- How To Get / Print Current Date in Unix / Linux Shell Script
- Print current date and time in Unix shell script
- Print Current Date in Unix
- Getting the current date and time in Linux shell script
- A list of date command format codes
- Sample shell script to display the current date and time
- Conclusion
- Display Date And Time In Linux
- Syntax
- Display date and time in Linux using the timedatectl
- TZ environment variable
- GUI Tool: Time Administration
- How to change date and time settings with Gnome based Linux desktop
- Conclusion
- Команда date в Linux
- Синтаксис команды date
- Примеры использования date
- Выводы
How To Get / Print Current Date in Unix / Linux Shell Script
H ow do I get the current date in Unix or Linux shell scripting and store it into a shell variable? How do I print the current date using Unix shell script? How can I display the current time in Linux shell script?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux or Unix |
| Est. reading time | 3 minutes |
You need to use the following syntax to print current date and time on screen:
Print current date and time in Unix shell script
To store current date and time to a variable, enter:
now=$(date)
OR
now=`date`
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Print Current Date in Unix
To print this date either use the printf or echo statement:
echo «$now»
echo «Current date: $now»
OR use the printf command:
printf «%s\n» «$now»
OR
printf «Current date and time in Linux %s\n» «$now»
Getting the current date and time in Linux shell script
You can format and display date using the following syntax:
Finding the current date and time in Linux or Unix using the date command
A list of date command format codes
| FORMAT code | Description |
|---|---|
| %% | a literal % |
| %a | locale’s abbreviated weekday name (e.g., Sun) |
| %A | locale’s full weekday name (e.g., Sunday) |
| %b | locale’s abbreviated month name (e.g., Jan) |
| %B | locale’s full month name (e.g., January) |
| %c | locale’s date and time (e.g., Thu Mar 3 23:05:25 2005) |
| %C | century; like %Y, except omit last two digits (e.g., 20) |
| %d | day of month (e.g., 01) |
| %D | date; same as %m/%d/%y |
| %e | day of month, space padded; same as %_d |
| %F | full date; same as %Y-%m-%d |
| %g | last two digits of year of ISO week number (see %G) |
| %G | year of ISO week number (see %V); normally useful only with %V |
| %h | same as %b |
| %H | hour (00..23) |
| %I | hour (01..12) |
| %j | day of year (001..366) |
| %k | hour, space padded ( 0..23); same as %_H |
| %l | hour, space padded ( 1..12); same as %_I |
| %m | month (01..12) |
| %M | minute (00..59) |
| %n | a newline |
| %N | nanoseconds (000000000..999999999) |
| %p | locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM; blank if not known |
| %P | like %p, but lower case |
| %q | quarter of year (1..4) |
| %r | locale’s 12-hour clock time (e.g., 11:11:04 PM) |
| %R | 24-hour hour and minute; same as %H:%M |
| %s | seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC |
| %S | second (00..60) |
| %t | a tab |
| %T | time; same as %H:%M:%S |
| %u | day of week (1..7); 1 is Monday |
| %U | week number of year, with Sunday as first day of week (00..53) |
| %V | ISO week number, with Monday as first day of week (01..53) |
| %w | day of week (0..6); 0 is Sunday |
| %W | week number of year, with Monday as first day of week (00..53) |
| %x | locale’s date representation (e.g., 12/31/99) |
| %X | locale’s time representation (e.g., 23:13:48) |
| %y | last two digits of year (00..99) |
| %Y | year |
| %z | +hhmm numeric time zone (e.g., -0400) |
| %:z | +hh:mm numeric time zone (e.g., -04:00) |
| %::z | +hh:mm:ss numeric time zone (e.g., -04:00:00) |
| %. z | numeric time zone with : to necessary precision (e.g., -04, +05:30) |
| %Z | alphabetic time zone abbreviation (e.g., EDT) |
Sample shell script to display the current date and time
Conclusion
You learned how to display the current date and time on Linux and Unix-like systems. We also explained how to store date or time in a shell variable. For more info see date command man page by typing the following date command or GNU/date help page here:
man date
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Display Date And Time In Linux
H ow do I display date and time in Linux using the command line and GUI options?
