- Увеличение системного кэша в Windows 10
- Как увеличить кэш
- Настройка автоочистки кэша
- Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
- Memory and Address Space Limits
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Vista
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home Server
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Embedded
- How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits
Увеличение системного кэша в Windows 10
Как увеличить кэш
Процесс увеличения места под кэш ОС Windows 10 происходит посредством изменения определенных параметров в системном реестре.
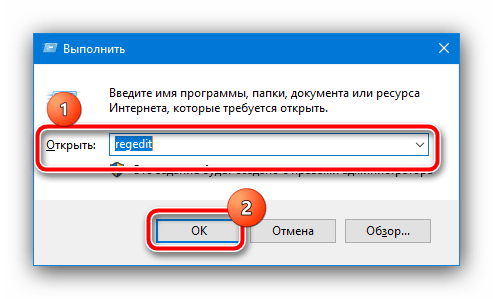
- Вызовите окно «Выполнить» сочетанием клавиш Win+R, затем введите в нем запрос regedit и нажмите «ОК».
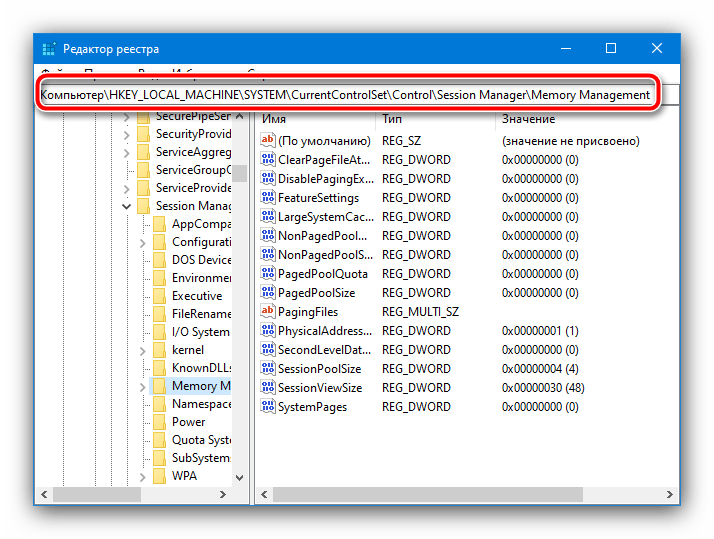
После запуска оснастки перейдите по следующему пути:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management
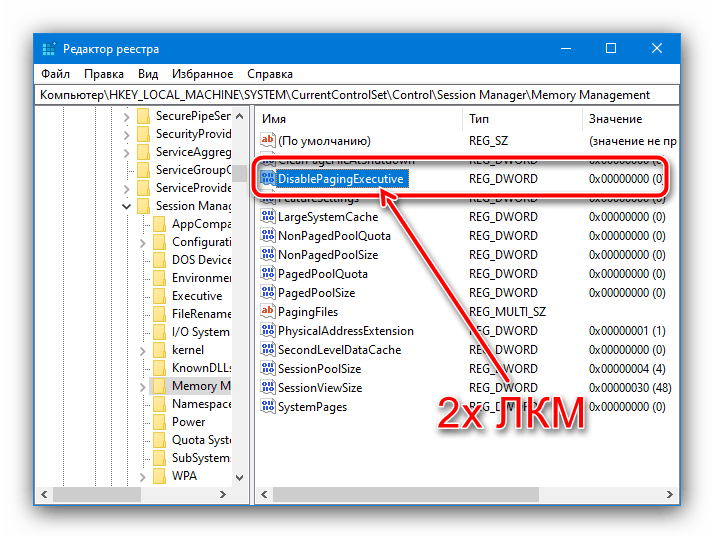
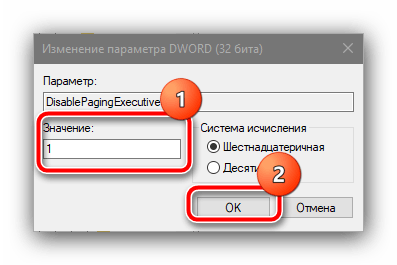
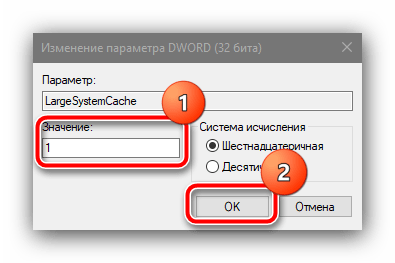
Установите значение 1, затем нажмите «ОК».
