- Настройка IPv6 в ОС Linux Debian v7.XX, Ubuntu v14.XX, CentOS v6.XX и FreeBSD v10.XX
- Linux Debian v7.XX, Ubuntu v14.XX
- CentOS v6.XX
- FreeBSD v10.XX
- Настройка маршрутизатора IPv6 на Linux
- Configuring the IPv6 default route
- Syntax
- Solved How to set IPv6 Gateway
- mahescho
- gkontos
- mahescho
- SirDice
- mahescho
- SirDice
- mahescho
- SirDice
- Red Hat Customer Portal
- Log in to Your Red Hat Account
- Red Hat Account
- Customer Portal
- Select Your Language
- Red Hat Training
- Chapter 20. Managing the default gateway setting
- 20.1. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using nmcli
- 20.2. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using the nmcli interactive mode
- 20.3. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using nm-connection-editor
- 20.4. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using control-center
- 20.5. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using nmstatectl
- 20.6. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using System Roles
- 20.7. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection when using the legacy network scripts
- 20.8. How NetworkManager manages multiple default gateways
- 20.9. Configuring NetworkManager to avoid using a specific profile to provide a default gateway
- 20.10. Fixing unexpected routing behavior due to multiple default gateways
Настройка IPv6 в ОС Linux Debian v7.XX, Ubuntu v14.XX, CentOS v6.XX и FreeBSD v10.XX

Linux Debian v7.XX, Ubuntu v14.XX
CentOS v6.XX
FreeBSD v10.XX
После внедрения поддержки IPv6, на хостинговой площадке компании в которой я работаю, у нас возникла необходимость автоматизировать настройку VDS соответствующим образом. Необходимо оговорится, что речь идет не о каком-либо туннелировании, а полноценной поддержке. Т.е. сетевая инфраструктура в дата-центре обеспечивает коммутацию и маршрутизацию IPv6, имеются соответствующие стыки по BGPv6 с магистральными провайдерами Internet.
Адреса назначаются и прописываются в настройках ОС статично, т.е. функционал автоматического конфигурирования IPv6 не задействуется. Это связано с особенностями учета адресного пространства и обеспечения безопасности. Задача осложняется тем, что адресов IPv4 и IPv6 у VDS может быть сразу несколько.
Linux Debian v7.XX, Ubuntu v14.XX
В достаточно свежих дистрибутивах ОС Linux уже присутствует полноценная поддержка IPv6. Поэтому доустанавливать что-либо вручную необходимости нет.
Рассмотрим пример настройки.
«/etc/network/interfaces»
Тут следует обратить внимание на два момента. Во-первых, все адреса IPv6 назначаются непосредственно на сам сетевой интерфейс: в отличие от IPv4 нет необходимости создавать виртуальные адаптеры типа «eth0:X». Во-вторых, шлюз по умолчанию для IPv6 указывается один раз для любого из адресов. Действовать он будет для всех.
Результат настроек в выводе команды «ifconfig»:
Базовую диагностику можно выполнить с помощью команд «ping6 -n -c 4 ipv6.google.com» и «traceroute -n -6 -I ipv6.google.com». Проверить MAC-адреса соседей: «ip -6 neighbor show». Изучить таблицу маршрутизации: «route -n6» или «ip -6 route show». Выяснить, какой из адресов IPv6 используется системой по умолчанию для исходящих подключений: «ip -6 route get 2a00:1450:4013:c01::65».
CentOS v6.XX
Настройка CentOS замысловатее из-за того, что опций несколько больше, и они раскиданы по нескольким файлам.
«/etc/sysconfig/network»
В целом картина аналогична Debian. Виртуальные сетевые интерфейсы «eth0:X» необходимы только для IPv4. Опции «NETWORKING_IPV6» и «IPV6INIT» включают поддержку IPv6. В «IPV6_DEFAULTGW» указываем шлюз по умолчанию. Первый адрес IPv6 назначается в «IPV6ADDR», все остальные перечисляются в «IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIES».
Вывод команды «ifconfig» аналогичен Debian:
FreeBSD v10.XX
В ОС FreeBSD уже также есть все необходимое для поддержки IPv6.
Рассмотрим пример настройки.
» /etc/rc.conf»
Основной адрес IPv6 указывается в опции «ifconfig_xn0_ipv6». Поскольку в FreeBSD механизм виртуальных сетевых интерфейсов для IPv4 не используется, то все дополнительные адреса, в том числе IPv6, перечисляются в «ifconfig_xn0_aliases».
Вывод команды «ifconfig» немного отличается от ОС Linux.
Инструмент для диагностики также немного другой: «ping6 -n -c 4 ipv6.google.com» и «traceroute6 -n ipv6.google.com». Проверить MAC-адреса соседей: «ndp -an». Изучить таблицу маршрутизации: «netstat -rn6». Выяснить, какой из адресов IPv6 используется системой по умолчанию для исходящих подключений: «route -nv6 get 2a00:1450:4013:c01::65».
