- Access Linux filesystems in Windows and WSL 2
- Getting started
- Accessing these files with File Explorer
- Limitations
- Give us your feedback!
- How do I access the WSL Linux file system from Windows?
- 6 Answers 6
- How to remotely control Linux Systems from Windows
- Why establish a remote connection to Linux from Windows?
- Linux Ubuntu:
- Find the IP address:
- Method 1:Remote Access using SSH (Secure Shell)
- Method 2:Using RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
- Method 3:Setting up a connection using Virtual Network Connection (VNC)
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Zeeman Memon
- Frequently Asked Questions about Windows Subsystem for Linux
- What is Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)?
- Who is WSL for?
- What can I do with WSL?
- Could you describe a typical development workflow that incorporates WSL?
- What is Bash?
- How does this work?
- Why would I use WSL rather than Linux in a VM?
- Why would I use, for example, Ruby on Linux instead of on Windows?
- What does this mean for PowerShell?
- Can I run ALL Linux apps in WSL?
- What Windows SKUs is WSL included in?
- What processors does WSL support?
- How do I access my C: drive?
- How do I set up Git Credential Manager? (How do I use my Windows Git permissions in WSL?)
- How do I use a Windows file with a Linux app?
- Are files in the Linux drive different from the mounted Windows drive?
- Why are there so many errors when I run apt-get upgrade?
- How do I uninstall a WSL Distribution?
- Why does ping generate permission denied errors?
- Why do I get «Error: 0x80040154» when I run bash.exe after upgrading Windows?
- How do I change the display language of WSL?
- Why do I not have internet access from WSL?
- How do I access a port from WSL in Windows?
- How can I back up my WSL distros, or move them from one drive to another?
- Where can I provide feedback?
Access Linux filesystems in Windows and WSL 2
September 10th, 2020
Starting with Windows Insiders preview build 20211, WSL 2 will be offering a new feature: wsl —mount . This new parameter allows a physical disk to be attached and mounted inside WSL 2, which enables you to access filesystems that aren’t natively supported by Windows (such as ext4).
So, if you’re dual booting with Windows & Linux using different disks, you can now access your Linux files from Windows!
Getting started
To mount a disk, open a PowerShell window with administrator privileges and run:
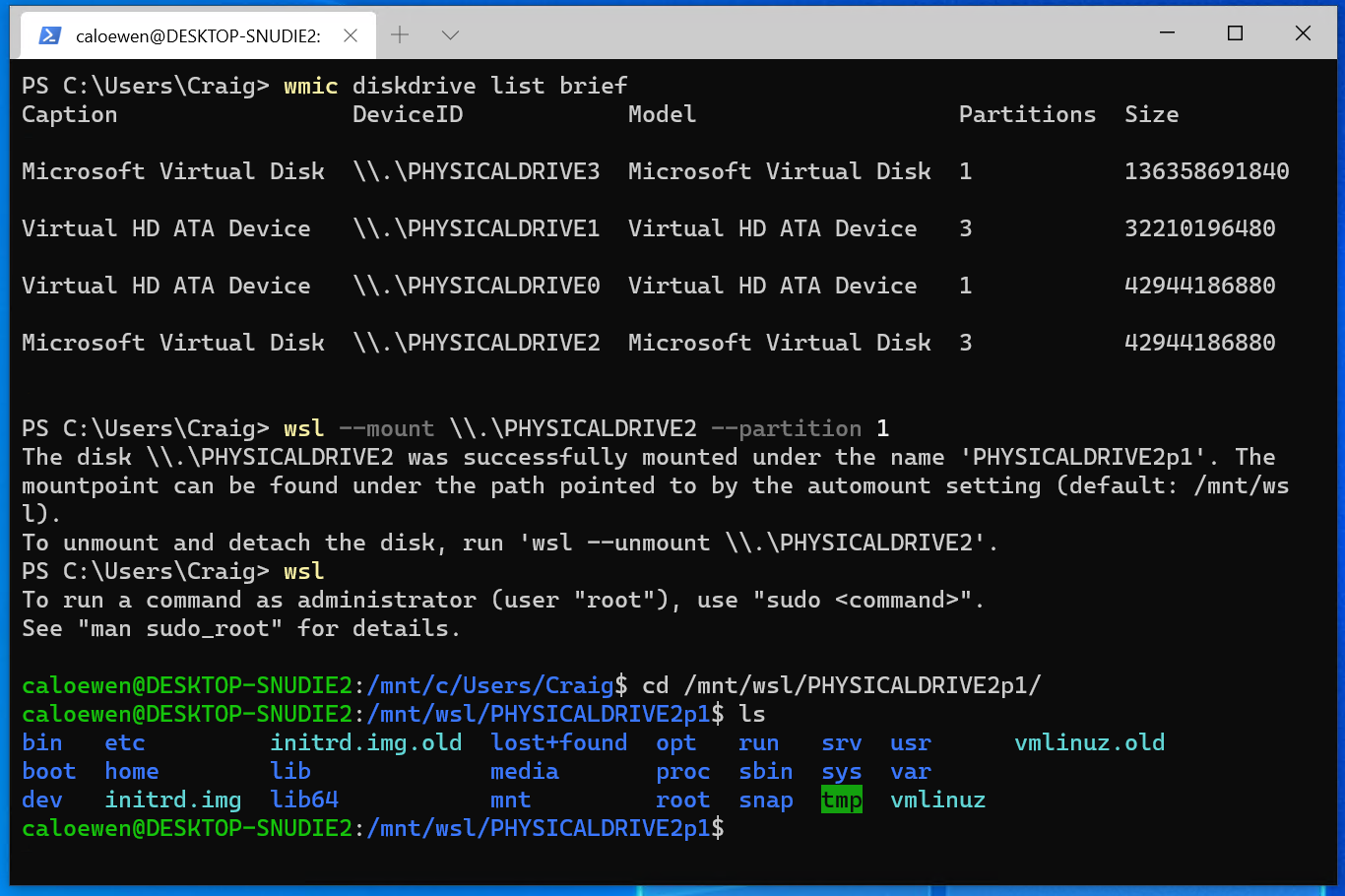
To list the available disks in Windows, run:
To unmount and detach the disk from WSL 2, run
The disks paths are available under the ‘DeviceID’ columns. Usually under the \\.\\\.\PHYSICALDRIVE* format. Below is an example of mounting a specific partition of a given hard disk into WSL and browsing its files.
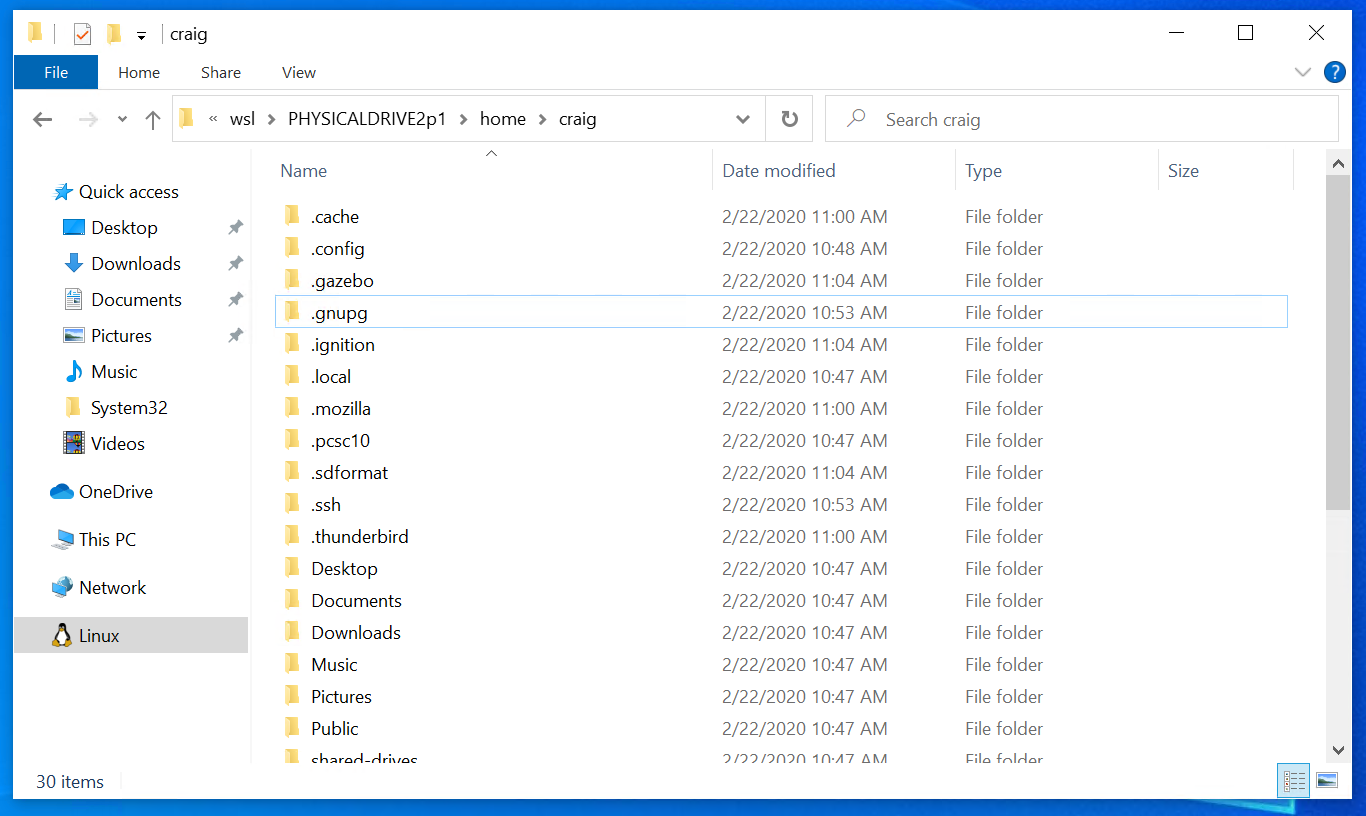
Accessing these files with File Explorer
Once mounted, it’s also possible to access these disks through the Windows explorer by navigating to \wsl$ and then to the mount folder.
Limitations
By default, wsl —mount attempts to mount the disk as ext4. To specify a filesystem, or for more advanced scenarios, check out Mount a disk in WSL 2.
Also please note that this feature comes with the limitation that only physical disks can be attached to WSL 2. At this time, it’s not possible to attach a single partition. More details on the limitations here.
Give us your feedback!
If you run into any issues, or have feedback for our team please file an issue on our Github , and if you have general questions about WSL you can find all of our team members that are on Twitter on this twitter list.
How do I access the WSL Linux file system from Windows?
I found that static files served from a Rails application running in /home/pupeno/projectx take more or less half as much time than the ones served from /mnt/c/Users/pupeno/projectx . It’s almost acceptable. I tried webrick and puma (as well as passenger and unicorn, which don’t work yet).
So, if I’m going to host my source code in /home/pupeno , how do I access from Windows applications such as RubyMine?
For the record, this is the application being served from the Windows file system:
and this is the Linux file system:
6 Answers 6
PM for Windows Command-Line here:
However, as of Windows 10 build 1903 (March 2019), we (finally!) exposed your distros’ filesystems to Windows!
Look forward to hearing how you get on with this feature. If you find any problems, please file issues on the WSL GitHub repo here: https://github.com/microsoft/wsl.
WSL mounts Windows partitions under /mnt . For example, you can modify files in c:\work on the mounted Windows filesystem by referencing them as /mnt/c/work .
Windows apps (cmd, file manager, etc), can access files in WSL in read-only mode by prepending with %LocalAppData%\lxss . Copying a file from the Windows filesystem to the WSL directories renders it unreadable, with a cryptic general I/O error . Files created in %LocalAppData%\lxss from Windows are not visible to WSL. Files created from WSL can be modified in Windows, and the modified file can subsequently be accessed by WSL.
How to remotely control Linux Systems from Windows
Why establish a remote connection to Linux from Windows?
Suppose you are running a business, and you have a meeting with board members in about 10 minutes. All of a sudden, you remember that your presentation file is on your home system; remote access can potentially save the day.
Or you are running a windows system in one location and your Linux system in another room, and you want to run some commands on your Linux or retrieve some files from your Linux, and your Linux is inaccessible, or you are just too lazy. Either way, in all cases, remote access provides great convenience and saves much time.
Linux Ubuntu:
Now out of all the popular Linux distros, Ubuntu is by far the most popular one. All of the other Linux distros combined make up a total of a mere 35% of Ubuntu (google search trends). Upon searching Linux, 161 million results appear, while the next most popular Linux distros i.e., the Debian Linux, has a mere 65.9 million search results, so keeping in mind the above stats, I will be using Ubuntu for this tutorial. To establish the connection, you would need to access the Ubuntu machine physically. But don’t worry, this is a one-time thing.
There are many methods through which you can remotely access your Linux from windows. Here I will be sharing three ways through which you can access remotely control Linux Systems from Windows.
Find the IP address:
Regardless of what method you use, finding the IP address of your system is required almost in every case. Following is an easy way to find the IP of your Linux system.
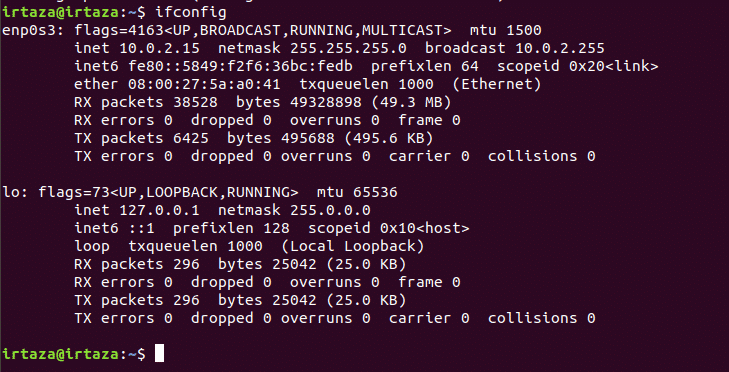
Go to the terminal in your Linux machine and type the following command:
Now enter the following command:
After writing the above command, your terminal window will look like this
You will find your IP address next to “inet” in the first section. In this case, as you can see from the above screenshot, the IP address is “10.0.2.15”
If the method mentioned above doesn’t work for you, you can try the following ways:
In the terminal, write the following command. Remember, this works for some of the Linux versions like Ubuntu.
Method 1:Remote Access using SSH (Secure Shell)
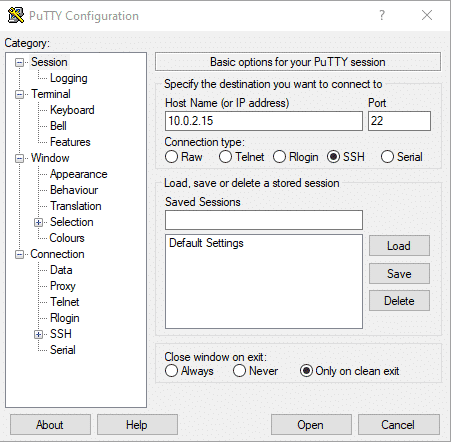
For this method, you should install the PuTTY software, as it’s better than using windows default SSH function. PuTTY establishes an SSH connection between your Linux and your Windows desktop, which gives you access to the Linux terminal.
After Installing the PuTTY software write the name of your Linux system, or it’s IP address under the “Host Name (or IP address)” label. Make sure to set the connection to SSH if it isn’t. Now click open. And voila, you now have access to the Linux command line.
Note: This will give only you access to the terminal, i.e., there will be no mouse control. Still, this is useful to install software using Terminal commands
Method 2:Using RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
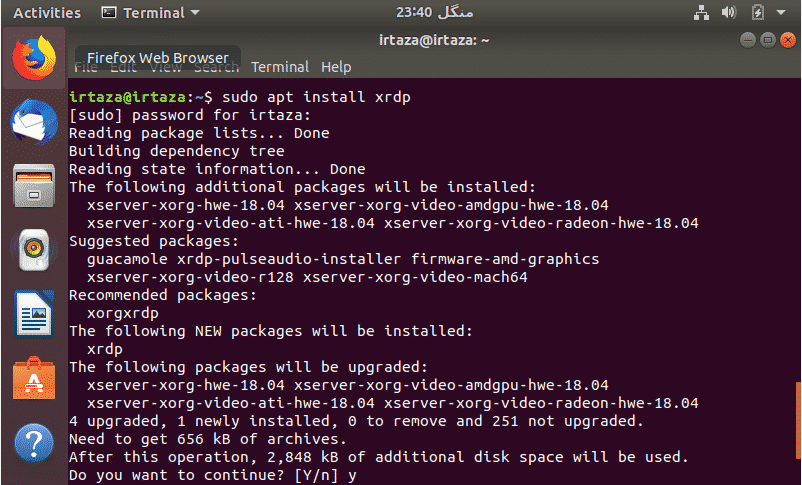
RDP is the easiest method so far. The RDP tool is already installed in the windows. So the windows system doesn’t require any work (software-wise). However, this is not the case for your Linux system. On your Linux system, you will need to install XRDP tool. For this open the terminal (Ctrl+ Alt+ T) and type the following command
Press “y” and hit enter. It will then continue to install.
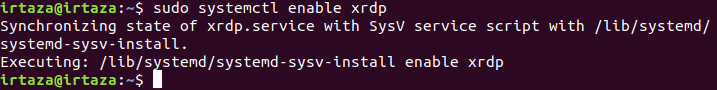
The first command will install the XRDP tool. The second command will allow the auto-enable on startup option. In other words, the xrdp tool will automatically start when the Linux boots. After this process completes. Go to your windows system and in search bar type “RDP.” Click on the “Remote Desktop App.”
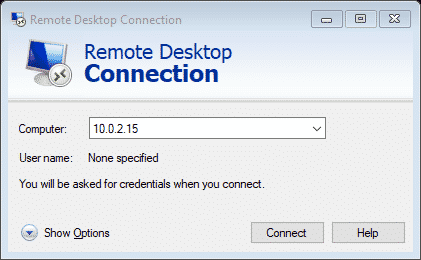
Type the IP address of your Linux system adjacent to the “Computer ” label, and click connect
Enter the Username and the Password of your Linux system.
TroubleShooting: Although connecting through RDP is the easiest method for remote connecting, some problems occur during connecting with Ubuntu. This started happening after the Ubuntu 18.4 LTS release. Linux doesn’t like it when it is accessed remotely when the user is logged in. So a simple solution is to try RDP after logging out of your Linux
Method 3:Setting up a connection using Virtual Network Connection (VNC)
You can also connect using VNC. As mention above, SSH provides access to the terminal (no mouse control). VNC provides access to the Linux desktop (full mouse control). However, there is some prerequisite for connecting using this method, i.e., you have to install some VNC software.
Go to your Linux system and type the following command to make sure it’s up to date
Now input the following command
Now create a password for your connection. You will be given a desktop number, mostly 1. Remember this number.
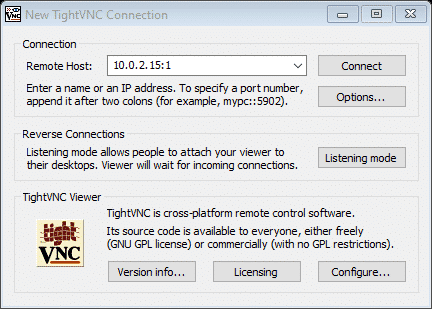
After this, install the VNC client on windows. These TightVNC tools are installed in bundles, so once installed, go to the windows search bar and search “TightVNC Viewer. “ Launch the app and enter the IP address of the Linux device.
Now enter the IP of your Linux system followed by the desktop number, as shown in the above screenshot.
Conclusion:
Now that you know these methods, you should know which way is best for your use.
- RDP uses xrdp which is open source
- SSH can be used to remote access the terminal
- VNC can be used instead of RDP, but it’s a little less secure
It is recommended to set up SSH regardless of what method you use as it makes the installation for the other two methods much more easier.
Ubuntu has a built-in remote desktop tool, which is VNC-compatible.
About the author
Zeeman Memon
Hi there! I’m a Software Engineer by degree, Blogger by skills who loves to write about tech, develop websites & do SEO. You can reach out to me on LinkedIn.
Frequently Asked Questions about Windows Subsystem for Linux
What is Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)?
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Windows 10 that enables you to run native Linux command-line tools directly on Windows, alongside your traditional Windows desktop and apps.
See the about page for more details.
Who is WSL for?
This is primarily a tool for developers, especially web developers, those working on open source projects, or deploying to Linux server environments. WSL is for anyone who likes using Bash, common Linux tools ( sed , awk , etc.) and Linux-first frameworks (Ruby, Python, etc.) but also enjoys using Windows productivity tools
What can I do with WSL?
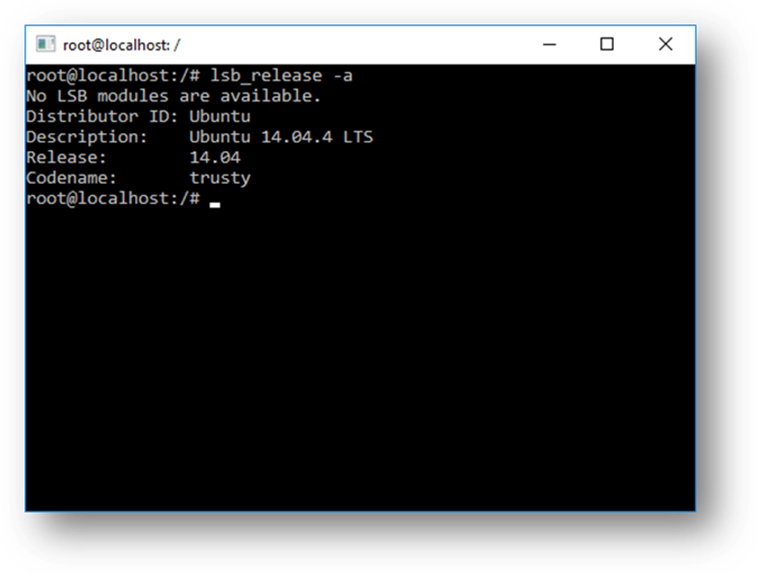
WSL enables you to run Linux in a Bash shell with your choice of distribution (Ubuntu, Debian, OpenSUSE, Kali, Alpine, etc). Using Bash, you can run command-line Linux tools and apps. For example, type lsb_release -a and hit enter; you’ll see details of the Linux distro currently running:
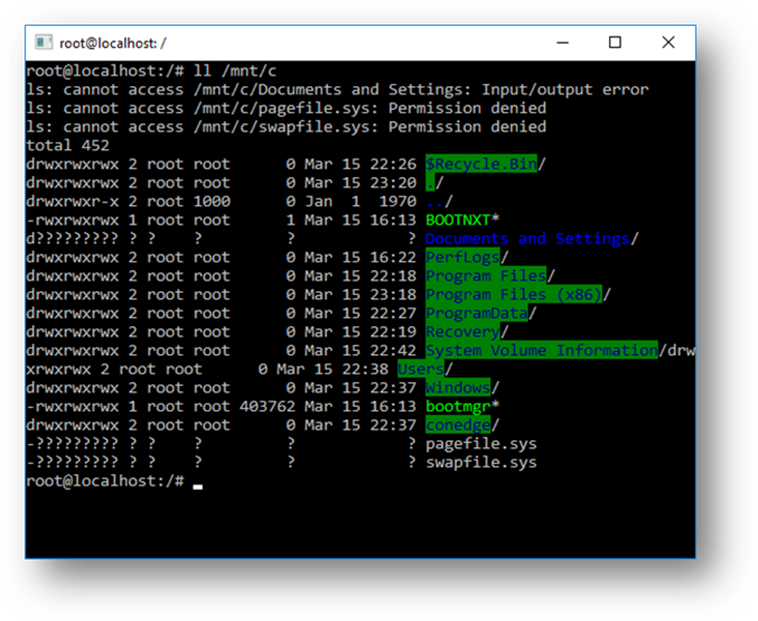
You can also access your local machine’s file system from within the Linux Bash shell – you’ll find your local drives mounted under the /mnt folder. For example, your C: drive is mounted under /mnt/c :
Could you describe a typical development workflow that incorporates WSL?
WSL targets a developer audience with the intent to be used as part of an inner development loop. Let’s say that Sam is creating a CI/CD pipeline (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery) and wants to test it first on a local machine (laptop) before deploying it to the cloud. Sam can enable WSL (& WSL 2 to improve speed and performance), and then use a genuine Linux Ubuntu instance locally (on the laptop) with whatever Bash commands and tools they prefer. Once the development pipeline is verified locally, Sam can then push that CI/CD pipeline up to the cloud (ie Azure) by making it into a Docker container and pushing the container to a cloud instance where it runs on a production-ready Ubuntu VM.
What is Bash?
Bash is a popular text-based shell and command-language. It is the default shell included within Ubuntu and other Linux distros, and in macOS. Users type commands into a shell to execute scripts and/or run commands and tools to accomplish many tasks.
How does this work?
Check out our blog where we go into detail about the underlying technology.
Why would I use WSL rather than Linux in a VM?
WSL requires fewer resources (CPU, memory, and storage) than a full virtual machine. WSL also allows you to run Linux command-line tools and apps alongside your Windows command-line, desktop and store apps, and to access your Windows files from within Linux. This enables you to use Windows apps and Linux command-line tools on the same set of files if you wish.
Why would I use, for example, Ruby on Linux instead of on Windows?
Some cross-platform tools were built assuming that the environment in which they run behaves like Linux. For example, some tools assume that they are able to access very long file paths or that specific files/folders exist. This often causes problems on Windows which often behaves differently from Linux.
Many languages like Ruby and node are often ported to, and run great, on Windows. However, not all of the Ruby Gem or node/NPM library owners port their libraries to support Windows, and many have Linux-specific dependencies. This can often result in systems built using such tools and libraries suffering from build and sometimes runtime errors or unwanted behaviors on Windows.
These are just some of issues that caused many people to ask Microsoft to improve Windows’ command-line tools and what drove us to partner with Canonical to enable native Bash and Linux command-line tools to run on Windows.
What does this mean for PowerShell?
While working with OSS projects, there are numerous scenarios where it’s immensely useful to drop into Bash from a PowerShell prompt. Bash support is complementary and strengthens the value of the command-line on Windows, allowing PowerShell and the PowerShell community to leverage other popular technologies.
Can I run ALL Linux apps in WSL?
No! WSL is a tool aimed at enabling users who need them to run Bash and core Linux command-line tools on Windows.
WSL does not yet support GUI desktops or applications (e.g. Gnome, KDE, etc.) Follow the Command Line Blog for updates.
Also, even though you will be able to run many popular server applications (e.g. Redis), we do not recommend WSL for hosting production services – Microsoft offers a variety of solutions for running production Linux workloads in Azure, Hyper-V, and Docker.
What Windows SKUs is WSL included in?
Windows Subsystem for Linux is available on the desktop version of Windows for Windows 10 Anniversary and Creators update or later.
Beginning in the Fall Creators update WSL will be available on both the desktop and server SKUs of Windows.
What processors does WSL support?
WSL supports x64 and ARM CPUs.
How do I access my C: drive?
Mount points for hard drives on the local machine are automatically created and provide easy access to the Windows file system.
/mnt/ /
Example usage would be cd /mnt/c to access c:\
How do I set up Git Credential Manager? (How do I use my Windows Git permissions in WSL?)
Git Credential Manager enables you to authenticate a remote Git server, even if you have a complex authentication pattern like Azure Active Directory or two-factor authentication. Git Credential Manager integrates into the authentication flow for services like GitHub and, once you’re authenticated to your hosting provider, requests a new authentication token. It then stores the token securely in the Windows Credential Manager. After the first time, you can use git to talk to your hosting provider without needing to re-authenticate. It will just access the token in the Windows Credential Manager.
