- Get started with Docker remote containers on WSL 2
- Overview of Docker containers
- Prerequisites
- Install Docker Desktop
- Develop in remote containers using VS Code
- Troubleshooting
- WSL docker context deprecated
- Trouble finding docker image storage folder
- Начало работы. Подготовка Windows для контейнеров Get started: Prep Windows for containers
- Предварительные требования Prerequisites
- Windows Server Windows Server
- Windows 10 Windows 10
- Установка Docker Install Docker
- Windows Admin Center; Windows Admin Center
- Дальнейшие действия Next steps
Get started with Docker remote containers on WSL 2
This step-by-step guide will help you get started developing with remote containers by setting up Docker Desktop for Windows with WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux, version 2).
Docker Desktop for Windows is available for free and provides a development environment for building, shipping, and running dockerized apps. By enabling the WSL 2 based engine, you can run both Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop on the same machine.
Overview of Docker containers
Docker is a tool used to create, deploy, and run applications using containers. Containers enable developers to package an app with all of the parts it needs (libraries, frameworks, dependencies, etc) and ship it all out as one package. Using a container ensures that the app will run the same regardless of any customized settings or previously installed libraries on the computer running it that could differ from the machine that was used to write and test the app’s code. This permits developers to focus on writing code without worrying about the system that code will be run on.
Docker containers are similar to virtual machines, but don’t create an entire virtual operating system. Instead, Docker enables the app to use the same Linux kernel as the system that it’s running on. This allows the app package to only require parts not already on the host computer, reducing the package size and improving performance.
Continuous availability, using Docker containers with tools like Kubernetes, is another reason for the popularity of containers. This enables multiple versions of your app container to be created at different times. Rather than needing to take down an entire system for updates or maintenance, each container (and it’s specific microservices) can be replaced on the fly. You can prepare a new container with all of your updates, set up the container for production, and just point to the new container once it’s ready. You can also archive different versions of your app using containers and keep them running as a safety fallback if needed.
To learn more, checkout the Introduction to Docker containers on Microsoft Learn.
Prerequisites
- Ensure your machine is running Windows 10, updated to version 2004, Build 18362 or higher.
- Enable WSL, install a Linux distribution, and update to WSL 2.
- Download and install the Linux kernel update package.
- Install Visual Studio Code(optional). This will provide the best experience, including the ability to code and debug inside a remote Docker container and connected to your Linux distribution.
- Install Windows Terminal(optional). This will provide the best experience, including the ability to customize and open multiple terminals in the same interface (including Ubuntu, Debian, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or whatever you prefer to use).
- Sign up for a Docker ID at Docker Hub(optional).
WSL can run distributions in both WSL version 1 or WSL 2 mode. You can check this by opening PowerShell and entering: wsl -l -v . Ensure that the your distribution is set to use WSL 2 by entering: wsl —set-version 2 . Replace with the distro name (e.g. Ubuntu 18.04).
In WSL version 1, due to fundamental differences between Windows and Linux, the Docker Engine couldn’t run directly inside WSL, so the Docker team developed an alternative solution using Hyper-V VMs and LinuxKit. However, since WSL 2 now runs on a Linux kernel with full system call capacity, Docker can fully run in WSL 2. This means that Linux containers can run natively without emulation, resulting in better performance and interoperability between your Windows and Linux tools.
Install Docker Desktop
With the WSL 2 backend supported in Docker Desktop for Windows, you can work in a Linux-based development environment and build Linux-based containers, while using Visual Studio Code for code editing and debugging, and running your container in the Microsoft Edge browser on Windows.
To install Docker (after already installing WSL 2):
Download Docker Desktop and follow the installation instructions.