В данном случае адресом по умолчанию является тот, что указан самым последним в выводе команды: «2a04:XXXX:1::12».
Источник
Настройка маршрутизатора IPv6 на Linux
В статье рассматривается пример настройки маршрутизатора для проброса IPv6 сети в локальную сеть и автонастройка клиентов.
Настройки должны подойти для любых linux-дистрибутивов, но могут отличаться нарпимер команды установки или названия пакетов. В статье примеры приведены для CentOS 6.5.
Исходное состояние:
- Есть аккаунт на tunnelbroker.net
- Чистый CentOS 6.5 с двумя интерфейсами: в локальную сеть и в публичный интернет с прямым (можно динамическим) IP-адресом.
Будет получено в итоге
Шлюз из локальной сети в IPv6-интернет, на котором разрешены исходящие подключения и запрещены входящие (чтобы кто попало в локальную сеть не ломился). Маршрутизатор анонсирует себя в локальной сети и клиенты автоматически настраиваются на сеть без состояния.
НЕ будет рассматриваться
Создание туннеля
- На tunnelbroker.net слева нажать ссылку «Create Regular Tunnel”
- Вписать текущий IP шлюзв в поле IPv4 Endpoint (Your side).
- С сервера, который будет шлюзом попинговать каждый предложенный IP из списка „Available Tunnel Servers” и выбрать сервер с минимальным пингом. Туннель привязывается к этому серверу и весь трафик будет идти через него. Поменять этот сервер потом можно будет только путем создания нового туннеля. Для целей статьи пусть это будет сервер 1.2.3.4. Нажать Create tunnel.
Подключение шлюза к туннелю
- Если на шлюзе настроен firewall — разрешить для выбранного сервера пинг-запросы и трафик по протоколу 41. Для простоты — можно разрешить весь трафик с сервера-шлюза.
При публикации некоторые кавычки поменялись с правильных на “красивые», так что как будет работать скрипт после копирования непонятно. Правильный вариант можно скачать тут.
Этот скрипт нужно запускать с параметрами up (включение шлюза) или down — выключение шлюза. Скрипт можно запускать много раз подряд. У меня он настроен для автозапуска после подключения к интернету в /etc/ppp/ip-up.local. После запуска этого скрипта IPv6-сеть появится на самом шлюзе, можно проверить попинговав сам брокера
Настройка маршрутизации трафика из/в локальную сеть
В этот момент если вручную настроить IPv6 на компьютерах локальной сети то он уже будет работать.
Автоматическая настройка клиентов
В этот момент IPv6 должен заработать в локальной сети для всех устройств которые поддерживают его автонастройку, можно проверять на сайте test-ipv6.com.
Источник
Configuring the IPv6 default route
The IPv6 default route (::/0) is a static route used for all traffic that has a destination network not reachable through any other IPv6 route in the routing table. For more information on static routes, see IPv6 static routing.
Syntax
ipv6 route ::/0 ipv6-gateway-addr distance 1 — 255
ipv6 route ::/0 ipv6-addr
Used in the global config context to configure the default route and gateway to use for traffic sent to the default route.
Specifies the default IPv6 route.
Specifies the next-hop router for traffic sent to the default route.
distance 1 — 255
Specifies the administrative distance to associate with a static route.
Default: 1; Range: 1 — 255
The no form of the command deletes the default route for the specified next-hop destination from the routing table.
Configuring the IPv6 default route
If 2001:db8:c::9f:35 is the IPv6 address of your ISP router, all non-local traffic could be directed to the ISP by configuring the following default route:
HP Switch(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:c::9f:35
To view the default route in the routing table, use show ipv6 route . See Viewing the IPv6 routing table.
Configuring the IPv6 hop limit
Viewing the IPv6 routing table
Copyright © 2015, 2016 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
Источник
Solved How to set IPv6 Gateway
mahescho
Member
Reaction score: 1
Messages: 25
on my Linux setup the IPv6 default gateway is set by
where xx:xx:xx::xx is the IPv6 address of the system itself.
Setting the gateway on FreeBSD by getting the FE80 addres by
is no option as it is a moving target at my hosters site.
How to set the default gateway?
gkontos
Daemon
Reaction score: 488
Messages: 2,160

Reactions: gutiersa
mahescho
Member
Reaction score: 1
Messages: 25
SirDice
Administrator
Reaction score: 12,211
Messages: 38,693
route -6 add default xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
mahescho
Member
Reaction score: 1
Messages: 25
Tried this bevor and right now again:
route -6 add default xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
route -6 add default xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx%vtnet0
does not work also.
