- Linux List All Environment Variables Command
- Linux list all environment variables command
- A list of the commonly used variables in Linux
- set and env command
- A note about env/set command
- Conclusion
- How to use Variables in Bash Programming
- Using variable from command line or terminal
- Example-1: Declaring and reading string data using variable
- Example-2: Combining two string variables
- Example-3: Concatenating strings with variables
- Example-4: Declaring and reading numeric data using variables
- Example-5: Doing arithmetic operation using bc command
- Using variables in bash file
- Example-6: Creating simple bash script
- Example-7: Using global and local variables
- Example-8: Using array variable
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
Linux List All Environment Variables Command
- printenv command – Print all or part of environment.
- env command – Display all exported environment or run a program in a modified environment.
- set command – List the name and value of each shell variable.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux or Unix |
| Est. reading time | 4 mintues |
Linux list all environment variables command
I recommend that you use the printenv command. The syntax is:
Fig.01: Command to see a list of all currently defined environment variables in a Linux bash terminal
A list of the commonly used variables in Linux
We use the printf command/echo command to display values of the shell varible in Linux.
| System Variable | Meaning | To view variable value type |
|---|---|---|
| BASH_VERSION | Holds the version of this instance of bash. | echo $BASH_VERSION |
| HOSTNAME | The name of the your computer. | echo $HOSTNAME |
| CDPATH | The search path for the cd command. | echo $CDPATH |
| HISTFILE | The name of the file in which command history is saved. | echo $HISTFILE |
| HISTFILESIZE | The maximum number of lines contained in the history file. | echo $HISTFILESIZE |
| HISTSIZE | The number of commands to remember in the command history. The default value is 500. | echo $HISTSIZE |
| HOME | The home directory of the current user. | echo $HOME |
| IFS | The Internal Field Separator that is used for word splitting after expansion and to split lines into words with the read builtin command. The default value is . | echo $IFS |
| LANG | Used to determine the locale category for any category not specifically selected with a variable starting with LC_. | echo $LANG |
| PATH | The search path for commands. It is a colon-separated list of directories in which the shell looks for commands. | echo $PATH |
| PS1 | Your prompt settings. | echo $PS1 |
| TMOUT | The default timeout for the read builtin command. Also in an interactive shell, the value is interpreted as the number of seconds to wait for input after issuing the command. If not input provided it will logou user. | echo $TMOUT |
| TERM | Your login terminal type. | echo $TERM export TERM=vt100 |
| SHELL | Set path to login shell. | echo $SHELL |
| DISPLAY | Set X display name | echo $DISPLAY export DISPLAY=:0.1 |
| EDITOR | Set name of default text editor. | export EDITOR=/usr/bin/vim |
set and env command
You can use the env / set command too:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
A note about env/set command
The env will only display a list of environment variables that have been exported and it will not show all bash variables. The set command allows you to change the values of shell options and set the positional parameters, or to display the names and values of shell variables. If no options or arguments are supplied, set displays the names and values of all shell variables and functions, sorted according to the current locale, in a format that may be reused as input for setting or resetting the currently-set variables. Hence, I recommend that you use printenv command to dump the list of all shell variables on screen. To save the list of all shell environment variables to a file, enter:
Use the grep command to search for particular variable:
Conclusion
You learned about listing all Linux shell environment variables. See the following resources for more information:
- Bash shell variables from the Linux shell scripting wiki.
- See the following man pages using the man command or help command:
man ‘printenv(1)’
man 1 bash
man 1 env
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Thank you aref ghobadi Aug 18, 2015 @ 8:33
Thank you for this useful information.
Thank you.It’s really helpful.
Thank you. This is a very informative.
Note that set will show all unexported shell variables (e.g. like PS1 , TMOUT ) whereas env or printenv will not.
Thanks for the input 🙂
With environment variables, what’s the maximum amount of characters a environment variable can have?
and is it possible to set this higher?
The theoretical max length of an environment variable is around 32,760 characters. The maximum size of an environment variable value depends upon execve(). Try:
false | xargs —show-limits
Which gives out:
On my box it went up to 512MiB and failed with the following message (see image here)[1]:
Источник
How to use Variables in Bash Programming
Using variable from command line or terminal
You don’t have to use any special character before the variable name at the time of setting value in BASH like other programming languages. But you have to use ‘$’ symbol before the variable name when you want to read data from the variable. You can set and get data from a variable from the terminal in the following way.
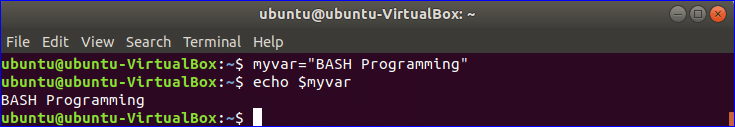
Example-1: Declaring and reading string data using variable
Run the following commands from the terminal.
Output:
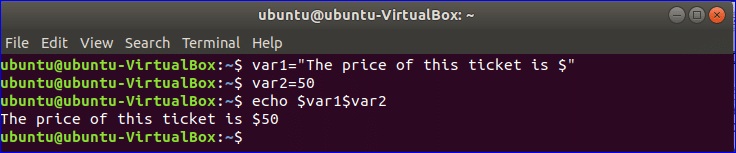
Example-2: Combining two string variables
You don’t have to use any operator to combine two or more strings like other languages. Here, $var1 is used to store string value and $var2 is used to store a numeric value. Run the following commands from the terminal to combine two variables $var1 and $var2.
Output:
**Note: You can print the value of the variable without any quotation but if you use quotations then you have to use double quotations.