To display date and time under Linux operating system using command prompt use the date command. It can also display the current time / date in the given FORMAT. We can set the system date and time as root user too.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux with the terminal application |
| Est. reading time | 3 minutes |
Syntax
Open a terminal and type the following command:
date
You can format the date as follows in dd-mm-yy format:
date +»%d-%m-%y»
Simply display the current time:
date «+%T»
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
To print the date of the day before yesterday, run:
date —date=’2 days ago’
Want to see the day of year of Christmas in the current year? Try:
date —date=’25 Dec’ +%j
Display the current full month name and the day of the month:
date ‘+%B %d’
Display date and time in Linux using the timedatectl
Most modern Linux distro with systemd use the timedatectl command. It is used to query and change the system clock and its settings, and enable or disable time synchronization services. All you have to do is type the following command:
$ timedatectl
TZ environment variable
The TZ environment tells Linux what time zone you are in. Many times when you want to change your time zone temporarily. For example, you might want to print the current date and time in “America/Los_Angeles” timezone even though you are in “Europe/London”. So we can set TZ, give a command like as follows when using TCSH/CSH:
setenv TZ timezone
For BASH/KSH/SH (see export command:
TZ=timezone; export TZ
Another option:
TZ=»America/Los_Angeles» date
TZ=»Asia/Tokyo» date
Use the following command to print a list of all timezones:
timedatectl list-timezones
timedatectl list-timezones | more
## filter out data using the grep command/egrep command ##
timedatectl list-timezones | grep -i Hong_kong
timedatectl list-timezones | grep -i paris
timedatectl list-timezones | grep -E -i ‘paris|london|kolkata’
The TZ Environment Variable on Linux
GUI Tool: Time Administration
The Time Administration Tool allows you to set the time, date and timezone of your system, as well as setting any time server to synchronize your local time server. Type the following command to start time admin tool:
sudo time-admin
## OR ##
time-admin
Fig.01: Linux Date and Time Administration Tool
How to change date and time settings with Gnome based Linux desktop
First, you need to Settings in Activities and then click Details in the sidebar. Make sure you click Date & Time in the sidebar to open the panel:
Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, you learned about the date command that you can use to see or change the date/time under Linux operating systems. We further explained how to use the GUI tools too. The date command has many more options. See man page by typing the following man command:
$ man date
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Команда date в Linux
Главное свойство утилит GNU/Linux — делать что-то одно, но эффективно. Яркий пример — команда date Linux, работающая с датой и временем. С её помощью можно извлекать любую дату в разнообразном формате, в том числе и рассчитывать прошлое и будущее время. Привилегированные пользователи могут перезаписывать системное время, используя её.
