- Копирование файлов в Linux
- Утилита копирования файлов cp
- Синтаксис и опции
- Примеры копирования файлов в linux
- Копирование файлов по регулярным выражениям в Linux
- Копирование содержимого файлов в Linux
- Специальное копирование файлов в Linux с помощью tar
- Выводы
- How do I copy folder with files to another folder in Unix/Linux? [closed]
- 3 Answers 3
- How can I copy the contents of a folder to another folder in a different directory using terminal?
- 8 Answers 8
- Simple example.
- How to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
- Using the cp Command to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
- Additional Options
- How to Copy File to Another Directory in Linux
- Copy Multiple Files from One Directory to Another in Linux
- Copy Using rsync Command
- Other Options
Копирование файлов в Linux
Копирование файлов — одна из задач, наиболее часто возникающих перед пользователями персонального компьютера. Конечно, можно открыть файловый менеджер, войти в нужную папку и скопировать файл с помощью контекстного меню — тут не о чем говорить. Но в этой статье я хотел бы рассмотреть копирование файлов в Linux с помощью терминала.
Не всегда есть доступ к файловому менеджеру: из-за различных поломок графическая оболочка на домашнем компьютере может быть недоступна, а на серверах используется только консольный интерфейс. К тому же копирование файлов Ubuntu через терминал намного эффективнее, и вы сами в этом убедитесь. Сегодня мы рассмотрим не только обычное копирование командой cp Linux, но и не совсем обычное: с помощью tar и find.
Утилита копирования файлов cp
Название утилиты cp — это сокращение от Copy, что означает копировать. Утилита позволяет полностью копировать файлы и директории.
Синтаксис и опции
Общий синтаксис cp выглядит вот так:
$ cp опции файл-источник файл-приемник
$ cp опции файл-источник директория-приемник/
После выполнения команды файл-источник будет полностью перенесен в файл-приемник. Если в конце указан слэш, файл будет записан в заданную директорию с оригинальным именем.
Утилита имеет несколько интересных опций, которые могут сильно помочь при нестандартных задачах копирования, поэтому давайте их рассмотрим:
- —attributes-only — не копировать содержимое файла, а только флаги доступа и владельца;
- -f, —force — перезаписывать существующие файлы;
- -i, —interactive — спрашивать, нужно ли перезаписывать существующие файлы;
- -L — копировать не символические ссылки, а то, на что они указывают;
- -n — не перезаписывать существующие файлы;
- -P — не следовать символическим ссылкам;
- -r — копировать папку Linux рекурсивно;
- -s — не выполнять копирование файлов в Linux, а создавать символические ссылки;
- -u — скопировать файл, только если он был изменён;
- -x — не выходить за пределы этой файловой системы;
- -p — сохранять владельца, временные метки и флаги доступа при копировании;
- -t — считать файл-приемник директорией и копировать файл-источник в эту директорию.
Примеры копирования файлов в linux
Теперь, когда вы знаете основные опции, можно перейти к практике. Например, мы хотим скопировать некую картинку из домашней папки в подкаталог pictures:
Или можем явно указать имя новой картинки:
Копирование папок осуществляется с помощью ключа -r:
После выполнения этой команды копирования
/папка будет скопирована в папку
/Документы. Главное, не забывайте поставить слэш в конце выражения или использовать опцию -t. Иначе папка
/документы будет перезаписана.
По умолчанию команда cp Linux перезаписывает существующие файлы или папки, но можно заставить утилиту спрашивать, нужно ли перезаписывать каждый файл, если вы не уверены в правильности составления команды:
Есть и противоположная опция -n, означающая «никогда не перезаписывать существующие файлы».
Опция -u полезна в следующем случае: вы знаете или предполагаете, что в директории, куда копируется файл, есть старая его версия, тогда оператор -u выполнит замену на новую версию:
Сp также поддерживает специальные символы замены * и ?. Например, следующая команда скопирует все файлы, начинающиеся на test:
Если нужно применить более сложные регулярные выражения, придётся комбинировать утилиту cp с find или egrep.
В случае, если важно сохранить права доступа к файлу и его владельца, нужно использовать опцию -p:
Для упрощения использования команды можно применять синтаксис фигурных скобок. Например, чтобы создать резервную копию файла, выполните:
Будет создан файл с таким же именем и расширением .bak
По умолчанию в cp не отображается прогресс копирования файла, что очень неудобно при работе с большими файлами, но его можно легко посмотреть с помощью утилиты cv.
