- Как удалить каталог Linux
- Как удалить каталог Linux
- Выводы
- Linux Delete All Files In Directory Using Command Line
- Linux Delete All Files In Directory
- How to remove all the files in a directory?
- Understanding rm command option that deleted all files in a directory
- Deleting hidden vs non-hidden files
- Bash remove all files from a directory including hidden files using the dotglob option
- Linux Remove All Files In Directory
- Conclusion
- Delete / Remove a Directory Linux Command
- Commands to remove a directory in Linux
- rmdir command syntax to delete directory in Linux
- Delete directory Linux Command
- How to see a diagnostic message for every directory processed
- Removing directories with rmdir and wildcards
- Linux remove entire directory including all files and sub-directories command
- Are you getting permission denied error message while removing directories?
- Use find command to delete unwanted directories
- How to find and remove all empty directories
- Conclusion
- How to remove files and directories quickly via terminal (bash shell) [closed]
- 4 Answers 4
Как удалить каталог Linux
В операционной системе Linux можно выполнить большинство действий через терминал. Удаление каталога Linux — это достаточно простое действие, которое можно выполнить просто открыв файловый менеджер.
Однако в терминале это делается немного быстрее и вы получаете полный контроль над ситуацией. Например, можете выбрать только пустые папки или удалить несколько папок с одним названием. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как удалить каталог Linux через терминал.
Как удалить каталог Linux
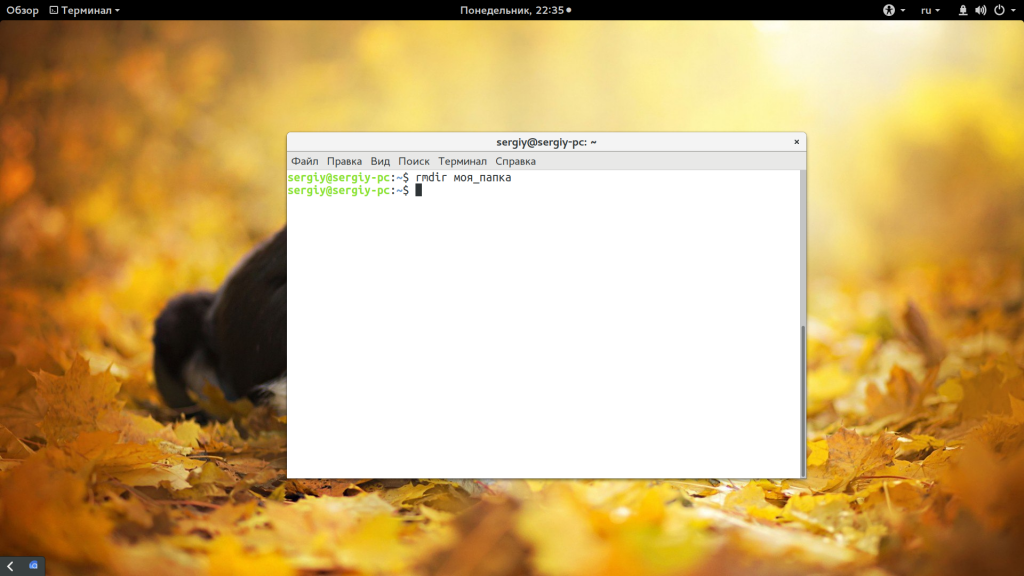
Существует несколько команд, которые вы можете использовать для удаления каталога Linux. Рассмотрим их все более подробно. Самый очевидный вариант — это утилита rmdir. Но с помощью нее можно удалять только пустые папки:
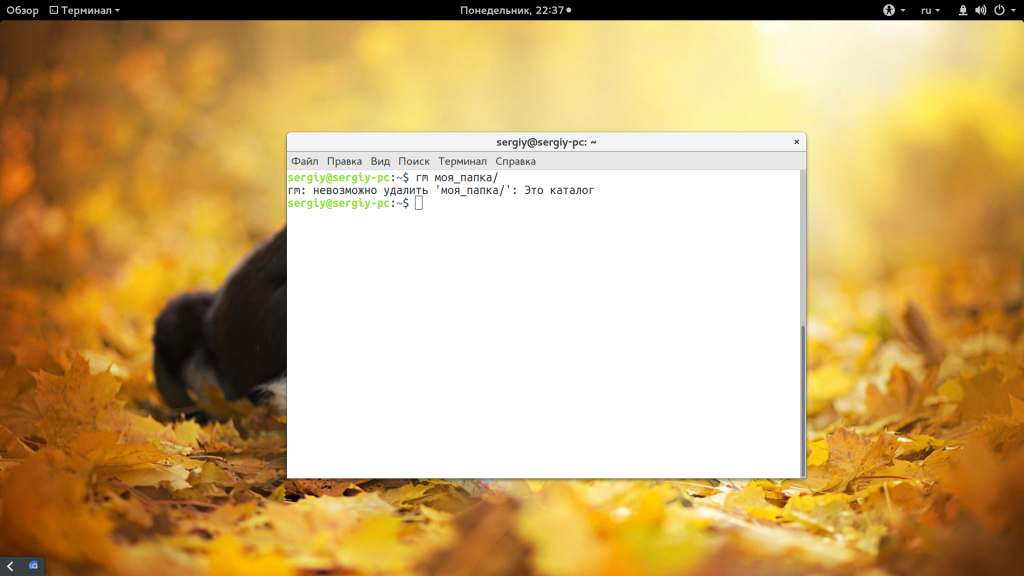
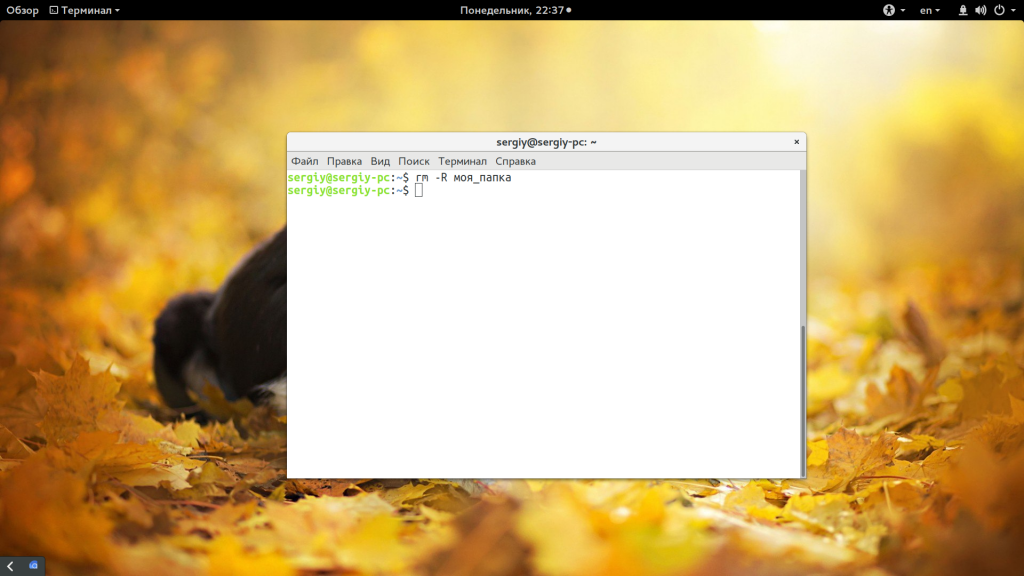
Другая команда, которую можно применить — это rm. Она предназначена для удаления файлов Linux, но может использоваться и для папок если ей передать опцию рекурсивного удаления -r:
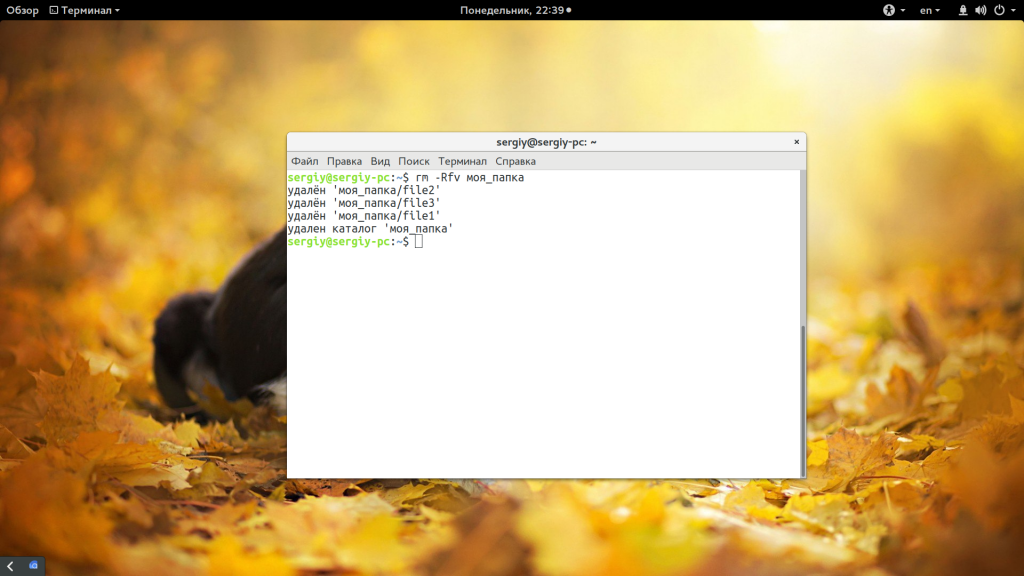
Такая команда уже позволяет удалить непустой каталог Linux. Но, можно по-другому, например, если вы хотите вывести информацию о файлах, которые удаляются:
rm -Rfv моя_папка
Команда -R включает рекурсивное удаление всех подпапок и файлов в них, -f — разрешает не удалять файлы без запроса, а -v показывает имена удаляемых файлов. В этих примерах я предполагаю что папка которую нужно удалить находится в текущей рабочей папке, например, домашней. Но это необязательно, вы можете указать полный путь к ней начиная от корня файловой системы:
rm -Rfv /var/www/public_html
Читайте подробнее про пути в файловой системе в статье путь к файлу Linux. Теперь вы знаете как удалить непустой каталог в консоли linux, далее усложним задачу, будем удалять папки, которые содержат определенные слова в своем имени:
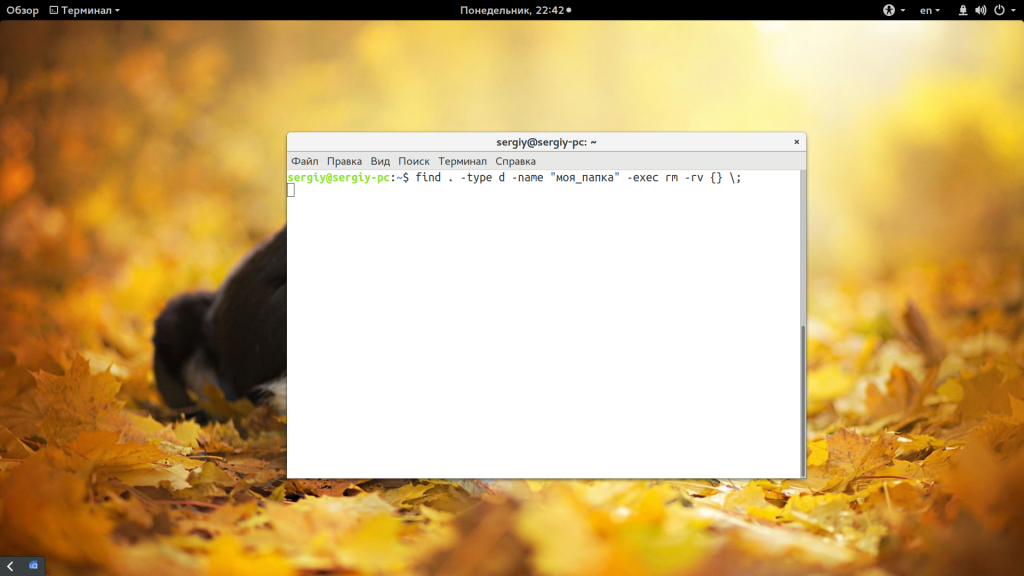
find . -type d -name «моя_папка» -exec rm -rf <> \;