Повторите действия предыдущего шага, но уже для пункта «LargeSystemCache».
Теперь системный кэш будет использовать куда большие значения памяти.
Настройка автоочистки кэша
В некоторых ситуациях увеличение системного кэша не приносит желаемого результата, а производительность компьютера даже ухудшается. Для решения этой проблемы стоит настроить автоматическую очистку сохранённых данных, в чём нам поможет оснастка «Планировщик заданий».
- По ссылке выше находится утилита очистки кэша – загрузите её в любое подходящее место.
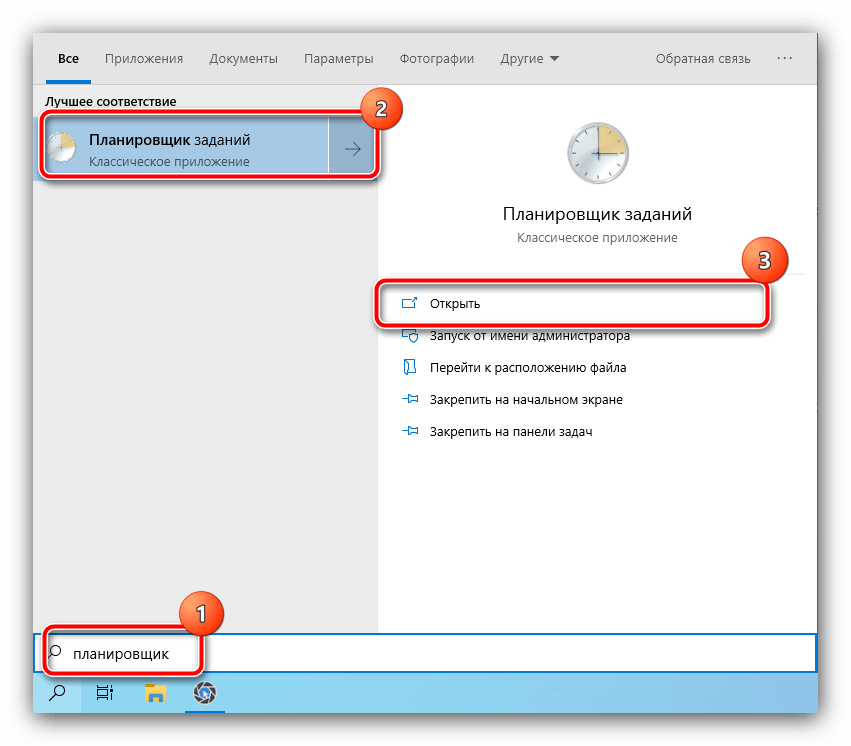
- Теперь вызовите «Поиск», где введите запрос планировщик и воспользуйтесь соответствующим результатом.
