- How to Format and Wipe Linux Disk Using Commands
- Can’t seem to clear your Linux disk space or not sure about disk formatting? Read this informative post about the working of different Linux commands to wipe or format the disk.
- Why Do We Need to Format and Wipe Linux Disk?
- How to Format a Linux Hard Drive?
- Step 1 Create a partition of the disk
- Step 2 Format the disk
- Step 3 Mount the file system (optional)
- How to Wipe a Hard Drive on Linux?
- 1 wipe
- 2 shred
- 4 scrub
- Tips for Formatting and Wiping Linux Disk
- Video Tutorial on How to Recover Data from Hard Disk After Disk Wipe
- What disk format does Linux use?
- Does a full format wipe data?
- How do I wipe Linux and install Windows?
- Does formatting remove Bitlocker?
- Linux Hard Disk Format Command
- Step #1 : Partition the new disk using fdisk command
- Step#2 : Format the new disk using mkfs.ext3 command
- Step#3 : Mount the new disk using mount command
- Step#4 : Update /etc/fstab file
- Task: Label the partition
How to Format and Wipe Linux Disk Using Commands
Can’t seem to clear your Linux disk space or not sure about disk formatting? Read this informative post about the working of different Linux commands to wipe or format the disk.
Theo Lucia
Sep 14, 2021 • Filed to: Answer Hard Drive Problems • Proven solutions
If you also own a Linux system, which is running on low disk space, then you might be facing a similar situation. Although Linux is one of the most popular open-source operating systems, it can be a bit complicated at times. For instance, there is no direct solution to do a Linux format disk using a dedicated GUI feature. Don’t worry – you can still erase the disk on Linux with the help of the right commands. Read on and clear your Linux disk space by following this extensive guide.
Content
Why Do We Need to Format and Wipe Linux Disk?
Before we get to know different ways to format a disk on Linux, it is vital to understand the reasons behind it. Ideally, there could be the following major reasons for wiping or formatting a disk on a Linux system:
- If your system is running low on free space, then you can choose to wipe the data of a partition or a disk.
- Sometimes, a system can become slow by having limited free space. By formatting its Linux drive, you can improve its performance as well.
- If your system has been corrupted by malware, then you can wipe the hard disk of your Linux to resolve this.
- Mostly, users prefer to do a Linux format disk before reselling their systems. This helps themВ protect their data.
- There could be an issue with the firmware or the system storage, which can be fixed after wiping a Linux disk.
How to Format a Linux Hard Drive?
Unlike Windows or macOS, there is not a dedicated disk management tool that can help us partition or format the disk. Therefore, we need to take the assistance of certain commands to format a Linux disk. If you are connecting your drive for the first time to your Linux system, then you need to create a partition beforehand. To implement this, you can enter the fdisk command. Once a partition is created, you can use the «mkfs.ext4» command to format the disk. Here’s a simple solution to format a disk on a Linux system.
Step 1 Create a partition of the disk
Firstly, connect the disk to your Linux system if you haven’t already and launch the Terminal window on it. You can enter the following command to check it:
sudo fdisk –l.
Now, to create a partition, enter the command «fdsk» in the following format:
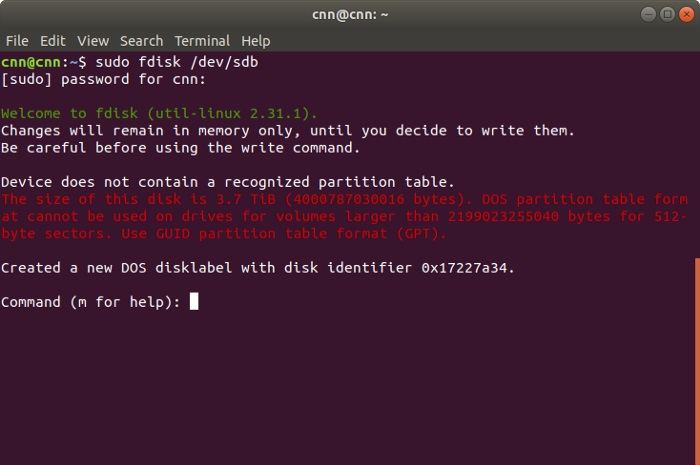
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb.