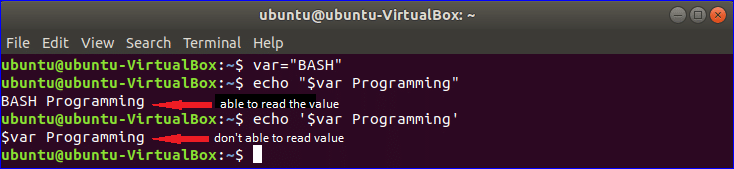
Example-3: Concatenating strings with variables
Double quotation can be used to read the value of the variable. In this example, single quotation is used on one echo statement and double quotation is used on another echo statement. Run the following commands from the terminal to check the output.
Output:
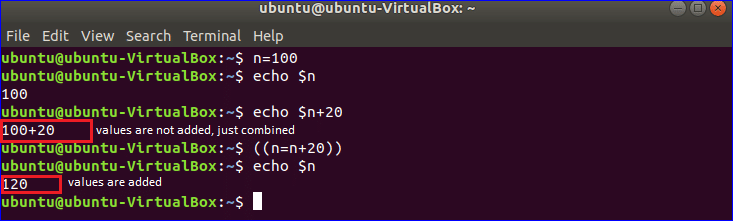
Example-4: Declaring and reading numeric data using variables
One of the major limitations of Bash programming is that it can’t perform arithmetic operations like other programming languages. Numeric values are taken as strings in BASH. So no arithmetic operation can be done by normal expression and it just combines the numeric values. If you write the expression with double first bracket then the arithmetic operation works properly. Run the following commands from the terminal.
Output:
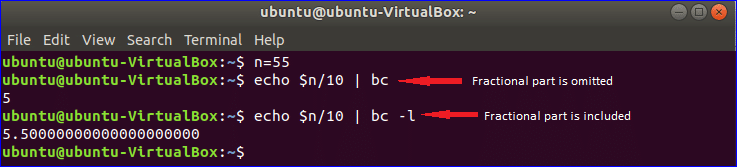
Example-5: Doing arithmetic operation using bc command
bc command is another way to do arithmetic operation in BASH. Run the following commands from the terminal. When you use bc command only for doing any arithmetic operation then fractional parts are omitted from the result. You have to use -l option with bc command to get the result with fractional value.
Output:
Using variables in bash file
You can define variable in bash file by the same way which are mentioned in above examples. You have to create file with .sh or .bash extension to run bash script.
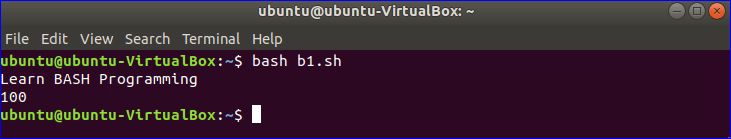
Example-6: Creating simple bash script
Copy the following code in a text editor and save the file with bash extension. In this script, one string and one numeric variables are declared.
str = «Learn BASH Programming»
#print string value
echo $str
#subtract 20 from numeric variable
( ( result = $num — 20 ) )
#print numeric value
echo $result
Output:
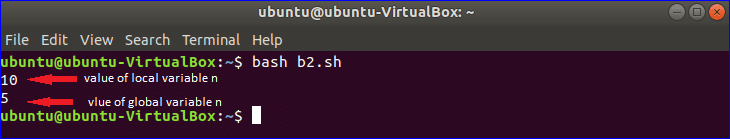
Example-7: Using global and local variables
In the following script, one global variable n and two local variables n and m are used.
When the function addition() is called then the value of the local variable n is taken for calculation but global variable n remains unchanged.
#!/bin/bash
n = 5
function addition ( )
<
local n = 6
local m = 4
( ( n =n+m ) )
echo $n
Output:
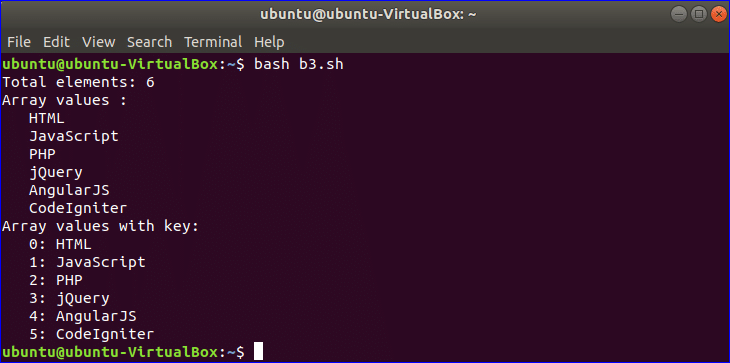
Example-8: Using array variable
Array variable is used to store a list of data. The following example shows how you use of array variable in bash script. The elements of any array are separated by space in BASH. Here, an array of 6 elements is declared. There is no built-in function or property to count the total elements of the array. # with * is used to count total elements. All elements are indicated by *. For loop is used here to iterate the array values. Reading array values and array values with key are shown in the next part of this script.
myarr = ( HTML JavaScript PHP jQuery AngularJS CodeIgniter )
#Count total number of elements of the array
total = $ <#myarr[*]>
echo «Total elements: $total «
#Print each element value of the array
echo «Array values :»
for val in $
do
printf » %s \n » $val
done
#Print each element value of the array with key
echo «Array values with key:»
for key in $
do
printf «%4d: %s \n » $key $
done
Output:
To use BASH variables properly you need a clear concept on the declaration and use of variables. This tutorial will help you to get a clear idea on BASH variables. After exercising the above examples properly you will be able to use variables more efficiently in your bash scripts.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.
Источник