SirDice
Administrator
Reaction score: 12,211
Messages: 38,693
mahescho
Member
Reaction score: 1
Messages: 25
I can set the route, no message, as usual when a command succeeded. Afterwards: No IPv6 connectivity. The only way I can get IPv6 connectivity is to check for the current router by ping6 ff02::2%vtnet0 and then set the default gateway I’ve found by route -6 add default xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx%vtnet0 where xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx is the FE80 address of the router determined by ping6 ff02::2%vtnet0 .
BTW: I think they do not use SLAAC or DHCPv6 as I get one /48 prefix for all my hosts and the hosts are located in different network segments so SLAAC or DHCPv6 can not work for one private prefix.
SirDice
Administrator
Reaction score: 12,211
Messages: 38,693
Источник
Red Hat Customer Portal
Log in to Your Red Hat Account
Your Red Hat account gives you access to your profile, preferences, and services, depending on your status.
If you are a new customer, register now for access to product evaluations and purchasing capabilities.
Need access to an account?
If your company has an existing Red Hat account, your organization administrator can grant you access.
Red Hat Account
Customer Portal
For your security, if you’re on a public computer and have finished using your Red Hat services, please be sure to log out.
Select Your Language
Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for RHEL 8
Chapter 20. Managing the default gateway setting
The default gateway is a router that forwards network packets when no other route matches the destination of a packet. In a local network, the default gateway is typically the host that is one hop closer to the internet.
20.1. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using nmcli
In most situations, administrators set the default gateway when they create a connection as explained in, for example, Configuring a static Ethernet connection using nmcli.
This section describes how to set or update the default gateway on a previously created connection using the nmcli utility.
Prerequisites
- At least one static IP address must be configured on the connection on which the default gateway will be set.
- If the user is logged in on a physical console, user permissions are sufficient. Otherwise, user must have root permissions.
Procedure
Set the IP address of the default gateway.
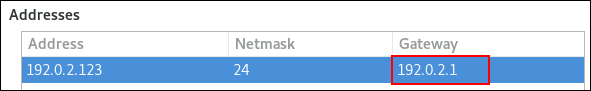
For example, to set the IPv4 address of the default gateway on the example connection to 192.0.2.1 :
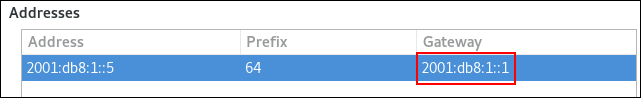
For example, to set the IPv6 address of the default gateway on the example connection to 2001:db8:1::1 :
Restart the network connection for changes to take effect. For example, to restart the example connection using the command line:
All connections currently using this network connection are temporarily interrupted during the restart.
Optionally, verify that the route is active.
To display the IPv4 default gateway:
To display the IPv6 default gateway:
Additional resources
20.2. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using the nmcli interactive mode
In most situations, administrators set the default gateway when they create a connection as explained in, for example, Configuring a dynamic Ethernet connection using the nmcli interactive editor.
This section describes how to set or update the default gateway on a previously created connection using the interactive mode of the nmcli utility.
Prerequisites
- At least one static IP address must be configured on the connection on which the default gateway will be set.
- If the user is logged in on a physical console, user permissions are sufficient. Otherwise, the user must have root permissions.
Procedure
Open the nmcli interactive mode for the required connection. For example, to open the nmcli interactive mode for the example connection:
Set the default gateway.
For example, to set the IPv4 address of the default gateway on the example connection to 192.0.2.1 :
For example, to set the IPv6 address of the default gateway on the example connection to 2001:db8:1::1 :
Optionally, verify that the default gateway was set correctly:
Save the configuration:
Restart the network connection for changes to take effect:
All connections currently using this network connection are temporarily interrupted during the restart.
Leave the nmcli interactive mode:
Optionally, verify that the route is active.
To display the IPv4 default gateway:
To display the IPv6 default gateway:
Additional resources
20.3. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using nm-connection-editor
In most situations, administrators set the default gateway when they create a connection. This section describes how to set or update the default gateway on a previously created connection using the nm-connection-editor application.
Prerequisites
- At least one static IP address must be configured on the connection on which the default gateway will be set.
Procedure
Open a terminal, and enter nm-connection-editor :
Set the IPv4 default gateway. For example, to set the IPv4 address of the default gateway on the connection to 192.0.2.1 :
Enter the address in the gateway field next to the IP range the gateway’s address is within:
Set the IPv6 default gateway. For example, to set the IPv6 address of the default gateway on the connection to 2001:db8:1::1 :
Enter the address in the gateway field next to the IP range the gateway’s address is within:
Restart the network connection for changes to take effect. For example, to restart the example connection using the command line:
All connections currently using this network connection are temporarily interrupted during the restart.
Optionally, verify that the route is active.