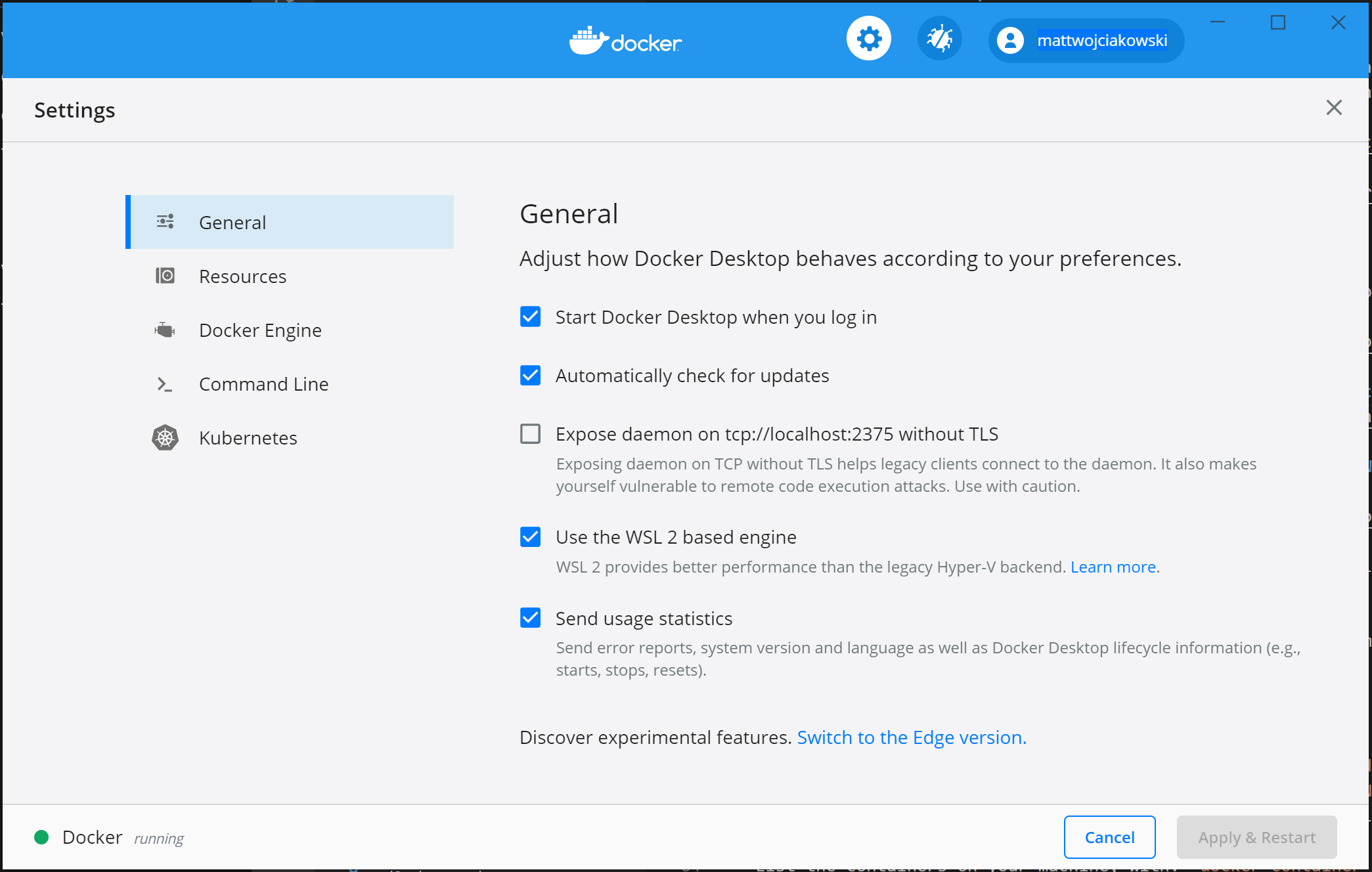
Once installed, start Docker Desktop from the Windows Start menu, then select the Docker icon from the hidden icons menu of your taskbar. Right-click the icon to display the Docker commands menu and select «Settings».
Ensure that «Use the WSL 2 based engine» is checked in Settings > General.