Утилита предустановлена во всех дистрибутивах GNU/Linux. В этой статье будут рассмотрены возможности date и способы применения этой команды.
Синтаксис команды date
Программа может выполнятся от имени обычного пользователя. Стандартный синтаксис команды (квадратные скобки обозначают необязательное наличие):
date [ ОПЦИИ ] . [ +ФОРМАТ ]
Ниже представлена таблица с часто применяемыми опциями для date.
| Опция | Длинный вариант | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| -d STRING | —date=STRING | Вывод даты по указанной строке (например ‘yesterday’, ‘tomorrow’, ‘last monday’). |
| -I | —iso-8601[=FMT] | Вывод даты в формате ISO 8601. FMT по умолчанию содержит ‘date’. Также может содержать ‘hourse’, ‘minutes’, ‘seconds’, ‘ns’ для отображения соответствующих значений и часовой пояс относительно UTC рядом с датой. |
| —rfc-3339=FMT | Вывод даты в формате RFC 3339. FMT по умолчанию содержит ‘date’. Также может содержать ‘seconds’ и ‘ns’ для отображения секунд или наносекунд. | |
| -r FILE | —reference=FILE | Вывод даты последней модификации указанного файла в формате по умолчанию. |
| -u | —utc | Вывод UTC-даты |
Аргумент ФОРМАТ отвечает за форматирование вывода даты. Для его указания необходимо поставить знак «+» и написать нужную маску. Наиболее популярные форматы:
| Формат | Значение |
|---|---|
| %% | Знак процента |
| %a | День недели текущей локали в короткой форме («Чтв») |
| %A | День недели текущей локали в длинной форме («Четверг») |
| %b | Месяц года текущей локали в короткой форме в родительном падеже («янв») |
| %B | Месяц года текущей локали в длинной форме в родительном падеже («января») |
| %c | Дата и время текущей локали без указания часового пояса |
| %С | Первые две цифры текущего года |
| %d | Числовой день месяца с ведущим нулём |
| %D | Дата в формате %m/%d/%y |
| %e | День месяца; аналог %_d |
| %F | Дата в формате %Y-%m-%d |
| %h | Аналог %b |
| %H | Часы (00..23) |
| %I | Часы (01..12) |
| %j | День года (001..366) |
| %m | Месяц (01..12) |
| %M | Минуты (00..59) |
| %n | Новая строка |
| %q | Квартал года |
| %S | Секунды (00..59) |
| %t | Знак табуляции |
| %T | Время в формате %H:%M:%S |
| %u | Числовой день недели; 1 — понедельник |
| %x | Дата в локальном формате |
| %X | Время в локальном формате |
| %Z | Аббревиатура временной зоны |
Примеры использования date
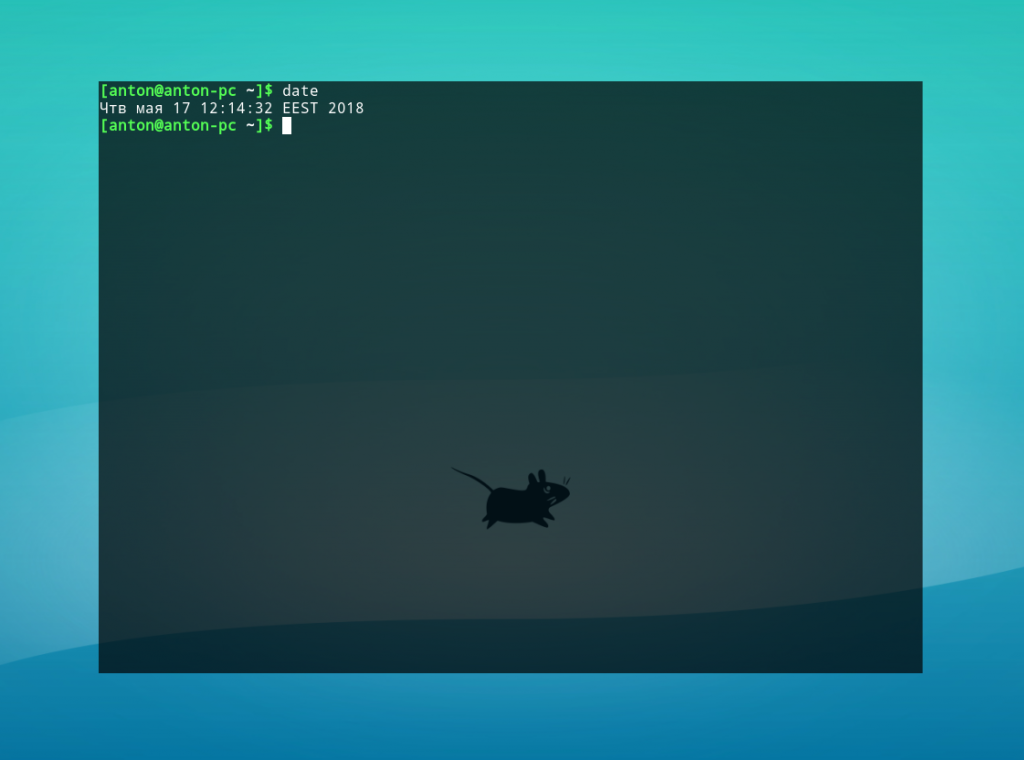
Введем команду без параметров.
Будет отображена текущая дата и время в соответствии с настройками локали системы.
Команда date без параметров по умолчанию применяет маску %a %b %d %X %Z. Поскольку все форматы должны быть переданы как один параметр (из-за принципа обработки данных командным интерпретатором Bash), пробелы между ними необходимо экранировать обратным слэшем (\) или взять в кавычки.
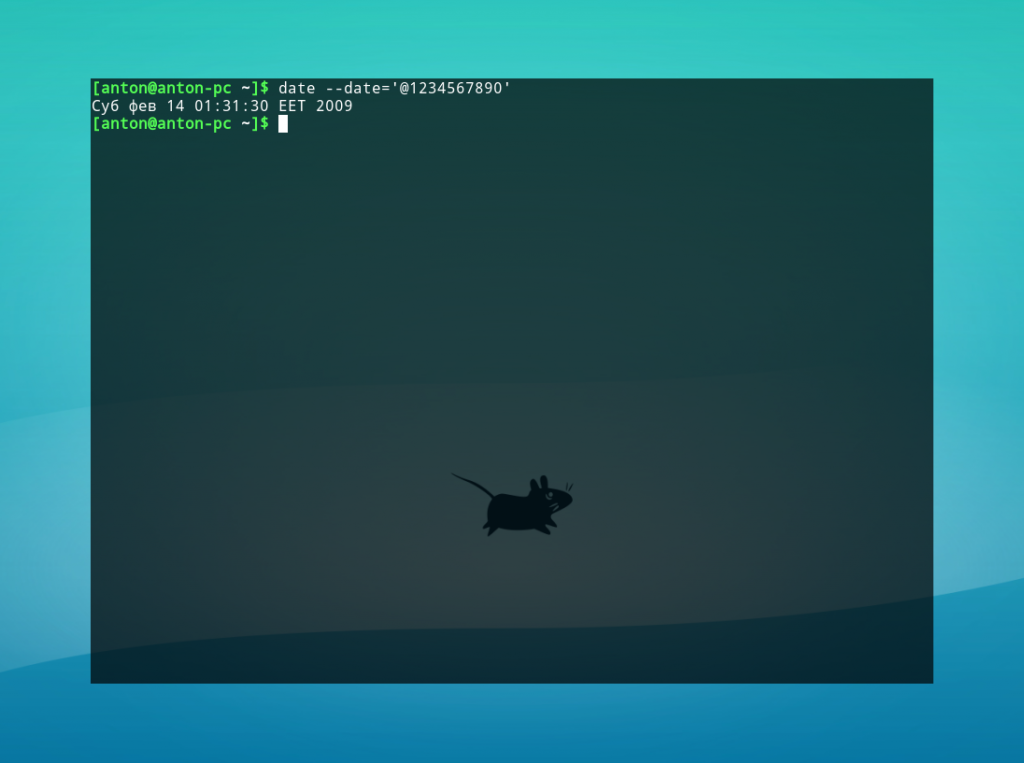
Особое внимание следует уделить параметру -d (—date). Его функциональность не слишком очевидна, но при этом наиболее обширна.