To display the IPv4 default gateway:
To display the IPv6 default gateway:
Additional resources
20.4. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using control-center
In most situations, administrators set the default gateway when they create a connection. This section describes how to set or update the default gateway on a previously created connection using the control-center application.
Prerequisites
- At least one static IP address must be configured on the connection on which the default gateway will be set.
- The network configuration of the connection is open in the control-center application.
Procedure
Set the IPv4 default gateway. For example, to set the IPv4 address of the default gateway on the connection to 192.0.2.1 :
Enter the address in the gateway field next to the IP range the gateway’s address is within:
Set the IPv6 default gateway. For example, to set the IPv6 address of the default gateway on the connection to 2001:db8:1::1 :
Enter the address in the gateway field next to the IP range the gateway’s address is within:
Back in the Network window, disable and re-enable the connection by switching the button for the connection to Off and back to On for changes to take effect.
All connections currently using this network connection are temporarily interrupted during the restart.
Optionally, verify that the route is active.
To display the IPv4 default gateway:
To display the IPv6 default gateway:
Additional resources
20.5. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using nmstatectl
You can set the default gateway of a network connection using the nmstatectl utility. This procedure describes how to set the default gateway of the existing enp1s0 connection to 192.0.2.1 .
Prerequisites
- At least one static IP address must be configured on the connection on which the default gateway will be set.
- The enp1s0 interface is configured, and the IP address of the default gateway is within the subnet of the IP configuration of this interface.
- The nmstate package is installed.
Procedure
Create a YAML file, for example
/set-default-gateway.yml , with the following contents:
Apply the settings to the system:
Additional resources
- For further details about nmstatectl , see the nmstatectl(8) man page.
- For more configuration examples, see the /usr/share/doc/nmstate/examples/ directory.
20.6. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection using System Roles
You can use the networking RHEL System Role to set the default gateway.
When you run a play that uses the networking RHEL System Role, the System Role overrides an existing connection profile with the same name if the settings do not match the ones specified in the play. Therefore, always specify the whole configuration of the network connection profile in the play, even if, for example, the IP configuration already exists. Otherwise, the role resets these values to their defaults.
Depending on whether it already exists, the procedure creates or updates the enp1s0 connection profile with the following settings:
- A static IPv4 address — 198.51.100.20 with a /24 subnet mask
- A static IPv6 address — 2001:db8:1::1 with a /64 subnet mask
- An IPv4 default gateway — 198.51.100.254
- An IPv6 default gateway — 2001:db8:1::fffe
- An IPv4 DNS server — 198.51.100.200
- An IPv6 DNS server — 2001:db8:1::ffbb
- A DNS search domain — example.com
Prerequisites
- The ansible and rhel-system-roles packages are installed on the control node.
- If you use a different remote user than root when you run the playbook, this user has appropriate sudo permissions on the managed node.
Procedure
If the host on which you want to execute the instructions in the playbook is not yet inventoried, add the IP or name of this host to the /etc/ansible/hosts Ansible inventory file:
/ethernet-connection.yml playbook with the following content:
Run the playbook:
To connect as root user to the managed host, enter:
To connect as a user to the managed host, enter:
The —ask-become-pass option makes sure that the ansible-playbook command prompts for the sudo password of the user defined in the -u user_name option.
If you do not specify the -u user_name option, ansible-playbook connects to the managed host as the user that is currently logged in to the control node.
Additional resources
- /usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.network/README.md
- ansible-playbook(1) man page
20.7. Setting the default gateway on an existing connection when using the legacy network scripts
This procedure describes how to configure a default gateway when you use the legacy network scripts. The example sets the default gateway to 192.0.2.1 that is reachable via the enp1s0 interface.
Prerequisites
- The NetworkManager package is not installed, or the NetworkManager service is disabled.
- The network-scripts package is installed.
Procedure
Set the GATEWAY parameter in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp1s0 file to 192.0.2.1 :
Add the default entry in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-enp0s1 file:
Restart the network:
20.8. How NetworkManager manages multiple default gateways
In certain situations, for example for fallback reasons, you set multiple default gateways on a host. However, to avoid asynchronous routing issues, each default gateway of the same protocol requires a separate metric value. Note that RHEL only uses the connection to the default gateway that has the lowest metric set.
You can set the metric for both the IPv4 and IPv6 gateway of a connection using the following command:
Do not set the same metric value for the same protocol in multiple connection profiles to avoid routing issues.
If you set a default gateway without a metric value, NetworkManager automatically sets the metric value based on the interface type. For that, NetworkManager assigns the default value of this network type to the first connection that is activated, and sets an incremented value to each other connection of the same type in the order they are activated. For example, if two Ethernet connections with a default gateway exist, NetworkManager sets a metric of 100 on the route to the default gateway of the connection that you activate first. For the second connection, NetworkManager sets 101 .
The following is an overview of frequently-used network types and their default metrics:
| Connection type | Default metric value |
|---|---|