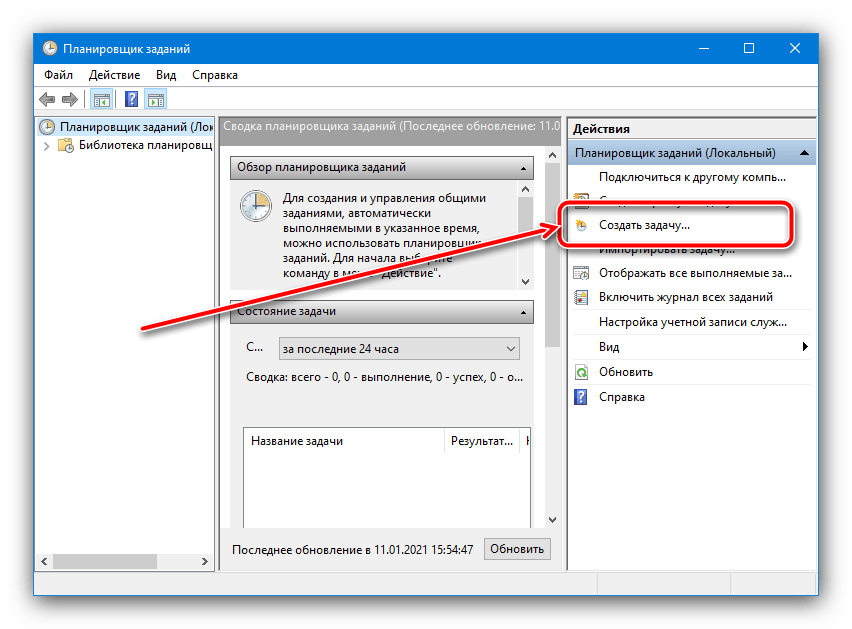
После запуска оснастки выберите действие «Создать задачу».
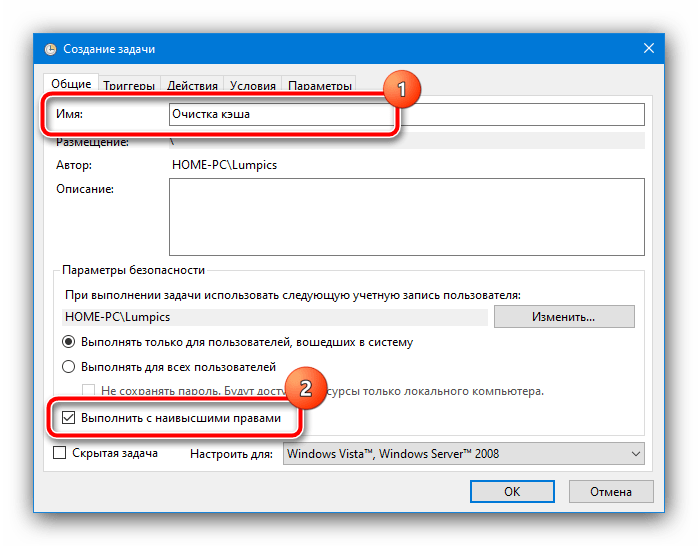
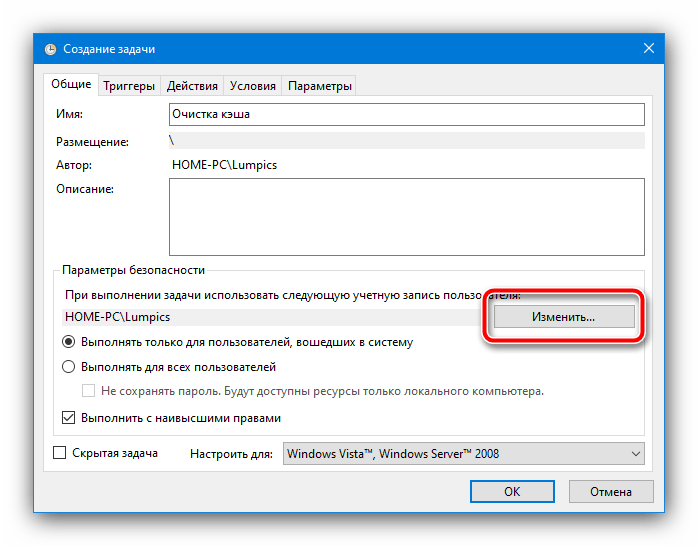
Теперь надо настроить учётную запись, от имени которой и будет выполняться задача. Кликните «Изменить»,
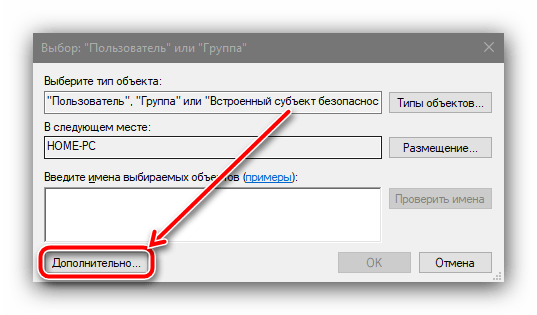
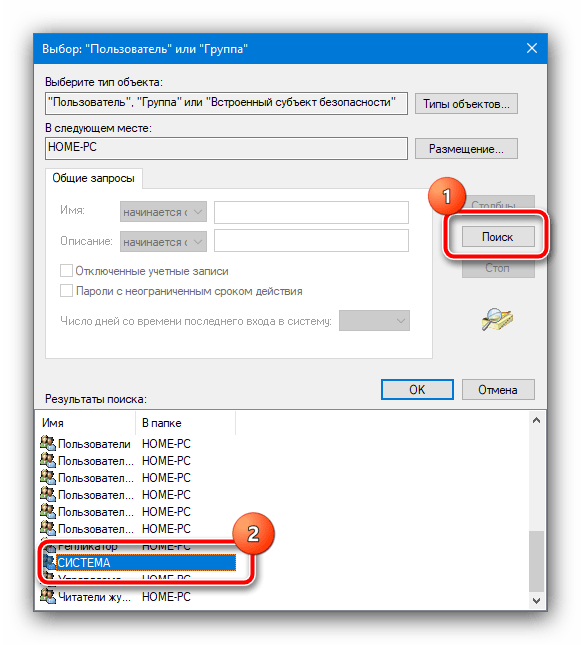
