one for network exploration and security/port scanning. It can report all the open ports in the system.
To list the open TCP ports, run the following nmap command. Here, the IP address is of the host computer:
Here, there are two portions of the command argument.
- -sT: This section tells nmap to scan for TCP ports.
- -p- : This tells nmap to scan for all 65535 ports. If not used, then nmap will scan only 1000 ports by default.
If you need to list the open UDP ports, then run the following nmap command:
To get both the open TCP and UDP ports, use the following command:
List open ports using netcat
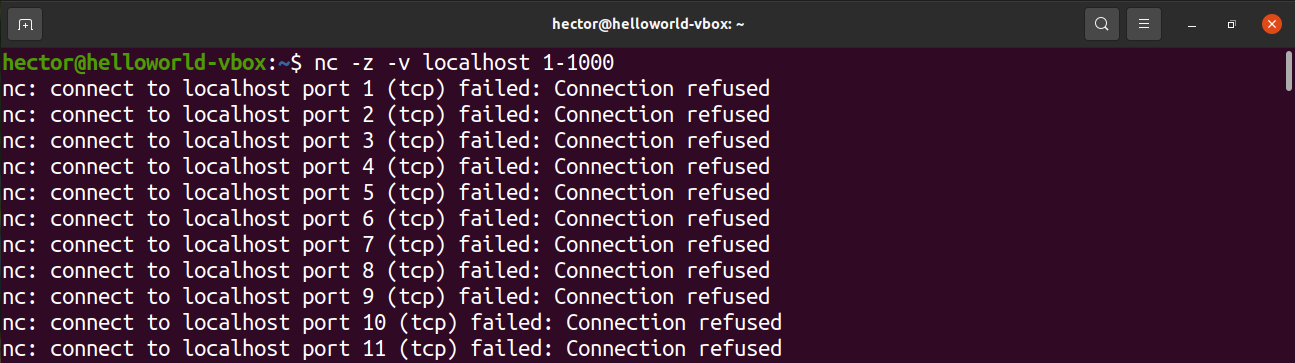
The netcat tool is a command line utility for reading and writing data across network connections over the TCP and UDP protocols. This tool can also be used for listing open ports. It can perform tests on a specific port or a range of ports.
The following netcat command will scan the port from 1 to 1000. The netcat command will perform the scan on TCP protocol by default:
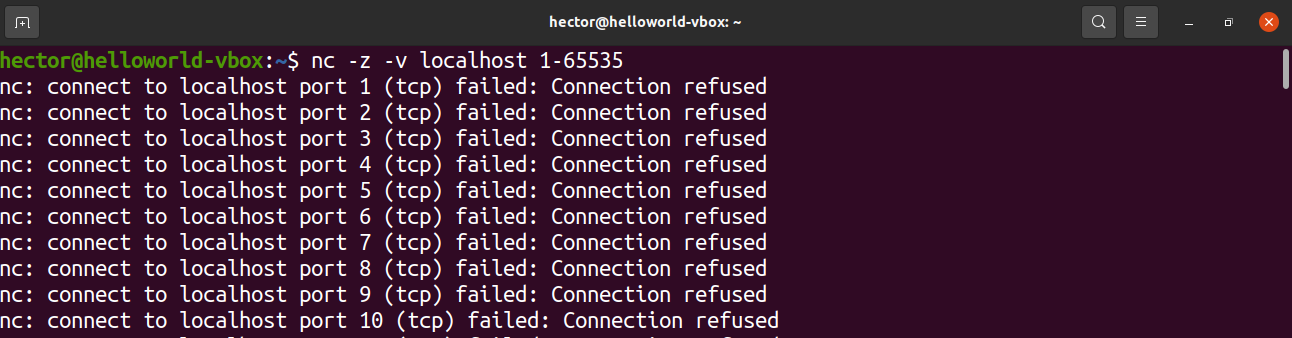
It can also be extended to the entire list of possible ports:
Let’s have a quick breakdown of the flags.
- z: Tells netcat to scan only for open ports without sending any data
- v: Tells netcat to run in verbose mode
To get only the open ports from this list, filter the output with grep for the term “succeeded”.
If you want to perform the scan on UDP protocol, then add the “-u” flag.
Final Thoughts
As demonstrated, there are tons of ways to scan for open ports on Linux. I suggest trying out all the methods before you decide which one to master. If you’re using a certain tool like netcat or nmap regularly, then mastering the associated methods will be the most beneficial.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
Источник
How to check open ports in Linux using the CLI
I need to list all open ports in Linux cloud server. How do I check open ports in Linux using the CLI? Can you give me the command to check open ports in Linux operating system?