Подробнее про команду find смотрите в отдельной статье. Если кратко, то -type d указывает, что мы ищем только папки, а параметром -name задаем имя нужных папок. Затем с помощью параметра -exec мы выполняем команду удаления. Таким же образом можно удалить только пустые папки, например, в домашней папке:
/ -empty -type d -delete
Как видите, в find необязательно выполнять отдельную команду, утилита тоже умеет удалять. Вместо домашней папки, можно указать любой нужный вам путь:
find /var/www/public_html/ -empty -type d -delete
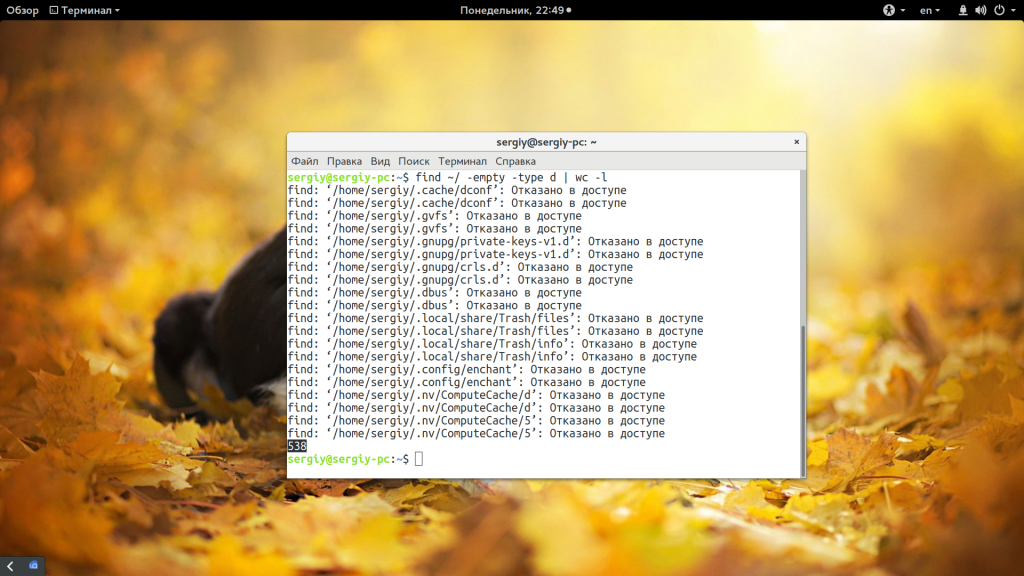
Перед удалением вы можете подсчитать количество пустых папок:
find /var/www/public_html/ -empty -type d | wc -l
Другой способ удалить папку linux с помощью find — использовать в дополнение утилиту xargs. Она позволяет подставить аргументы в нужное место. Например:
/ -type f -empty -print0 | xargs -0 -I <> /bin/rm «<>«
Опция -print0 выводит полный путь к найденному файлу в стандартный вывод, а затем мы передаем его команде xargs. Опция -0 указывает, что нужно считать символом завершения строки \0, а -I — что нужно использовать команду из стандартного ввода.