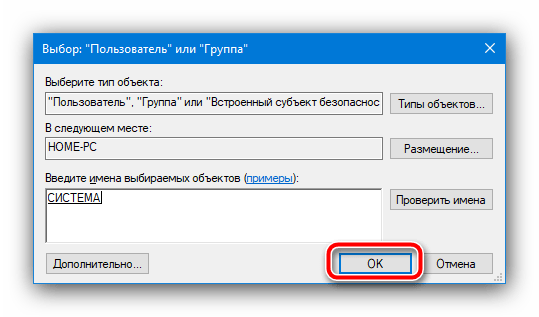
В этом окне воспользуйтесь кнопкой «Поиск», найдите в перечне ниже и выберите позицию, которая обозначена как «Система».
Нажимайте «ОК» во всех запущенных средствах, кроме «Планировщика заданий».
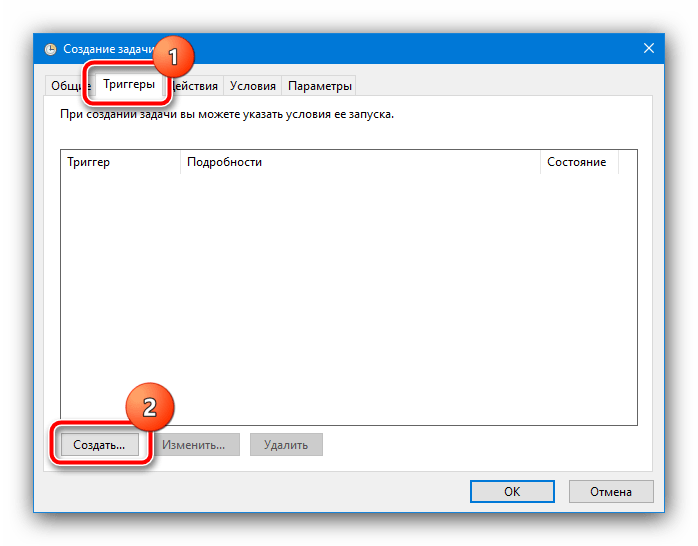
По возвращении в утилиту создания задач перейдите на вкладку «Триггеры» и кликните «Создать».