Копирование файлов по регулярным выражениям в Linux
В утилите find можно применять различные условия и регулярные выражения для поиска файлов. Я уже немного писал о ней в статье как найти новые файлы в Linux. Мы можем скопировать все найденные с помощью find файлы, вызвав для каждого из них команду cp. Например, копируем все файлы в текущей директории, содержащие в имени только цифры:
find . -name 1 -exec cp <>
Здесь точка указывает на текущую директорию, а параметр name задает регулярное выражение. Параметром exec мы задаем, какую команду нужно выполнить для обнаруженных файлов. Символ <> — подставляет имя каждого файла.
Но не find‘ом единым такое делается. То же самое можно получить, запросив список файлов директории в ls, отфильтровав его по регулярному выражению egrep и передав имена файлов по очереди в cp с помощью xargs:
/ | egrep ‘[a-zA-Z]’ | xargs cp -t
Это не совсем удобный способ копировать файлы Linux, но всё же он возможен. Будут скопированы все файлы из домашней директории, содержащие в имени только английские буквы.
Копирование содержимого файлов в Linux
Вы можете не только копировать сами файлы, но и управлять их содержимым. Например, склеить несколько файлов в один или разрезать файл на несколько частей. Утилита cat используется для вывода содержимого файла, в комбинации с операторами перенаправления вывода Bash вы можете выполнять копирование содержимого файла Linux в другой файл. Например:
cat файл1 > файл2
Если файл был не пустым, он будет перезаписан. Или мы можем склеить два отдельных файла в один:
cat файл1 файл2 > файл3
Специальное копирование файлов в Linux с помощью tar
Linux интересен тем, что позволяет выполнять одно и то же действие различными путями. Копирование в Linux тоже может быть выполнено не только с помощью cp. При переносе системных файлов в другой каталог, резервном копировании системных файлов и т.д. важно чтобы сохранились атрибуты, значения владельцев файлов и символические ссылки как они есть без какой-либо модификации.
Утилита cp тоже может справиться с такой задачей? если указать опцию -p, но можно использовать утилиту архивации tar. Мы не будем создавать никаких файлов архивов, а построим туннель. Первая часть команды пакует файл и отправляет на стандартный вывод, а другая сразу же распаковывает в нужную папку:
tar cf — /var | ( cd /mnt/var && tar xvf — )
Здесь мы полностью копируем содержимое папки /var в папку /mnt/var. Так вы можете копировать папку Linux, причём абсолютно любую или даже целую операционную систему.
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете, как выполняется копирование файлов Ubuntu и в Linux в целом. Как видите, в терминале это выполняется намного быстрее и эффективнее, чем с помощью графического интерфейса, если помнить нужные команды. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Источник
How do I copy folder with files to another folder in Unix/Linux? [closed]
Want to improve this question? Update the question so it’s on-topic for Stack Overflow.
Closed 8 years ago .
I am having some issues to copy a folder with files in that folder into another folder. Command cp -r doesn’t copy files in the folder.
3 Answers 3
The option you’re looking for is -R .
- If destination doesn’t exist, it will be created.
- -R means copy directories recursively . You can also use -r since it’s case-insensitive.
- To copy everything inside the source folder (symlinks, hidden files) without copying the source folder itself use -a flag along with trailing /. in the source (as per @muni764 ‘s / @Anton Krug ‘s comment):
You are looking for the cp command. You need to change directories so that you are outside of the directory you are trying to copy.
If the directory you’re copying is called dir1 and you want to copy it to your /home/Pictures folder:
Linux is case-sensitive and also needs the / after each directory to know that it isn’t a file.
is a special character in the terminal that automatically evaluates to the current user’s home directory. If you need to know what directory you are in, use the command pwd .
When you don’t know how to use a Linux command, there is a manual page that you can refer to by typing:
at a terminal prompt.
Also, to auto complete long file paths when typing in the terminal, you can hit Tab after you’ve started typing the path and you will either be presented with choices, or it will insert the remaining part of the path.
Источник
How can I copy the contents of a folder to another folder in a different directory using terminal?
I am trying to copy the contents of a folder to another folder in a different directory using terminal.
Would somebody be able to provide me an example of the command line syntax required to achieve this?
8 Answers 8
You can copy the content of a folder /source to another existing folder /dest with the command
The -a option is an improved recursive option, that preserve all file attributes, and also preserve symlinks.
The . at end of the source path is a specific cp syntax that allow to copy all files and folders, included hidden ones.
An alternate is rsync :
The advantages of rsync are:
- After the initial sync, it will then copy only the files that have changed.
- You can use it over a network, convenient for files in $HOME, especially config files.
Lets say you have a folder called folder1 in your
, inside folder1 is 1 file called file1 and 2 folders called sub1 and sub2 each with other files and folders inside them.
To copy all the contents of
/new_folder1 you would use
new_folder1 would then contain all the files and folders from folder1 .
cp is the command to copy using a terminal, -r makes it recursively (so, current directory + further directories inside current)
/folder1 is the origin folder,
/new_folder1 is the destination folder for the files/folders inside the origin.
sign). Maybe because the destination folder was in /opt, which resides in another file system. And thank you Portablejim to remember the hidden file thing!
/new_folder1/folder1 instead of copying the contents over.
Simple example.
Copy the directory dir_1 and its contents (files) into directory dir_2:
Copy only the contents (files) of dir_1 into directory dir_2:
_files_ is a placeholder for the actual files located in the directory.
Check this http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/copy-folder-linux-command-line/ for more information on copying folder. Hope this helps.
cp is a Linux command for copying files and directories. The syntax is as follows:
In this example copy /home/vivek/letters folder and all its files to /usb/backup directory:
-a : Preserve the specified attributes such as directory an file mode, ownership, timestamps, if possible additional attributes: context, links, xattr, all.
-v : Explain what is being done.
-r : Copy directories recursively. Example
Copy a folder called /tmp/conf to /tmp/backup:
I like this command
Some of the commonly used options in rsync command are listed below:
- -v, –verbose: Verbose output
- -q, –quiet: suppress message output
- -a, –archive: archive files and directory while synchronizing ( -an equal to following options -rlptgoD)
- -r, –recursive: sync files and directories recursively
- -b, –backup: take the backup during synchronization
- -u, –update: don’t copy the files from source to destination if destination files are newer
- -l, –links: copy symlinks as symlinks during the sync
- -n, –dry-run: perform a trial run without synchronization
- -e, –rsh=COMMAND: mention the remote shell to use in rsync
- -z, –compress: compress file data during the transfer
- -h, –human-readable: display the output numbers in a human-readable format
- –progress: show the sync progress during transfer
If there are two folders: (with write permission)
If you are inside the folder called PORTAL where you want to copy all content of another folder say DATA at the same level then you will do
vimal@vimal-D3H:/var/www/html/PORTAL$ cp -a ../DATA/. .
You have to notice 2 dots. Last dot says copy here in present folder
one following /DATA/. says that all the CONTENTS inside DATA folder to be copied, and not the DATA folder itself.
If you remove this trailing «.» from /DATA/
then whole DATA folder will be copied inside PORTAL(from where you are coping).
Источник
How to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
This guide will show you how to copy files and directories in Linux by executing commands from the command line. Furthermore, the commands listed below detail how to create system-wide backups or filter out and copy only specific files.
Note: These Linux commands can only be run from a terminal window. If your version of Linux boots to a desktop graphical interface, launch a terminal window by pressing CTRL-ALT-F2 or CTRL-ALT-T.
Using the cp Command to Copy Files and Directories in Linux
The cp command is the primary method for copying files and directories in Linux. Virtually all Linux distributions can use cp . The basic format of the command is:
This Linux command creates a copy of the my_file.txt file and renames the new file to my_file2.txt.
By default, the cp command runs in the same directory you are working in. However, the same file cannot exist twice in the same directory. You’ll need to change the name of the target file to copy in the same location. Some users will add _old, some will add a number, and some will even change the three-letter extension (e.g., .bak instead of .txt).
You may not get a warning before Linux overwrites your file – be careful, or see below for the –i option.
Additional Options
Additional options can be used in combination with the cp command:
- –v verbose: shows the progress of multiple copied files
- –ppreserve: keeps the same attributes, like creation date and file permissions
- –f force: force the copy by deleting an existing file first
- –i interactive: prompts for confirmation, highly advised
- –Rrecursive: copies all files and subfolders in a directory
- –u update: copy only if source is newer than destination
Note: The -p (preserve) option forces the system to preserve the following source file attributes: modification time, access time, user ID (UID), group ID (GID), file flags, file mode, access control lists (ACLs), and extended attributes (EAs).
How to Copy File to Another Directory in Linux
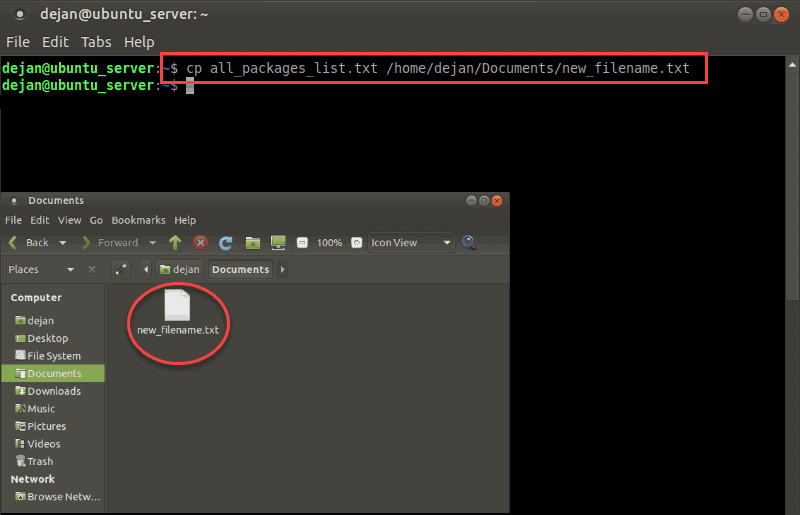
To copy a file from the directory you’re working in to a different location, use the command:
You don’t need to rename the file unless there’s already one with the same name in the target directory.
To specify a path for the source file:
This lets you copy without having to change directories. The cp command will create the /new_directory if it doesn’t exist.
To rename and copy a file to a different path:
This option is useful for creating backups of configuration files, or for copying data to a storage device.
Note: Learn how to move directories in Linux.
Copy Multiple Files from One Directory to Another in Linux
You may need to copy more than one file at a time.
List each file to be copied before the target directory:
This example created a copy of all three files in the /new_directory folder.
Use a wildcard to specify all files that share a string of characters:
This would find all the files with the .jpg extension in the /pictures directory, and copy them into the /new_directory folder.
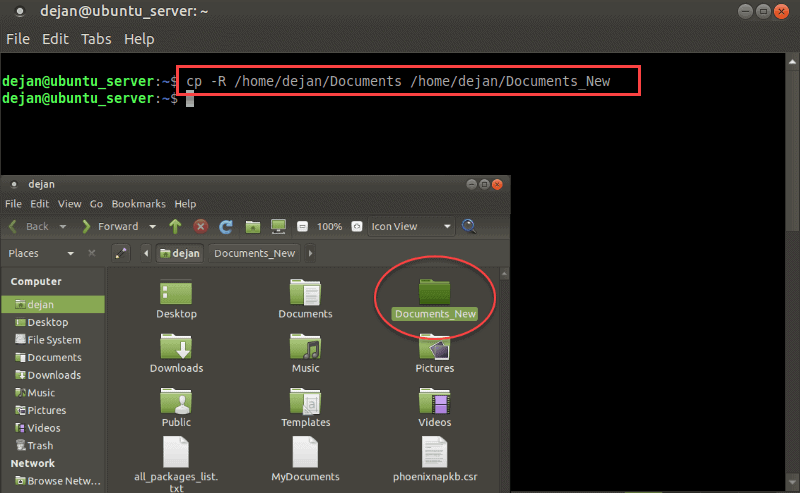
To copy an entire folder and its subfolders and files, use the –R option:
–R stands for recursive, which means “everything in that location.” This would copy all the files, as well as all the directories, to the /new_directory folder.
Copy Using rsync Command
The rsync command in Linux is used to synchronize or transfer data between two locations. Usage is similar to cp , but there are a few key differences to note.
To copy a single file, enter the following into a terminal:
- The –a option means all, and is included with rsync commands – this preserves subdirectories, symbolic links, and other metadata.
- Replace the my_file.txt file in the working directory.
- Replace /new_directory/ with the destination.
- Using my_file_backup.txt as the target indicates the file will be renamed during the copy.
To copy a directory with rsync, enter the following:
This copies the contents of the /etc/docker/ directory to /home/backup/docker/. Make sure to keep the slashes. Omitting the slash on the source directory will copy the contents into a subdirectory.
To omit files from being copied, check out our guide on how to exclude files and directories in data transfer using rsync command.
Other Options
The ls command is a handy partner to the cp command in Linux.
To list the contents of a directory enter the command:
The example above displays all the files in /directory. Use this command after copying to verify the files were copied successfully.
To change directories, use cd and the name of the directory. For example:
The command prompt will change to display that you’ve changed directories.
Now you understand how to copy files in Linux. The cp command is a versatile and powerful tool for managing and backing up files.
Источник