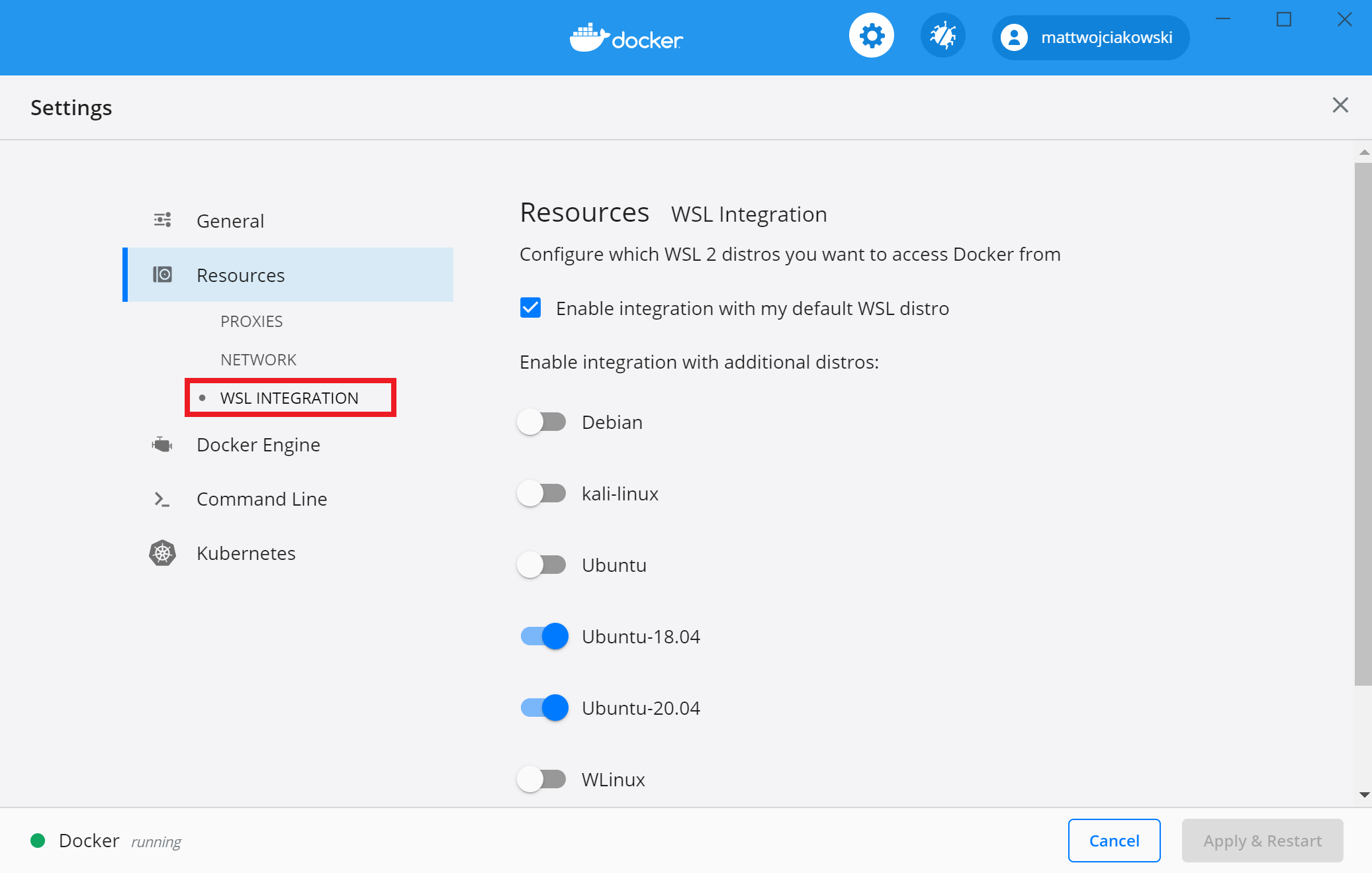
Select from your installed WSL 2 distributions which you want to enable Docker integration on by going to: Settings > Resources > WSL Integration.
To confirm that Docker has been installed, open a WSL distribution (e.g. Ubuntu) and display the version and build number by entering: docker —version
Test that your installation works correctly by running a simple built-in Docker image using: docker run hello-world
Here are a few helpful Docker commands to know:
- List the commands available in the Docker CLI by entering: docker
- List information for a specific command with: docker —help
- List the docker images on your machine (which is just the hello-world image at this point), with: docker image ls —all
- List the containers on your machine, with: docker container ls —all or docker ps -a (without the -a show all flag, only running containers will be displayed)
- List system-wide information regarding the Docker installation, including statistics and resources (CPU & memory) available to you in the WSL 2 context, with: docker info
Develop in remote containers using VS Code
To get started developing apps using Docker with WSL 2, we recommend using VS Code, along with the Remote-WSL extension and Docker extension.
Install the VS Code Remote-WSL extension. This extension enables you to open your Linux project running on WSL in VS Code (no need to worry about pathing issues, binary compatibility, or other cross-OS challenges).
Install the VS code Remote-Containers extension. This extension enables you to open your project folder or repo inside of a container, taking advantage of Visual Studio Code’s full feature set to do your development work within the container.
Install the VS Code Docker extension. This extension adds the functionality to build, manage, and deploy containerized applications from inside VS Code. (You need the Remote-Container extension to actually use the container as your dev environment.)
Let’s use Docker to create a development container for an existing app project.