Если вы хотите полностью удалить папку Linux, так, чтобы ее невозможно было восстановить, то можно использовать утилиту wipe. Она не поставляется по умолчанию, но вы можете ее достаточно просто установить:
sudo apt install wipe
Теперь для удаления каталога Linux используйте такую команду:
Опция -r указывает, что нужно удалять рекурсивно все под папки, -f — включает автоматическое удаление, без запроса пользователя, а -i показывает прогресс удаления. Так вы можете удалить все файлы в папке linux без возможности их восстановления поскольку все место на диске где они были будет несколько раз затерто.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как удалить каталог linux, а также как удалить все файлы в папке linux без возможности их будущего восстановления. Как видите, это очень просто, достаточно набрать несколько команд в терминале. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Источник
Linux Delete All Files In Directory Using Command Line
Linux Delete All Files In Directory
The procedure to remove all files from a directory:
- Open the terminal application
- To delete everything in a directory run: rm /path/to/dir/*
- To remove all sub-directories and files: rm -r /path/to/dir/*
Let us see some examples of rm command to delete all files in a directory when using Linux operating systems.
How to remove all the files in a directory?
Suppose you have a directory called /home/vivek/data/. To list files type the ls command:
$ ls
Understanding rm command option that deleted all files in a directory
- -r : Remove directories and their contents recursively.
- -f : Force option. In other words, ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt. Dangerous option. Be careful.
- -v : Verbose option. Show what rm is doing on screen.
Deleting hidden vs non-hidden files
In Linux, any file or directory that starts with a dot character called a dot file. It is to be treated as hidden file. To see hidden files pass the -a to the ls command:
ls
ls -a
ls -la
To remove all files except hidden files in a directory use:
rm /path/to/dir/*
rm -rf /path/to/dir/*
rm *
In this example, delete all files including hidden files, run:
rm -rf /path/to/dir1/<*,.*>
rm -rfv /path/to/dir1/
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Bash remove all files from a directory including hidden files using the dotglob option
If the dotglob option set, bash includes filenames beginning with a ‘.’ in the results of pathname expansion. In other words, turn on this option to delete hidden files:
See GNU/bash man page for the shopt command online here:
man bash
help shopt
Linux Remove All Files In Directory
As I said earlier one can use the unlink command too. The syntax is:
unlink filename
For example, delete file named foo.txt in the current working directory, enter:
unlink foo.txt
It can only delete a single file at a time. You can not pass multiple files or use wildcards such as *. Therefore, I strongly recommend you use the rm command as discussed above.
Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, you learned how to remove or delete all the files in a directory using the rm command. Linux offers a few more options to find and delete files. Please see the following tutorials:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Delete / Remove a Directory Linux Command
Commands to remove a directory in Linux
There are two command to delete a folder in Linux:
- rmdir command – Deletes the specified empty directories and folders in Linux.
- rm command – Delete the file including sub-directories. You can delete non-empty directories with rm command in Linux.
Let us see some examples and usage in details delete the directories.
rmdir command syntax to delete directory in Linux
The rmdir command remove the DIRECTORY(ies), if they are empty. The syntax is:
rmdir directory-name
rmdir [option] directory-name
Open the terminal application and run command to delete given directory. For example, delete a folder named dir1:
rmdir dir1
Delete directory Linux Command
Open a command line terminal (select Applications > Accessories > Terminal), and then type the following command to remove a directory called /tmp/docs:
rmdir /tmp/docs
If a directory is not empty you will get an error message that read as follows:
rmdir letters
Sample outputs:
You can cd to the directory to find out and list all files:
$ cd letters
$ ls
Delete those files or directories. In this next example, remove data, foo and bar if bar were empty, foo only contained bar and data only contained foo directories:
cd /home/nixcraft
rmdir -p data/foo/bar
Where,
- -p : Each directory argument is treated as a pathname of which all components will be removed, if they are empty, starting with the last most component.