To troubleshoot server problems and to avoid security issue, one needs to find out open TCP and UDP ports. In this tutorial, you will learn the different Linux commands to check open ports in Linux for auditing and securing the server.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux command line |
| Est. reading time | 5 minutes |
What the hell are a TCP and UDP ports?
A port is nothing but a 16-bit number between 0 to 65535. For example, TCP port number 22 may be forwarded to the OpenSSH server. Therefore, 22 port number is a way to identify the sshd (OpenSSH server) process.
Port numbers
- The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023.
- The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151.
- The Dynamic and Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535.
A registered port is a network port assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and stored in /etc/services file. Use the cat command or grep command/egrep command to view port numbers and service mappings:
Display a list of applications and their ports assigned by IANA
Check open ports in Linux
The procedure to monitor and display open ports in Linux is as follows:
- Open a Linux terminal application
- Use ss command to display all open TCP and UDP ports in Linux.
- Another option is to use the netstat command to list all ports in Linux.
- Apart from ss / netstat one can use the lsof command to list open files and ports on Linux based system.
- Finally, one can use nmap command to check TCP and UDP ports too.
Let us see all commands and examples in details.
Using netstat to list open ports
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- -t : All TCP ports
- -u : All UDP ports
- -l : Display listening server sockets
- -p : Show the PID and name of the program to which each socket belongs
- -n : Don’t resolve names
- | grep LISTEN : Only display open ports by applying grep command filter.
Use ss to list open ports
The ss command is used to dump socket statistics. It allows showing information similar to netstat. It can display more TCP and state information than other tools. The syntax is:
sudo ss -tulpn
Sample outputs:
Listening ports and applications using lsof command
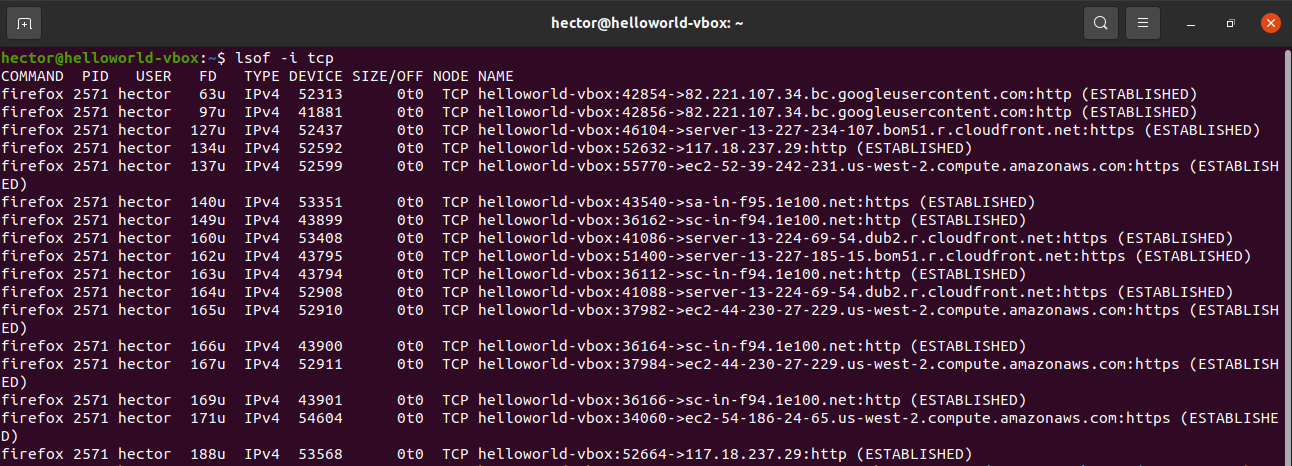
Let us run the following to check open TCP and UDP ports using the lsof command:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
Where,
- -i : Look for listing ports
- -P : Inhibits the conversion of port numbers to port names for network files. Inhibiting the conversion may make lsof run a little faster. It is also useful when port name lookup is not working properly.
- -n : Do not use DNS name
- | grep LISTEN : Again only show ports in LISTEN state using the grep command as filter.