For this example, I’ll use the source code from my Hello World tutorial for Django in the Python development environment set up docs. You can skip this step if you prefer to use your own project source code. To download my HelloWorld-Django web app from GitHub, open a WSL terminal (Ubuntu for example) and enter: git clone https://github.com/mattwojo/helloworld-django.git
Always store your code in the same file system that you’re using tools in. This will result in faster file access performance. In this example, we are using a Linux distro (Ubuntu) and want to store our project files on the WSL file system \\wsl\ . Storing project files on the Windows file system would significantly slow things down when using Linux tools in WSL to access those files.
From your WSL terminal, change directories to the source code folder for this project:
Open the project in VS Code running on the local Remote-WSL extension server by entering:
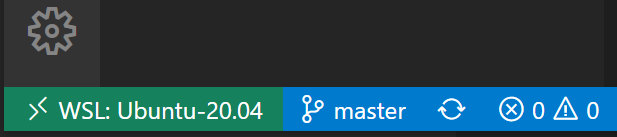
Confirm that you are connected to your WSL Linux distro by checking the green remote indicator in the bottom-left corner of your VS Code instance.
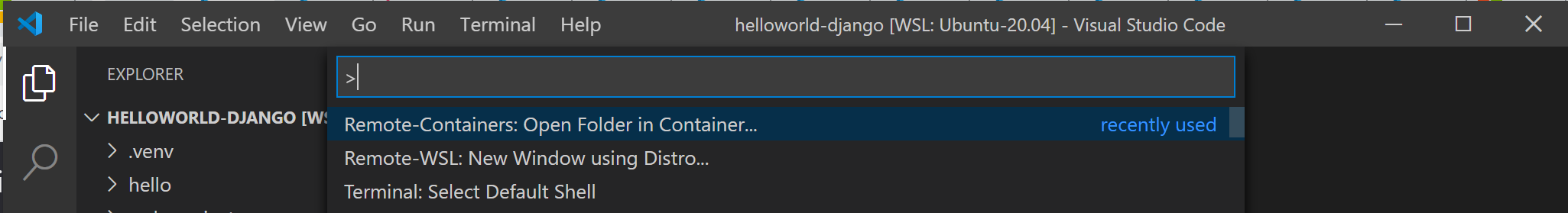
From the VS Code command pallette (Ctrl + Shift + P), enter: Remote-Containers: Open Folder in Container. If this command doesn’t display as you begin to type it, check to ensure that you’ve installed the Remote Container extension linked above.
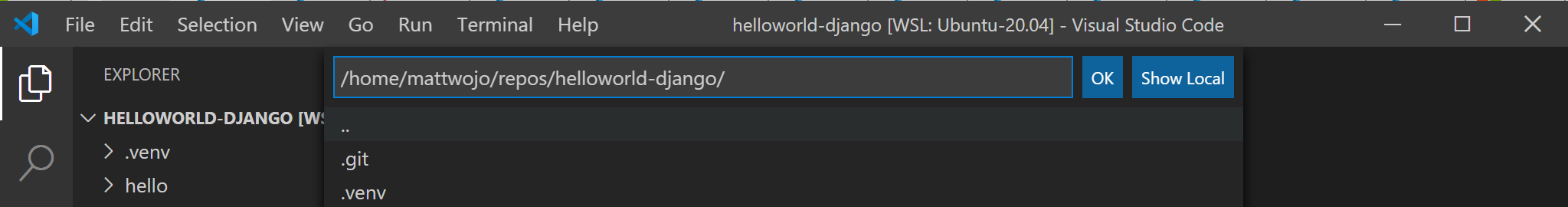
Select the project folder that you wish to containerize. In my case, this is \\wsl\Ubuntu-20.04\home\mattwojo\repos\helloworld-django\
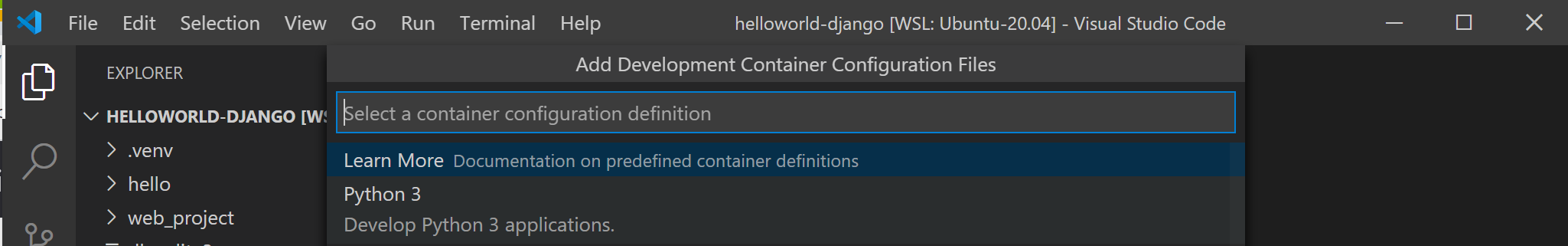
A list of container definitions will appear, since there is no DevContainer configuration in the project folder (repo) yet. The list of container configuration definitions that appears is filtered based on your project type. For my Django project, I’ll select Python 3.