How to see a diagnostic message for every directory processed
Pass the -v option to the rmdir command:
$ rmdir -v dir1
Sample outputs:
Removing directories with rmdir and wildcards
We can use wildcards such as ‘*’ and ‘?’ to match and delete multiple directories. For example:
$ ls -l dir*
We have three dirs named dir1, dir2, and dir3. To delete all directories starting with ‘dir’ in the current, you would use the following command:
rmdir -v dir*
Linux remove entire directory including all files and sub-directories command
To remove all directories and subdirectories use the rm command. For example, remove *.doc files and all sub-directories and files inside letters directory, type the following command:
Warning : All files including subdirectories will be deleted permanently when executed the following commands.
$ rm -rf letters/
Sample session:
Where,
- -r : Attempt to remove the file hierarchy rooted in each file argument i.e. recursively remove subdirectories and files from the specified directory.
- -f : Attempt to remove the files without prompting for confirmation, regardless of the file’s permissions
Are you getting permission denied error message while removing directories?
Only owners can delete their directories. However, a sysadmin can delete any directories created by anyone on the system. The syntax is:
sudo rmdir /path/to/dir/
sudo rm -rf dir2
When prompted, you need to provide root user or sudo user password.
Use find command to delete unwanted directories
Say you want to find out all directories named ‘session’ and delete them in the current directory, run:
find . -type d -iname ‘session’ -delete
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How to find and remove all empty directories
Run:
find . -type d -iname ‘session’ -empty -delete
Where,
- -type d : Only search for directories and ignore all other files.
- -iname ‘session’ : Search directory named ‘session’. You can use wildcards here too. For example, -iname ‘dir*’ .
- -empty : Only match empty directories
- -delete : Deletes all found empty directories only
To delete all ‘.DS_store’ directories stored in /var/www/html, run:
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type d -name .DS_Store -exec rm <> \;
OR
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type d -name .DS_Store -exec rm <> +
The -exec option to the find command run an external command named rm to delete all files. The “ rm <> +/ ” is a better option as it uses one rm command to delete all .DS_Store directories.
Conclusion
This page showed how to delete a directory when it is empty. Further, it showed, how to remove folders using the rm and rmdir commands. See rm help page page for more info:
- For more information read man pages: rm(1)
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to remove files and directories quickly via terminal (bash shell) [closed]
Want to improve this question? Update the question so it’s on-topic for Stack Overflow.
Closed 6 years ago .
From terminal window:
When I use the rm command it can only remove files.
When I use the rmdir command it only removes empty folders.
If I have a directory nested with files and folders within folders with files and so on, is there any way to delete all the files and folders without all the strenuous command typing?
If it makes a difference, I am using the mac bash shell from terminal, not Microsoft DOS or linux.
4 Answers 4
-r «recursive» -f «force» (suppress confirmation messages)
Would remove everything (folders & files) in the current directory.
But be careful! Only execute this command if you are absolutely sure, that you are in the right directory.
Yes, there is. The -r option tells rm to be recursive, and remove the entire file hierarchy rooted at its arguments; in other words, if given a directory, it will remove all of its contents and then perform what is effectively an rmdir .
The other two options you should know are -i and -f . -i stands for interactive; it makes rm prompt you before deleting each and every file. -f stands for force; it goes ahead and deletes everything without asking. -i is safer, but -f is faster; only use it if you’re absolutely sure you’re deleting the right thing. You can specify these with -r or not; it’s an independent setting.
And as usual, you can combine switches: rm -r -i is just rm -ri , and rm -r -f is rm -rf .
Also note that what you’re learning applies to bash on every Unix OS: OS X, Linux, FreeBSD, etc. In fact, rm ‘s syntax is the same in pretty much every shell on every Unix OS. OS X, under the hood, is really a BSD Unix system.
Источник