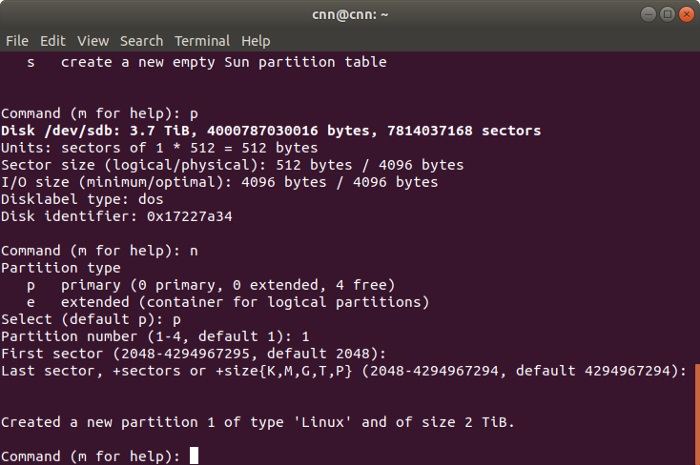
This will launch the results of the fdisk command. If you want, you can type «m» to get help. It will display a list of the supported parameters. You can type «n» to create a new partition, «d» to delete the partition, «p» to check the partition table, and so on.
Firstly, press «p» and enter to view the partition table. This will let you know about the disk identifier and the sector space. Subsequently, enter the «n» command to create a new partition. You will be given an option to create a primary or an extended partition. Press «p» to create a new primary partition and give it a number from 1 to 4. If you want to create a single partition, then enter «1».
Step 2 Format the disk
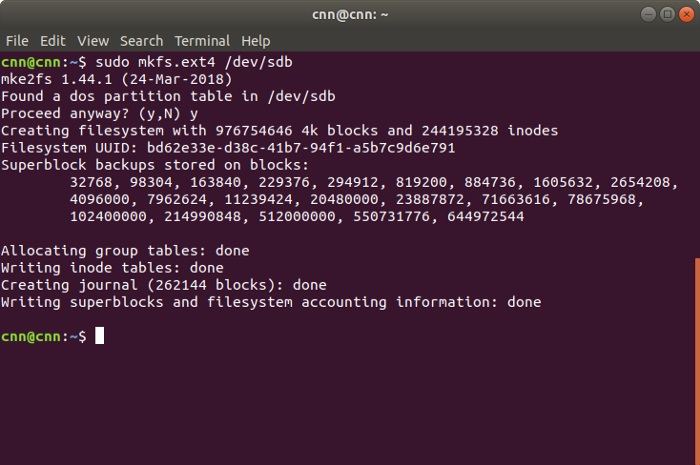
Great! Once you have created the relevant partition on your Linux system, you can format it by entering the command –
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb.
This will make the system look for the available partitions on the drive. When you are asked to confirm your choice, just press «y». Afterward, wait for a while as the selected partitions would be formatted on the Linux system.
Step 3 Mount the file system (optional)
If you want, you can mount the file system as well. To do this, you can use the «mkdir /data» command to make a directory. After that, end the following command to mount it:
mount /dev/sdb1 /data.
How to Wipe a Hard Drive on Linux?
If you are planning to resell your system or are concerned about your privacy, then you should consider wiping the drive instead. Unlike formatting a disk, wiping it will erase the data and make the recovery process harder than before. Thankfully, there are multiple commands to do Linux wipe the disk. Here are some simple solutions to wipe a hard drive on Linux.