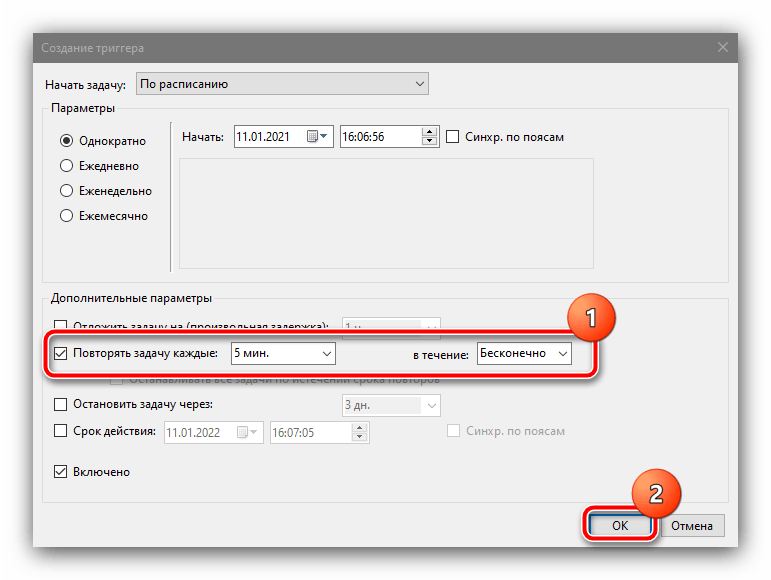
Здесь отметьте опцию «Повторять задачу каждые» и выберите интервал «5 минут», а в выпадающем меню «в течении» – пункт «Бесконечно» и нажмите «ОК».
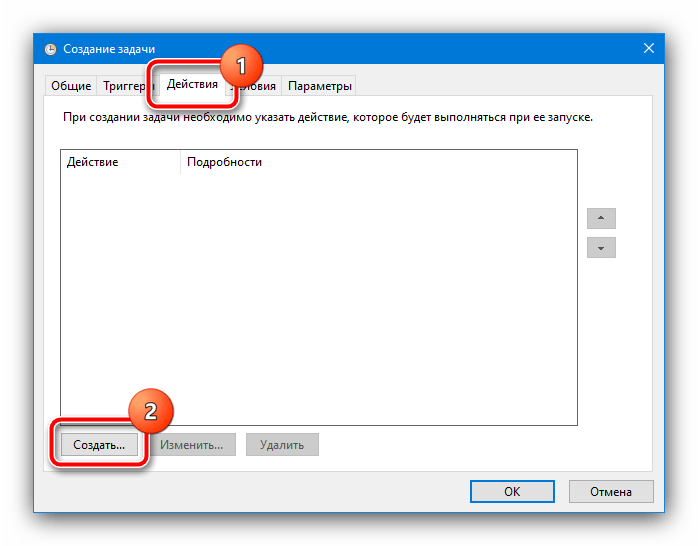
Перейдите на вкладку «Действия» и воспользуйтесь кнопкой «Создать».