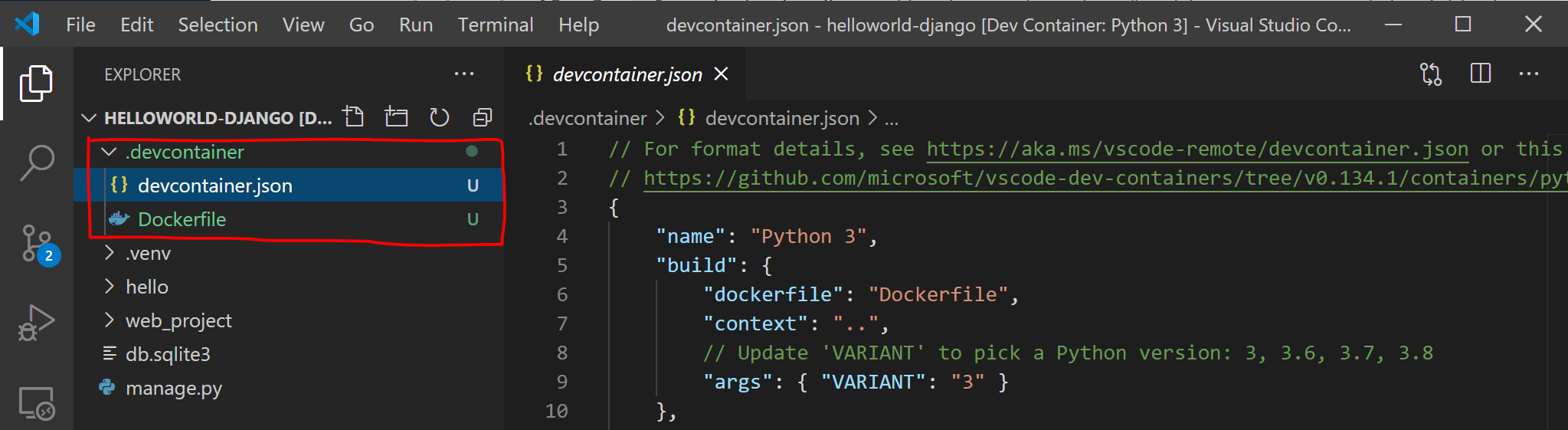
A new instance of VS Code will open, begin building our new image, and once the build completed, will start our container. You will see that a new .devcontainer folder has appeared with container configuration information inside a Dockerfile and devcontainer.json file.
To confirm that your project is still connected to both WSL and within a container, open the VS Code integrated terminal (Ctrl + Shift +
). Check the operating system by entering: uname and the Python version with: python3 —version . You can see that the uname came back as «Linux», so you are still connected to the WSL 2 engine, and Python version number will be based on the container config that may differ from the Python version installed on your WSL distribution.