1 wipe
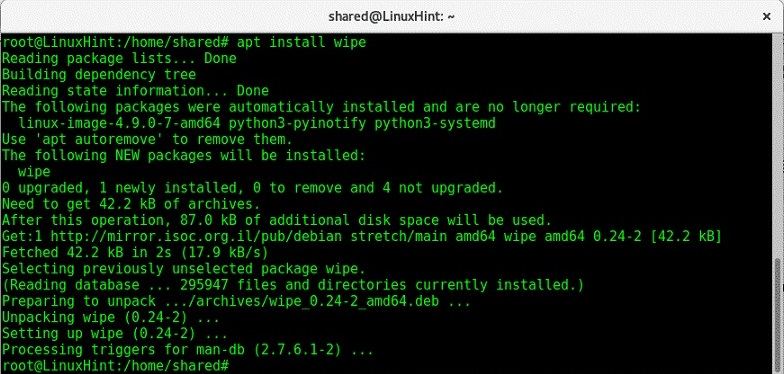
As the name suggests, the command is used to wipe data from a magnetic disk. Though, a lot of Linux systems do not have the command readily installed. In this case, you can use the apt install command first.
# apt install wipe.
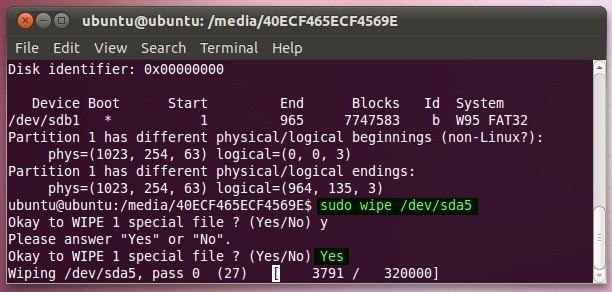
Once it is done, just use the «wipe» command in the format — wipe [options] target. For instance, to wipe a partition, simply enter the command:
Confirm your choice, by entering «yes» and wait as the selected partition would be wiped.
2 shred
This is one of the best ways to protect your private data on a Linux system. Ideally, this works as a dedicated shredder – that would overwrite your data with something else, making the recovery process harder. This Linux based command has the following syntax:
shred [option] target
As you know, «target» would specify the location you wish to shred. It can be a partition, folder, or file name. Subsequently, it can have the following options.
- -n: To overwrite data «n» times
- -f: To change permission and allow the writing operation
- -u: Truncates the files after shredding them
- -s: To provide the size to shred
- -u: To remove the file after shredding
- -v: To enable the verbose mode
- -z: To add zeros to the final overwriting process
Therefore, you can wipe the Linux disk, by entering a command like this:
# shred -vfz -n 10 /dev/sda2.
This will follow ten passes of overwriting on the provided location, making it impossible for a recovery tool to retrieve data from it.
If you are running short on time, then consider using the «dd» command to erase disk on a Linux system. Instead of generating random data, it will overwrite the entire disk with strings of zeros. Therefore, it will take less time to wipe the disk and protecting your information. Although, it provides certain options that you can use to customize the process.
dd if=source of=target [Options].
Make sure that you run the command prompt and as a super-user. Here’s a simple demonstration of the same.
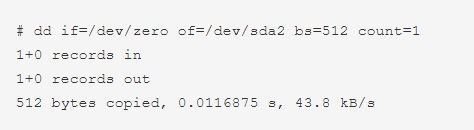
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda2 bs=512 count=1.
The command will overwrite the target location with a string of zeros, as specified in the source. Also, this will copy 512 bytes in a single count. One of the major advantages of this is the time taken by the dd command is lesser than shred.
4 scrub
Lastly, you can also take the assistance of the «scrub» command to overwrite your disk with specific patterns. Sometimes, the patterns can be randomly generated by the system too. Since the command is not present in every Linux system by default, you might need to install it first. To do this, you can use the apt install command.
Once it is done, just enter the command in the following syntax:
scrub [option]В target.
Even if you don’t provide an option and just specifies the target location to wipe, the command will work. Though, you would be asked to verify your choice to erase disk on Linux entirely. Here’s a quick example of the same:
Tips for Formatting and Wiping Linux Disk
After getting to know about these popular commands to create new disk space on Linux, you would certainly be able to format or wipe it. Besides that, you can consider following these tips to format or wipe the Linux disk successfully.