To set up Git Credential Manager for use with a WSL distribution, open your distribution and enter this command:
Now any git operation you perform within your WSL distribution will use the credential manager. If you already have credentials cached for a host, it will access them from the credential manager. If not, you’ll receive a dialog response requesting your credentials, even if you’re in a Linux console.
How do I use a Windows file with a Linux app?
One of the benefits of WSL is being able to access your files via both Windows and Linux apps or tools.
WSL mounts your machine’s fixed drives under the /mnt/ folder in your Linux distros. For example, your C: drive is mounted under /mnt/c/
Using your mounted drives, you can edit code in, for example, C:\dev\myproj\ using Visual Studio / or VS Code, and build/test that code in Linux by accessing the same files via /mnt/c/dev/myproj .
IMPORTANT NOTE: One of the key limitations of using WSL is that directly accessing/changing files in your Linux distros’ file system using Windows apps or tools is not supported. See: Do not change Linux files using Windows apps and tools
Are files in the Linux drive different from the mounted Windows drive?
Files under the Linux root (i.e. / ) are controlled by WSL which mimics Linux specific behavior, including but not limited to:
- Files which contain invalid Windows filename characters
- Symlinks created for non-admin users
- Changing file attributes through chmod and chown
- File/folder case sensitivity
Files in mounted drives are controlled by Windows and have the following behaviors:
- Support case sensitivity
- All permissions are set to best reflect the Windows permissions
Why are there so many errors when I run apt-get upgrade?
Some packages use features that we haven’t implemented yet. udev , for example, isn’t supported yet and causes several apt-get upgrade errors.
To fix issues related to udev , follow the following steps:
Write the following to /usr/sbin/policy-rc.d and save your changes.
Add execute permissions to /usr/sbin/policy-rc.d
Run the following commands
How do I uninstall a WSL Distribution?
On builds prior to 1709 (16299) open a command prompt and run:
WSL distributions installed from the store can be uninstalled like any other Windows app, by right-clicking on the app tile and clicking Uninstall, or via PowerShell using the Remove-AppxPackage cmdlet).
Why does ping generate permission denied errors?
In WSL builds Properties -> Uncheck «Use legacy console»
Why do I get «Error: 0x80040154» when I run bash.exe after upgrading Windows?
The «Windows Subsystem for Linux» feature may be disabled during a Windows update. If this happens the Windows feature must be re-enabled. Instructions for enabling the «Windows Subsystem for Linux» feature can be found in the Installation Guide.
How do I change the display language of WSL?
WSL install will try to automatically change the Ubuntu locale to match the locale of your Windows install. If you do not want this behavior you can run this command to change the Ubuntu locale after install completes. You will have to relaunch bash.exe for this change to take effect.
The below example changes to locale to en-US:
Why do I not have internet access from WSL?
Some users have reported issues with specific firewall applications blocking internet access in WSL. The firewalls reported are:
- Kaspersky
- AVG
- Avast
- Symantec Endpoint Protection
- F-Secure
In some cases turning off the firewall allows for access. In some cases simply having the firewall installed looks to block access.
How do I access a port from WSL in Windows?
WSL shares the IP address of Windows, as it is running on Windows. As such you can access any ports on localhost e.g. if you had web content on port 1234 you could https://localhost:1234 into your Windows browser.
How can I back up my WSL distros, or move them from one drive to another?
The best way to backup or move your distros is via the export/import commands available in Windows Version 1809 and later. You can export your entire distribution to a tarball using the wsl —export command. You can then import this distro back into WSL using the wsl —import command, which can name a new drive location for the import, allowing you to backup and save states of (or move) your WSL distributions.
Please note that traditional backup services that backup files in your AppData folders (like Windows Backup) will not corrupt your Linux files.
Where can I provide feedback?
You can share feedback and ask questions through multiple channels.
If you have technical issues, or want to request new features please go to our Github issue tracker:
If you’d like to stay up to date with the latest WSL news you can do so with:
- Our command-line team blog
- Twitter. Please follow @craigaloewen on Twitter to learn of news, updates, etc.