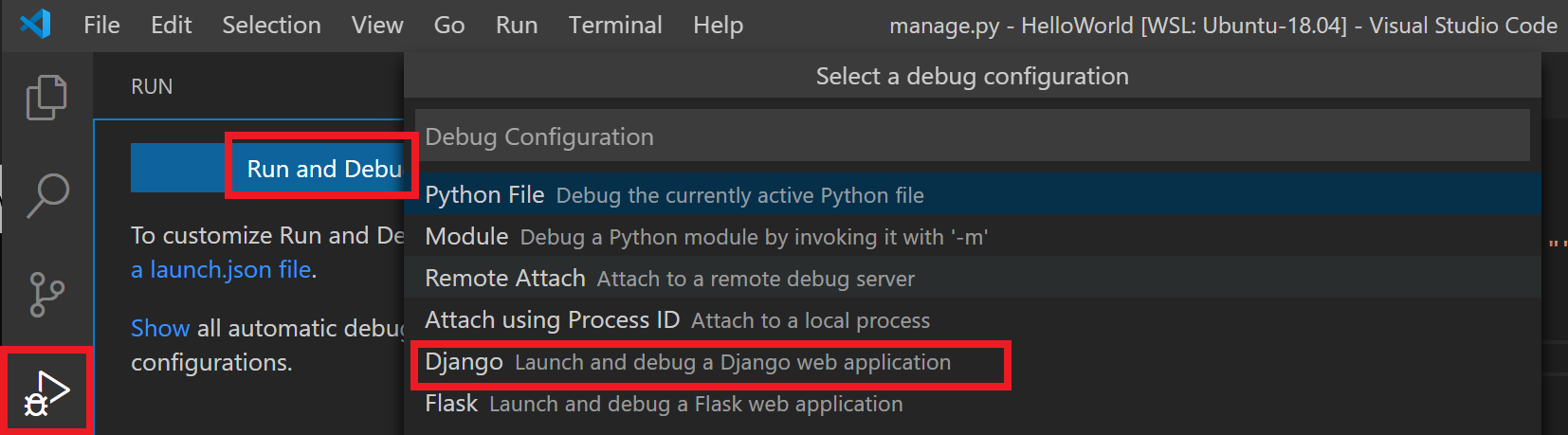
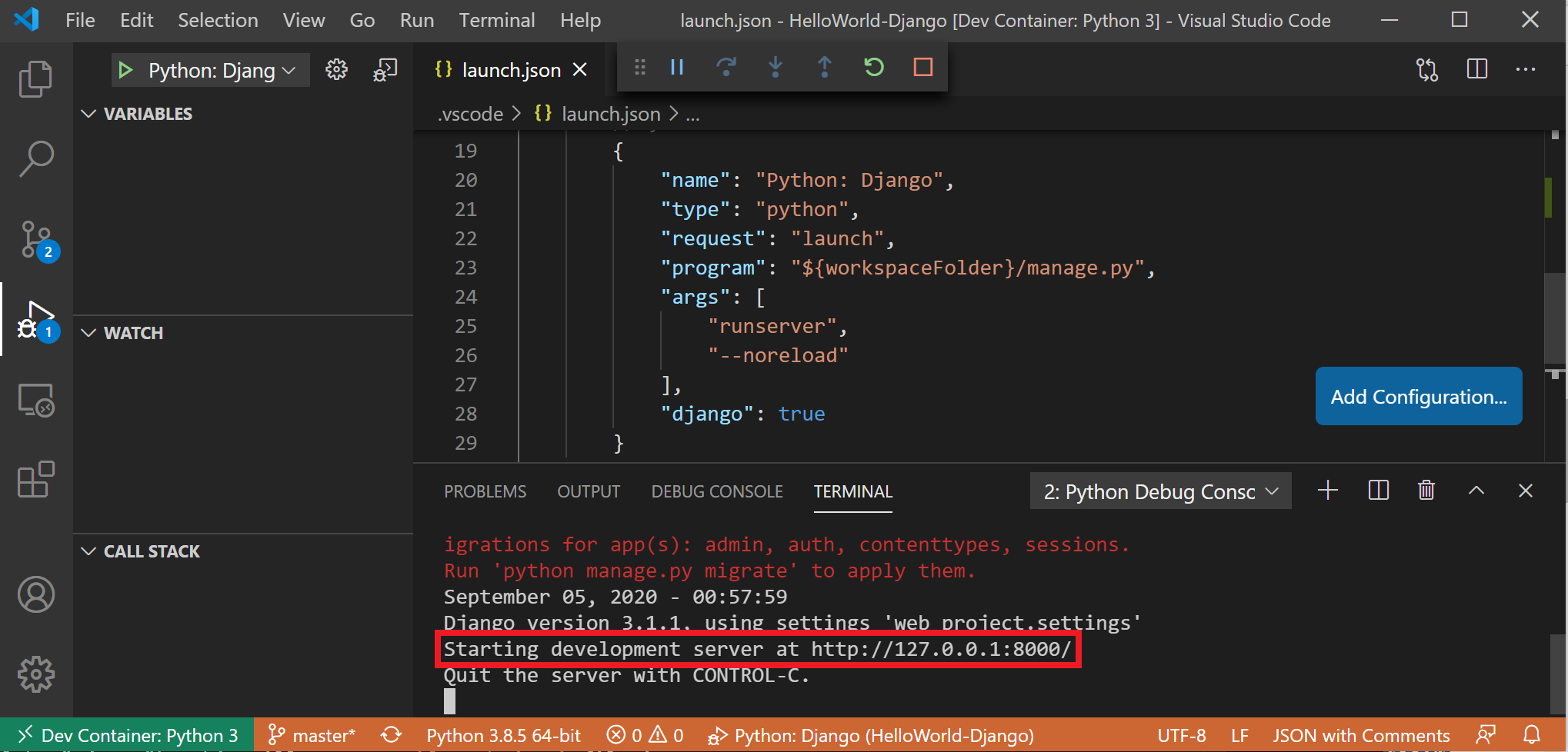
To run and debug your app inside of the container using Visual Studio Code, first open the Run menu (Ctrl+Shift+D or select the tab on the far left menu bar). Then select Run and Debug to select a debug configuration and choose the configuration that best suites your project (in my example, this will be «Django»). This will create a launch.json file in the .vscode folder of your project with instructions on how to run your app.
From inside VS Code, select Run > Start debugging (or just press the F5 key). This will open a terminal inside VS Code and you should see a result saying something like: «Starting development server at http://127.0.0.1:8000/ Quit the server with CONTROL-C.» Hold down the Control key and select the address displayed to open your app in your default web browser and see your project running inside of its container.
You have now successfully configured a remote development container using Docker Desktop, powered by the WSL 2 backend, that you can code in, build, run, deploy, or debug using VS Code!
Troubleshooting
WSL docker context deprecated
If you were using an early Tech Preview of Docker for WSL, you may have a Docker context called «wsl» that is now deprecated and no longer used. You can check with the command: docker context ls . You can remove this «wsl» context to avoid errors with the command: docker context rm wsl as you want to use the default context for both Windows and WSL2.
Possible errors you might encounter with this deprecated wsl context include: docker wsl open //./pipe/docker_wsl: The system cannot find the file specified. or error during connect: Get http://%2F%2F.%2Fpipe%2Fdocker_wsl/v1.40/images/json?all=1: open //./pipe/docker_wsl: The system cannot find the file specified.
Trouble finding docker image storage folder
Docker creates two distro folders to store data:
You can find these folders by opening your WSL Linux distribution and entering: explorer.exe . to view the folder in Windows File Explorer. Enter: \\wsl\ \mnt\wsl replacing with the name of your distribution (ie. Ubuntu-20.04) to see these folders.
Find more on locating docker storage locations in WSL, see this issue from the WSL repo or this StackOverlow post.
For more help with general troubleshooting issues in WSL, see the Troubleshooting doc.
Начало работы. Подготовка Windows для контейнеров Get started: Prep Windows for containers
Из этого руководства вы узнаете, как выполнить следующие задачи: This tutorial describes how to:
Предварительные требования Prerequisites
Windows Server Windows Server
Чтобы запустить контейнеры в Windows Server, вам нужен физический сервер или виртуальная машина под управлением Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019 или Windows Server 2016. To run containers on Windows Server, you need a physical server or virtual machine running Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, or Windows Server 2016.
Windows 10 Windows 10
Для запуска контейнеров в Windows 10 необходимо следующее: To run containers on Windows 10, you need the following:
- Одна физическая компьютерная система под управлением Windows 10 Профессиональная или Корпоративная с юбилейным обновлением (версия 1607) или более поздней версии. One physical computer system running Windows 10 Professional or Enterprise with Anniversary Update (version 1607) or later.
- Необходимо включить Hyper-V. Hyper-V should be enabled.
Начиная с Windows 10 с обновлением от октября 2018 г. мы не запрещаем пользователям запускать контейнер Windows в режиме изоляции процессов в Windows 10 Корпоративная или Профессиональная для целей разработки и тестирования. Starting with the Windows 10 October Update 2018, we no longer disallow users from running a Windows container in process-isolation mode on Windows 10 Enterprise or Professional for dev/test purposes. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе вопросов и ответов. See the FAQ to learn more.
Контейнеры Windows Server по умолчанию используют изоляцию Hyper-V в Windows 10, чтобы разработчики получили ту же версию ядра и ту же конфигурацию, что и в рабочей среде. Windows Server Containers use Hyper-V isolation by default on Windows 10 in order to provide developers with the same kernel version and configuration that will be used in production. Дополнительные сведения об изоляции Hyper-V см. в разделе документации с описанием концепций. Learn more about Hyper-V isolation in the Concepts area of our docs.
Установка Docker Install Docker
Первым шагом станет установка Docker. Это нужно для работы с контейнерами Windows. The first step is to install Docker, which is required for working with Windows containers. Docker предоставляет стандартную среду выполнения для контейнеров, а также основной API и интерфейс командной строки (CLI). Docker provides a standard runtime environment for containers, with a common API and command-line interface (CLI).
Дополнительные сведения о конфигурации см. в статье Подсистема Docker в Windows. For more configuration details, see Docker Engine on Windows.
Чтобы установить Docker в Windows Server, можно использовать модуль PowerShell поставщика OneGet, который опубликован корпорацией Майкрософт, под именем DockerMicrosoftProvider. To install Docker on Windows Server, you can use a OneGet provider PowerShell module published by Microsoft called the DockerMicrosoftProvider. Этот поставщик включает поддержку контейнеров в Windows, а также устанавливает подсистему и клиент Docker. This provider enables the containers feature in Windows and installs the Docker engine and client. Вот как это сделать. Here’s how:
Откройте сеанс PowerShell с повышенными привилегиями и установите поставщик Docker-Microsoft PackageManagement из коллекции PowerShell. Open an elevated PowerShell session and install the Docker-Microsoft PackageManagement Provider from the PowerShell Gallery.
Если будет предложено установить поставщик NuGet, введите Y и установите его. If you’re prompted to install the NuGet provider, type Y to install it as well.
С помощью модуля PackageManagement PowerShell установите последнюю версию Docker. Use the PackageManagement PowerShell module to install the latest version of Docker.
Когда в PowerShell появится запрос, доверять ли источнику пакета DockerDefault, введите A , чтобы продолжить установку. When PowerShell asks you whether to trust the package source ‘DockerDefault’, type A to continue the installation.
После установки перезагрузите компьютер. After the installation completes, restart the computer.
Если позже вам потребуется обновить Docker, выполните следующие действия: If you want to update Docker later:
- Проверьте установленную версию с помощью следующей команды: Check the installed version using:
- Найдите текущую версию с помощью следующей команды: Find the current version using:
- Когда все будет готово, запустите обновление с помощью следующей команды: When you’re ready, upgrade using:
- Затем выполните следующую команду: Then, followed with:
Windows Admin Center; Windows Admin Center
Вы можете использовать Windows Admin Center для корректной настройки компьютера Windows Server в качестве узла контейнера. You can use Windows Admin Center to properly set up a Windows Server machine as a container host. Чтобы начать работу, убедитесь, что в вашем экземпляре Windows Admin Center установлена последняя версия расширения «Контейнеры». To get started, ensure you have the latest Containers extension installed on your Windows Admin Center instance. Дополнительные сведения об установке и настройке расширений см. в документации по Windows Admin Center. For more information on how to install and configure extensions, check out the Windows Admin Center documentation. Установив расширение «Контейнеры», выберите компьютер Windows Server, который нужно настроить, и выберите вариант «Контейнеры»: With the Containers extension installed, target the Windows Server machine you want to configure and select the Containers option:
Нажмите кнопку Установить. Click the Install button. Windows Admin Center запустит настройку Windows Server и Docker в фоновом режиме. Windows Admin Center will start the configuration of Windows Server and Docker in the background. После завершения процесса можно обновить страницу и просмотреть другие функции расширения «Контейнеры». After the process is complete, you can refresh the page and see the other functionalities of the Containers extension.
Вы можете установить Docker в Windows 10 Профессиональная и Корпоративная, выполнив описанные ниже действия. You can install Docker on Windows 10 Professional and Enterprise editions by using the following steps.
Скачайте и установите Docker Desktop, создав бесплатную учетную запись Docker, если у вас ее нет. Download and install Docker Desktop, creating a free Docker account if you don’t have one already. Дополнительные сведения см. в документации по Docker. For more details, see the Docker documentation.
Во время установки выберите контейнеры Windows в качестве типа контейнеров по умолчанию. During installation, set the default container type to Windows containers. Чтобы переключиться после установки, можно использовать элемент Docker в области уведомлений Windows (как показано ниже) либо следующую команду в командной строке PowerShell: To switch after installation completes, you can use either the Docker item in the Windows system tray (as shown below), or the following command in a PowerShell prompt:
Дальнейшие действия Next steps
Теперь, когда ваша среда полностью настроена, перейдите по приведенной ниже ссылке, чтобы узнать, как запустить контейнер. Now that your environment has been configured correctly, follow the link to learn how to run a container.