- Make sure that you have logged in as a super-user (administrator) while wiping a disk. This will make the entire process a whole lot easier.
- Not every command might be installed on your system. Therefore, you can consider checking its status or installing it beforehand.
- Although there are third-party applications available to shred and wipe a disk, it is recommended to use reliable commands. If you use a readily available tool, then make sure it is from a trusted source with a positive reputation in the industry.
- Always double-check the command before entering it (particularly the syntax and the location). One small error and you might end up causing irrevocable damage to your system.
- Most importantly, take a backup of your important files before wiping the Linux disk. This will make sure that you have a second copy of your vital data in advance.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Data from Hard Disk After Disk Wipe
Recent Videos from Recoverit
That’s a wrap, folks! Now when you know how to format or wipe disk on Linux, you can easily meet your requirements. In case if you have accidentally deleted your data or have formatted a drive, then use a reliable data recovery solution likeВ Wondershare Recoverit. Using it, you can just attach your Linux device to a PC and later extract the lost or inaccessible content from it. Go ahead and try some of these methods and feel free to share your shortcuts or tips in the comments below.
What disk format does Linux use?
Linux is a very versatile operating system and has its own disk format which is EXT, which can be presented in its EXT2, EXT3 and EXT4 versions. However, this is not the only file system that can be supported by this operating system; FAT32 and NTFS systems are fully supported as well as HFS.
Does a full format wipe data?
Not necessarily. Although the information will not be accessible through Windows file explorer. This does not mean that the information is not physically stored on disk yet. Formatting a disk is equivalent to giving disk permission to overwrite where information previously was. Eventually, the residual information will be completely overwritten.
How do I wipe Linux and install Windows?
If you want to remove Linux and install Windows, the procedure is quite simple. First, back up your information. Once you have done this, you will need to insert your bootable DVD or flash drive that has the Windows installer on it. Then you have to follow the steps and in the type of installation, you will choose «custom», then you will erase the partition where Linux is installed and you will be able to install Windows.
Does formatting remove Bitlocker?
As part of Windows security and protection mechanisms, BitLocker has been developed. For security reasons, BitLocker can only be removed by typing its password or, in case you forgot it, the recovery key. If you do not have any of them, it is suggested to format the device, since this process will delete all the information –including BitLocker— contained to reset all settings to the factory default.
Источник
Linux Hard Disk Format Command
Q. I’ve installed a new 250GB SATA hard disk on our office CentOS Linux server. How do I format a hard disk under Linux operating system from a shell prompt?
A. . There are total 4 steps involved for hard disk upgrade and installation procedure:
Step #1 : Partition the new disk using fdisk command
Following command will list all detected hard disks:
# fdisk -l | grep ‘^Disk’
Output:
A device name refers to the entire hard disk. For more information see Linux partition naming convention and IDE drive mappings.
To partition the disk – /dev/sdb, enter:
# fdisk /dev/sdb
The basic fdisk commands you need are:
- m – print help
- p – print the partition table
- n – create a new partition
- d – delete a partition
- q – quit without saving changes
- w – write the new partition table and exit
Step#2 : Format the new disk using mkfs.ext3 command
To format Linux partitions using ext2fs on the new disk:
# mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Step#3 : Mount the new disk using mount command
First create a mount point /disk1 and use mount command to mount /dev/sdb1, enter:
# mkdir /disk1
# mount /dev/sdb1 /disk1
# df -H
Step#4 : Update /etc/fstab file
Open /etc/fstab file, enter:
# vi /etc/fstab
Append as follows:
Save and close the file.
Task: Label the partition
You can label the partition using e2label. For example, if you want to label the new partition /backup, enter
# e2label /dev/sdb1 /backup
You can use label name insted of partition name to mount disk using /etc/fstab:
LABEL=/backup /disk1 ext3 defaults 1 2
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
yah thats good for understand………
i have 48TB storage server in raid 5, how do i format this server?
to format the corresponding hdd you need a RAM(Random Access Memory) 1 YB(yota byte)
1YB=1024 ZB
1ZB=1024 XB
1XB=1024 PB
1PB=1024 TB
LOL, I’ve got 1 UB (UnniByte) RAM on my Server
1UB=1024YB
1YB=1024 ZB
1ZB=1024 XB
1XB=1024 PB
1PB=1024 TB
Is it possible to format my 1.4 MB floppy now?