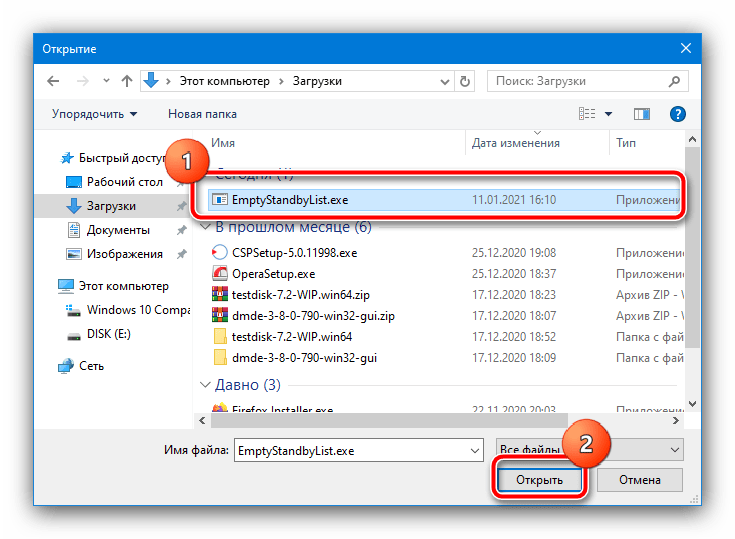
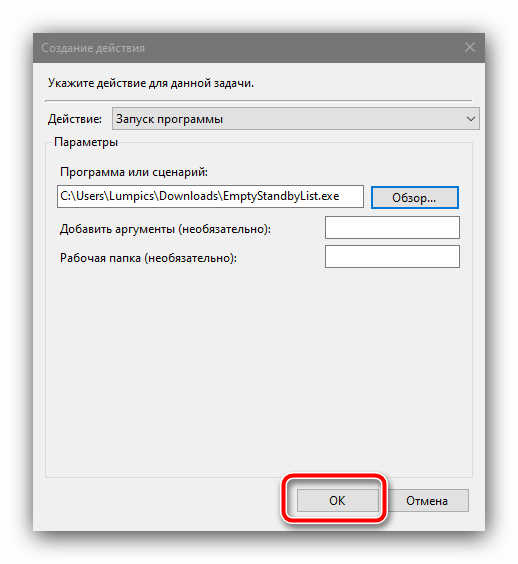
Здесь убедитесь, что в поле «Действия» установлено «Запуск программы», после чего воспользуйтесь кнопкой «Обзор» и с помощью «Проводника» выберите файл, полученный на шаге 1.
Нажмите «ОК» во всех открытых окнах и закрывайте «Планировщик задач».
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases.
Limits on memory and address space vary by platform, operating system, and by whether the IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE value of the LOADED_IMAGE structure and 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT) are in use. IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE is set or cleared by using the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE linker option.
4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications. Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT.
Limits on physical memory for 32-bit platforms also depend on the Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows 32-bit Windows systems to use more than 4 GB of physical memory.
Memory and Address Space Limits
The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Unless otherwise noted, the limits in this table apply to all supported releases.
| Memory type | Limit on X86 | Limit in 64-bit Windows | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User-mode virtual address space for each 32-bit process | 2 GB Up to 3 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and 4GT | 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared (default) 4 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| User-mode virtual address space for each 64-bit process | Not applicable | With IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set (default): x64: WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB x64: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB Intel Itanium-based systems: 7 TB 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kernel-mode virtual address space | 2 GB From 1 GB to a maximum of 2 GB with 4GT | WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paged pool | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with Service PackВ 1 (SP1), the paged pool can also be limited by the PagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server and Windows ServerВ 2003: 530 MB WindowsВ XP: 490 MB | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: 128 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonpaged pool | 75% of RAM or 2 GB, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space and physical memory. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, the nonpaged pool can also be limited by the NonPagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 256 MB, or 128 MB with 4GT. | RAM or 128 GB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM) WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7 and Windows ServerВ 2008: 75% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB WindowsВ Vista: 40% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System cache virtual address space (physical size limited only by physical memory) | Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space or the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, system cache virtual address space can also be limited by the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 860 MB with LargeSystemCache registry key set and without 4GT; up to 448 MB with 4GT. | Always 1 TB regardless of physical RAM WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 1 TB depending on configuration and RAM. Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 10.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2016.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 8.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2012. Windows ServerВ 2012 is available only in X64 editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 7.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 is available only in 64-bit editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008. Limits greater than 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows VistaThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ Vista.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home ServerWindows Home Server is available only in a 32-bit edition. The physical memory limit is 4 GB. Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003В R2. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 2 (SP2). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 1 (SP1). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows XPThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ XP.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows EmbeddedThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Embedded.
How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limitsDevices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions. Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can. X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the «lost» memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk. |