Пример 1. Вычисление даты по числу секунд, прошедших с 1 января 1970 года.
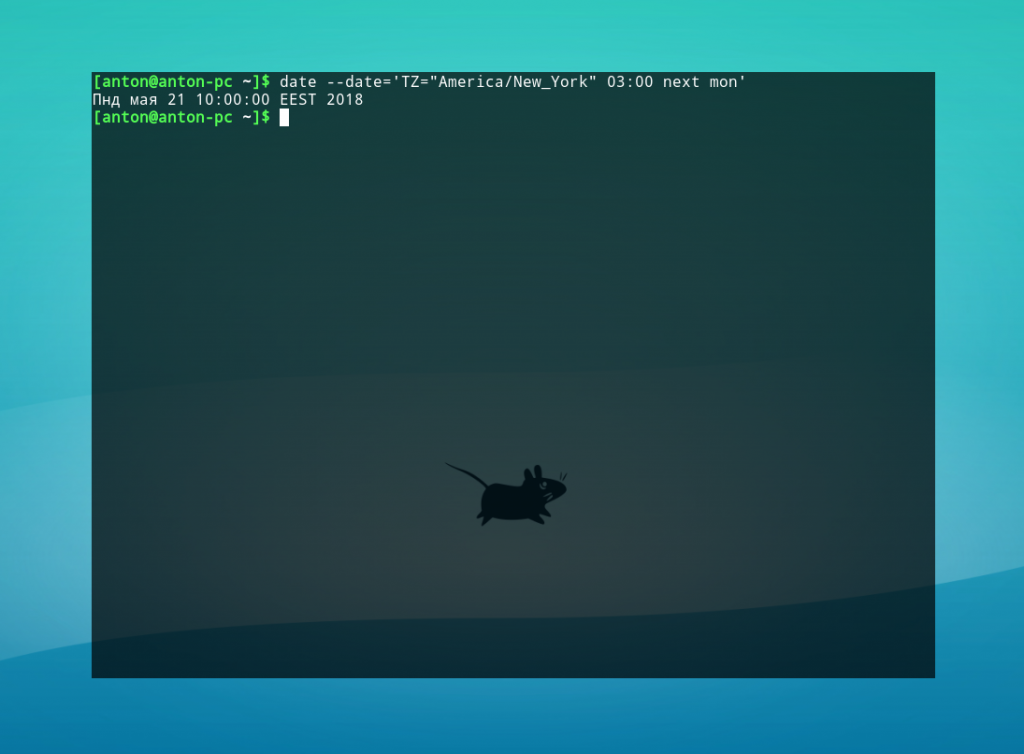
Пример 2. Вычисление даты и времени следующего понедельника при указании часового пояса Нью-Йорка в 03:00.
date —date=’TZ=»America/New_York» 03:00 next mon’
Обратите внимание: указывать название дня недели или месяца можно в любом регистре, в короткой или длинной форме. Параметры next и last обозначают следующий и прошедший, соответственно, ближайшие дни недели.
Пример 3. Если текущий день месяца — последний, сформировать отчет о занятости дискового пространства корневого и домашнего каталога в файл report.
#!/bin/bash
if [[ $(date —date=’next day’ +%d) = ’01’ ]]; then
df -h / /home > report
Такой скрипт можно использовать для автоматизации работы с помощью демона crontab или anacron.
Выводы
Команда date Linux является эффективным инструментом работы с датой и временем, с широкой возможностью их расчёта для прошедших или будущих показателей. Также она применяется в написании сценариев в командном интерпретаторе Bash.
Источник