I have 90’90 power of per zylions! So what? You’ve only got a pint of milk. does your processor register .
Use LVM directly or read this tutorial which explains how to create partition larger than 2TB
How do I format a harddisk using linux system call
thank you fro valuable information
how to format a disk by cpp programe?is there any sample code ?
Thank you very much this valuable information.
/dev/sdb1 /disk1 ext3 defaults 1 2
The above line what is mean by defaults and what is 1 2 ?
can u explain those two things !
This is directly from the arch linux (amazing) documentation:
- The first number is “dump”: used by the dump utility to decide when to make a backup. Dump checks the entry and uses the number to decide if a file system should be backed up. Possible entries are 0 and 1. If 0, dump will ignore the file system; if 1, dump will make a backup. Most users will not have dump installed, so they should put 0 for the entry.
- The second number is “pass”: used by fsck to decide which order filesystems are to be checked. Possible entries are 0, 1 and 2. The root file system should have the highest priority 1 – all other file systems you want to have checked should have a 2. File systems with a value 0 will not be checked by the fsck utility.
IN my system both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX , I’ve installed. after that
I want to format the linux OS from my system.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr., so i can remove LUNUX OS from my system.
BY both method (i)Text command and
(ii)without Text command.
Hey man I also have same problem .did u got any methods to remove . please help man
verrrrrrrrry useful i’ve searched for 2 days for this thanks
Thank you very much this valuable information. Very useful this
Thanks
B. Sathish.
I have installed CentOS ..
now i want my disk to be fully formatted like a new one. with no files on it..
i remember doing it by booting in DOS mode in Win98..
Please tell how can i do it..
Thank you.
nice and clear.
Excellent and easy. Thanx
Nice information and esp. the link that you posted for Anikat. Information really useful pal. Thanks a ton..
Regards
Charanjit Singh Cheema
Thank you, this is the kind of fast reference that one is always looking for
Well, this saved me an hour of banging my head against the wall… well written! thanks!
Yes. Very useful. Thanks.
help me to see the out put of the php programe, i have php 2007 developer
Very simple and useful, thanks 🙂
Great. Searched for a long time to find this, very well done. Thanks!
Can any one tell me what the mean by 1,2 in default and when i create a raid partition is there any change in default charcter or it is sama as ” default” .
IN my Laptop both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX, i’ve safe the problem in windows hal.dll file is corrupted.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr.
Good Recipe for what I did in UNIX for years with the simple format command.
You boiled it down to an excellent example…
very helpfull , thanks.
very first command (fdisk /dev/sdb) failed. message is “Unable to open /dev/sdb”. any suggestions?
Is there any software to bound two NIC to use on ip address for both NICs.
Thank you very much these are very good and easy way commands to understand for the people.
how to format linex form my system plz reply solution at my email
thanks alot . that was really usefull
how many formatting for window and linux
plz sand ams on my email address
I deleted the panel in ubuntu by mistake.. how can i get the default panels?
The above steps are so good and easy to format
Thank u Very much for your Formating steps.
a very nice article. thank you for sharing.
how do installed linux …. with command . tell me all command….
IN my system both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX , I’ve installed. after that
I want to format the linux OS from my system.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr., so i can remove LUNUX OS from my system.
BY both method (i)Text command and
(ii)without Text command.
Good article.
Note: this works on centos 5.5 … fyi.
This is beautiful. There are some who care out there..
IN my system both WINDOWS-XP and LINUX , I’ve installed. after that
I want to format the linux OS from my system.
so please send to me tricks or method on Email addr., so i can remove LUNUX OS from my system.
BY both method
(i)Text command and
(ii)without Text command.
Источник