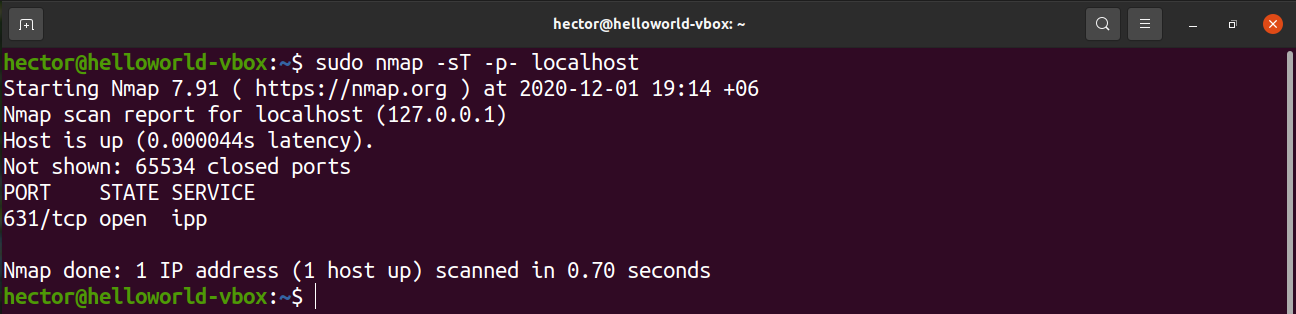
nmap command
In addition, to above commands one can use the nmap command which is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. We are going to use nmap to find and list open ports in Linux:
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.254 ##[ list open UDP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 127.0.0.1 ##[ list open TCP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sTU -O 192.168.2.24
Sample outputs:
The open port doesn’t mean anyone from outside can access those ports
So far, you know how to find and list open TCP and UDP ports on Linux. However, those ports can still be blocked by software, cloud, or hardware firewall. Hence, you need to verify that your corporate firewall is not blocking incoming or outgoing access. For instance on Linux server we list or dump firewall rules using the following syntax:
sudo iptables -S
# IPv6
sudo ip6tables -S
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding out open ports is one of the most fundamental duties of a Linux system administrator for security reasons. Therefore, close down all unwanted ports and configure firewall such as UFW and FirewallD to open or block ports as per your requirements. After reading this tutorial, you should have a good understanding of how to check for open ports in Linux. See IANA’s offical list of TCP, UDP and other ports here for more information.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to check if port is in use on Linux or Unix
H ow do I determine if a port is in use under Linux or Unix-like system? How can I verify which ports are listening on Linux server? How do I check if port is in use on Linux operating system using the CLI?
It is important you verify which ports are listening on the server’s network interfaces. You need to pay attention to open ports to detect an intrusion. Apart from an intrusion, for troubleshooting purposes, it may be necessary to check if a port is already in use by a different application on your servers. For example, you may install Apache and Nginx server on the same system. So it is necessary to know if Apache or Nginx is using TCP port # 80/443. This quick tutorial provides steps to use the netstat, nmap and lsof command to check the ports in use and view the application that is utilizing the port.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | lsof, ss, and netstat on Linux |
| Est. reading time | 3 minutes |
How to check if port is in use in
To check the listening ports and applications on Linux:
- Open a terminal application i.e. shell prompt.
- Run any one of the following command on Linux to see open ports:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo ss -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo lsof -i:22 ## see a specific port such as 22 ##
sudo nmap -sTU -O IP-address-Here - For the latest version of Linux use the ss command. For example, ss -tulw
Let us see commands and its output in details.
Option #1: lsof command
The syntax is:
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
$ doas lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN ### [OpenBSD] ###
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Check the listening ports and applications with lsof command
Option #2: netstat command
You can check the listening ports and applications with netstat as follows.
Linux netstat syntax
Run netstat command along with grep command to filter out port in LISTEN state:
$ netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
The netstat command deprecated for some time on Linux. Therefore, you need to use the ss command as follows:
sudo ss -tulw
sudo ss -tulwn
sudo ss -tulwn | grep LISTEN
Where, ss command options are as follows:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
- -t : Show only TCP sockets on Linux
- -u : Display only UDP sockets on Linux
- -l : Show listening sockets. For example, TCP port 22 is opened by SSHD server.
- -p : List process name that opened sockets
- -n : Don’t resolve service names i.e. don’t use DNS
FreeBSD/MacOS X netstat syntax
$ netstat -anp tcp | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -anp udp | grep LISTEN
OpenBSD netstat syntax
$ netstat -na -f inet | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -nat | grep LISTEN
Option #3: nmap command
The syntax is:
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.13 ##[ list open UDP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 192.168.2.13 ##[ list open TCP ports ]##
Sample outputs:
Fig.02: Determines which ports are listening for TCP connections using nmap
A note about Windows users
You can check port usage from Windows operating system using following command:
netstat -bano | more
netstat -bano | grep LISTENING
netstat -bano | findstr /R /C:»[LISTEING]»
Conclusion
This page explained command to determining if a port is in use on Linux or Unix-like server. For more information see the nmap command and lsof command page online here
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник