- How to delete a user account on Ubuntu Linux
- How to delete a user account on Ubuntu
- Ubuntu delete user account command
- How to verify that user has been deleted from Ubuntu
- Как добавлять и удалять пользователей в Ubuntu 20.04
- Подготовка
- Добавление пользователя из командной строки
- Добавление пользователя через графический интерфейс
- Удаление пользователя из командной строки
- Удаление пользователя через графический интерфейс
- Выводы
- How To: Linux Delete / Remove User Account Using userdel
- Linux delete user command syntax
- userdel command examples
- A Note About /etc/login.defs File
- Complete example to remove user account from Linux
- See also:
- Управление пользователями на Ubuntu и Debian
- Первоначальные требования для системы Debian
- Как добавить нового пользователя?
- Как удалить пользователя?
- Как изменить пароль пользователя?
- How to Add and Delete Users on Ubuntu 18.04
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Adding a User
- Granting a User Sudo Privileges
- Adding the New User to the Sudo Group
- Specifying Explicit User Privileges in /etc/sudoers
- Testing Your User’s Sudo Privileges
- Deleting a User
- Conclusion
How to delete a user account on Ubuntu Linux
How to delete a user account on Ubuntu
- Open the terminal app
- Login to server using the ssh user@server-ip-here command
- Run sudo deluser —remove-home userNameHere command to delete a user account on Ubuntu
- Verify it by running id command
Let us see all commands in details to remove a user account in Ubuntu.
Ubuntu delete user account command
Say you would like to delete a user named ubuntu, run:
$ sudo deluser —remove-home ubuntu
If you want to backup files before removing user account, try:
## create a dir to store backups ##
$ sudo mkdir /oldusers-data
$ sudo chown root:root /oldusers-data
$ sudo chmod 0700 /oldusers-data
$ sudo deluser —remove-home —backup-to /oldusers-data/ ubuntu
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How to verify that user has been deleted from Ubuntu
Use the id command or grep command as follows:
$ id ubuntu
$ grep ‘^ubuntu’ /etc/passwd
Источник
Как добавлять и удалять пользователей в Ubuntu 20.04
Одна из первых задач при подготовке новой системы Ubuntu — это добавление и удаление пользователей. У каждого пользователя могут быть разные уровни разрешений и определенные настройки для различных приложений командной строки и графического интерфейса.
В этой статье объясняется, как добавлять и удалять учетные записи пользователей в Ubuntu 18.04.
Подготовка
Только root или пользователи с привилегиями sudo могут создавать и удалять пользователей.
Новых пользователей можно создать двумя способами:
- Из командной строки.
- Через графический интерфейс.
Добавление пользователя из командной строки
В Ubuntu есть два инструмента командной строки, которые вы можете использовать для создания новой учетной записи: useradd и adduser .
useradd — это утилита низкого уровня. adduser — это сценарий, написанный на Perl, который действует как дружественный интерактивный интерфейс для useradd .
Добавление нового пользователя происходит быстро и легко, просто вызовите команду adduser за которой следует имя пользователя. Например, чтобы создать новую учетную запись пользователя с именем username вы должны запустить:
Вам будет задан ряд вопросов. Введите и подтвердите новый пароль пользователя. Ответить на все остальные вопросы необязательно.
В конце вам будет предложено подтвердить, что введенная вами информация верна.
Команда создаст домашний каталог нового пользователя и скопирует в него файлы из /etc/skel . В домашнем каталоге пользователь может писать, редактировать и удалять файлы и каталоги.
Если вы хотите, чтобы новый пользователь мог выполнять административные задачи, вам необходимо добавить пользователя в группу sudo :
Добавление пользователя через графический интерфейс
Если вас не устраивает командная строка, вы можете добавить новую учетную запись пользователя через графический интерфейс. Для этого выполните следующие действия:
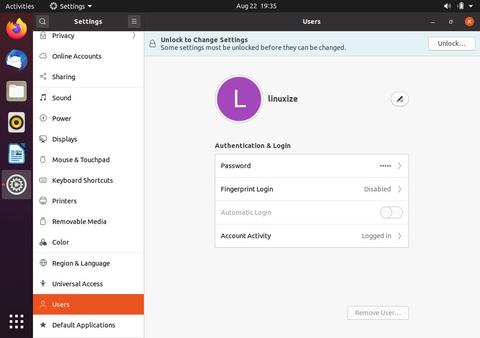
Откройте окно настроек и перейдите на вкладку «Пользователи».
Нажмите кнопку «Разблокировать» и при появлении запроса введите пароль пользователя.
После ввода пароля кнопка «Разблокировать» изменится на зеленую кнопку «Добавить пользователя».
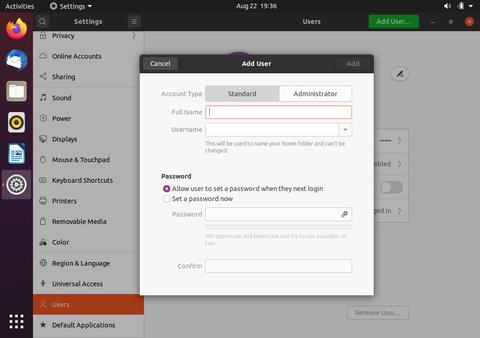
Нажмите кнопку «Добавить пользователя», появится диалоговое окно «Добавить пользователя»:
Выберите, должен ли новый пользователь быть стандартным пользователем или администратором, и введите информацию. После этого нажмите кнопку «Добавить».
Удаление пользователя из командной строки
В Ubuntu вы можете использовать две команды для удаления учетной записи пользователя: userdel и его интерактивный интерфейс deluser .
Чтобы удалить пользователя, вызовите команду deluser и передайте имя пользователя в качестве аргумента:
Приведенная выше команда не удаляет пользовательские файлы.
Если вы хотите удалить пользователя, его домашний каталог и почтовый ящик, используйте флаг —remove-home :
Удаление пользователя через графический интерфейс
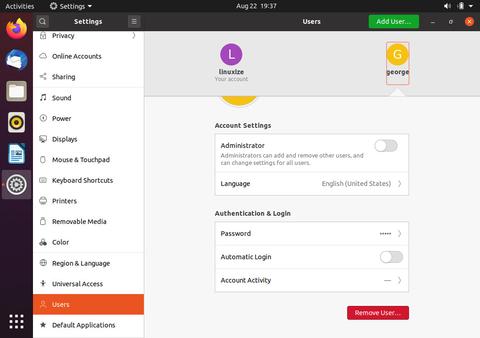
Откройте окно настроек и перейдите на вкладку «Пользователи».
Нажмите кнопку «Разблокировать» и при появлении запроса введите пароль пользователя.
Нажмите на имя пользователя, которое хотите удалить, и в правом нижнем углу вы увидите красную кнопку «Удалить пользователя …».
Нажмите кнопку «Удалить пользователя …», и вам будет предложено сохранить или удалить домашний каталог пользователя. Нажатие на одну из этих кнопок удаляет пользователя.
Выводы
Мы показали вам, как добавлять и удалять пользователей в Ubuntu 20.04. Знание того, как добавлять и удалять пользователей — один из основных навыков, которые должен знать пользователь Linux.
Не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии, если у вас есть вопросы.
Источник
How To: Linux Delete / Remove User Account Using userdel
H ow do I remove a user’s access from my server? How do I delete a user account under Linux operating systems include home directory and running cron jobs?
You need to use the userdel command to delete a user account and related files from user account under Linux operating system. The userdel command must be run as root user on Linux.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux |
| Est. reading time | 4 minutes |
Linux delete user command syntax
The syntax is as follows to remove a user account on Linux.
userdel userName
userdel [options] userName
userdel -r userName
userdel command examples
Let us remove the user named vivek or account named vivek from the local Linux system / server / workstation, enter:
# userdel vivek
Next, delete the user’s home directory and mail spool pass the -r option to userdel for a user named ashish, enter:
# userdel -r ashish
Explains how to delete user account with home directory in Linux
A Note About /etc/login.defs File
Default values are taken from the information provided in the /etc/login.defs file for RHEL (Red Hat) based distros. Debian and Ubuntu Linux based system use /etc/deluser.conf file:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Complete example to remove user account from Linux
The following is recommend procedure to delete a user from the Linux server. First, lock user account, enter:
# passwd -l vivek
OR set the date on which the user account will be disabled (syntax is usermod —expiredate YYYY-MM-DD userNameHere ):
# usermod —expiredate 1 vivek
If user try to login, he or she will get the following message:
Next, backup files from /home/vivek to /nas/backup
# tar -zcvf /nas/backup/account/deleted/v/vivek.$uid.$now.tar.gz /home/vivek/
Please replace $uid, $now with actual UID and date/time. Tye userdel command will not allow you to remove an account if the user is currently logged in. You must kill any running processes which belong to an account that you are deleting, enter:
# pgrep -u vivek
# ps -fp $(pgrep -u vivek)
# killall -KILL -u vivek
Delete at jobs, enter
# find /var/spool/at/ -name «[^.]*» -type f -user vivek -delete
Remove cron jobs, enter:
# crontab -r -u vivek
Delete print jobs, enter:
# lprm vivek
To find all files owned by user vivek, enter:
# find / -user vivek -print
You can find file owned by a user called vivek and change its ownership as follows:
# find / -user vivek -exec chown newUserName:newGroupName <> \;
Finally, delete user account called vivek, enter:
# userdel -r vivek
Sample session:
Fig.01: Delete User Accounts with Home Directory and All Data In Linux
See also:
- Help: Old Employees Accessing The Linux Server.
- /etc/passwd – The basic attributes of users.
- /etc/shadow – The basic attributes of users password.
- /etc/group – The basic attributes of groups.
- Man pages – ps(1)
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Управление пользователями на Ubuntu и Debian
В инструкции описано создание, удаление и изменение пользователей операционной системы Ubuntu или Debian.
Первоначальные требования для системы Debian
Многие из команд в этом руководстве требуют привилегий суперпользователя. Если при использовании команды sudo появляется следующая ошибка:
bash: sudo: command not found
Вам необходимо активировать режим суперпользователя, установить команду sudo и добавить своего пользователя в группу sudo:
su —
apt-get install sudo -y
usermod -aG sudo yourusername
Как добавить нового пользователя?
В Ubuntu и Debian есть два инструмента командной строки, которые вы можете использовать для создания новой учетной записи пользователя: useradd и adduser.
useradd — это низкоуровневая утилита для добавления новых пользователей, а adduser — дружественный интерактивный интерфейс для useradd, написанный на Perl.
Для создания новой учетной записи пользователя операционной системы с именем username с помощью команды adduser, выполните следующую команду:
sudo adduser username
В результате появится диалог, в котором необходимо ввести пароль и дополнительную информацию:
Adding new group `username’ (1000) .
Adding new user `username’ (1000) with group `username’ .
Creating home directory `/home/username’ .
Copying files from `/etc/skel’ .
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Changing the user information for username
Enter the new value, or press ENTER for the default
Full Name []: Name
Room Number []: 100
Work Phone []: 123-45-45
Is the information correct? [Y/n] Y
Команда создает домашний каталог для нового пользователя и скопирует туда файлы из каталога /etc/skel.
По умолчанию членам группы sudo предоставляется доступ sudo.
Если необходимо, чтобы у вновь созданного пользователя были права администратора, добавьте его в группу sudo:
sudo usermod -aG sudo username
Как удалить пользователя?
Существует два инструмента командной строки, которые можно использовать для удаления учетной записи пользователя: userdel и deluser. Рекомендуем использовать команду deluser, так как она более дружественная, чем низкоуровневая userdel.
Чтобы удалить пользователя, не удаляя пользовательские файлы и каталоги, выполните:
sudo deluser username
Если необходимо удалить домашний каталог пользователя и его содержимое, используйте флаг —remove-home:
sudo deluser —remove-home username
В результате появится следующее сообщение:
Removing user `username’ .
Warning: group `username’ has no more members.
Как изменить пароль пользователя?
Для изменения собственного пароля используйте команду passwd без дополнительных аргументов:
В системном диалоге необходимо будет ввести старый пароль и указать новый:
Changing password for username.
(current) UNIX password:
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Для изменения пароля для другого пользователя необходимы права администратора и имя пользователя:
Источник
How to Add and Delete Users on Ubuntu 18.04
Published on September 12, 2019
Not using Ubuntu 18.04?
Choose a different version or distribution.
Introduction
Adding and removing users on a Linux system is one of the most important system administration tasks to familiarize yourself with. When you create a new system, you are often only given access to the root account by default.
While running as the root user gives you complete control over a system and its users, it is also dangerous and can be destructive. For common system administration tasks, it is a better idea to add an unprivileged user and carry out those tasks without root privileges. You can also create additional unprivileged accounts for any other users you may have on your system. Each user on a system should have their own separate account.
For tasks that require administrator privileges, there is a tool installed on Ubuntu systems called sudo . Briefly, sudo allows you to run a command as another user, including users with administrative privileges. In this guide we will cover how to create user accounts, assign sudo privileges, and delete users.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this guide, you will need:
- Access to a server running Ubuntu 18.04. Ensure that you have root access to the server. To set this up, follow our Initial Server Setup Guide for Ubuntu 18.04.
Adding a User
If you are signed in as the root user, you can create a new user at any time by typing:
If you are signed in as a non-root user who has been given sudo privileges, you can add a new user by typing:
Either way, you will be asked a series of questions. The procedure will be:
- Assign and confirm a password for the new user
- Enter any additional information about the new user. This is entirely optional and can be skipped by hitting ENTER if you don’t wish to utilize these fields.
- Finally, you’ll be asked to confirm that the information you provided was correct. Enter Y to continue.
Your new user is now ready for use. You can now log in using the password that you entered.
If you need your new user to have access to administrative functionality, continue on to the next section.
Granting a User Sudo Privileges
If your new user should have the ability to execute commands with root (administrative) privileges, you will need to give the new user access to sudo . Let’s examine two approaches to this problem: adding the user to a pre-defined sudo user group, and specifying privileges on a per-user basis in sudo ’s configuration.
Adding the New User to the Sudo Group
By default, sudo on Ubuntu 18.04 systems is configured to extend full privileges to any user in the sudo group.
You can see what groups your new user is in with the groups command:
By default, a new user is only in their own group which adduser creates along with the user profile. A user and its own group share the same name. In order to add the user to a new group, we can use the usermod command:
The -aG option here tells usermod to add the user to the listed groups.
Specifying Explicit User Privileges in /etc/sudoers
As an alternative to putting your user in the sudo group, you can use the visudo command, which opens a configuration file called /etc/sudoers in the system’s default editor, and explicitly specify privileges on a per-user basis.
Using visudo is the only recommended way to make changes to /etc/sudoers , because it locks the file against multiple simultaneous edits and performs a sanity check on its contents before overwriting the file. This helps to prevent a situation where you misconfigure sudo and are prevented from fixing the problem because you have lost sudo privileges.
If you are currently signed in as root, type:
If you are signed in as a non-root user with sudo privileges, type:
Traditionally, visudo opened /etc/sudoers in the vi editor, which can be confusing for inexperienced users. By default on new Ubuntu installations, visudo will instead use nano , which provides a more convenient and accessible text editing experience. Use the arrow keys to move the cursor, and search for the line that looks like this:
Below this line, add the following highlighted line. Be sure to change newuser to the name of the user profile that you would like to grant sudo privileges:
Add a new line like this for each user that should be given full sudo privileges. When you are finished, you can save and close the file by hitting CTRL+X , followed by Y , and then ENTER to confirm.
Testing Your User’s Sudo Privileges
Now, your new user is able to execute commands with administrative privileges.
When signed in as the new user, you can execute commands as your regular user by typing commands as normal:
You can execute the same command with administrative privileges by typing sudo ahead of the command:
You will be prompted to enter the password of the regular user account you are signed in as.
Deleting a User
In the event that you no longer need a user, it is best to delete the old account.
You can delete the user itself, without deleting any of their files, by typing the following command as root:
If you are signed in as another non-root user with sudo privileges, you could instead type:
If, instead, you want to delete the user’s home directory when the user is deleted, you can issue the following command as root:
If you’re running this as a non-root user with sudo privileges, you would instead type:
If you had previously configured sudo privileges for the user you deleted, you may want to remove the relevant line again by typing:
Or use this if you are a non-root user with sudo privileges:
This will prevent a new user created with the same name from being accidentally given sudo privileges.
Conclusion
You should now have a fairly good handle on how to add and remove users from your Ubuntu 18.04 system. Effective user management will allow you to separate users and give them only the access that they are required to do their job.
For more information about how to configure sudo , check out our guide on how to edit the sudoers file here.
Источник