- 7 Ways to Create a File in Linux Terminal
- 1) Create a file with touch command
- 2) Create a file with cat command
- 3) Create a file with echo command
- 4) Create a file with printf command
- 5) Create a file with nano text editor
- 6) Create a file with vi text editor
- 7) Create a file with vim text editor
- Conclusion
- Как создать файл в терминале
- 1. Редактор nano
- 2. Редактор Vi
- 3. Оператор перенаправления >
- 4. Оператор перенаправления вывода >>
- 5. Оператор перенаправления 2>
- 6. Оператор перенаправления и head
- 7. Команда cp
- 8. touch
- 9. Утилита dd
- Создание специальных файлов в Linux
- Выводы
- How to Create a file in Ubuntu Linux using command & GUI
- Create a file in Ubuntu 20.04 using GUI & right-click
- Command-Line to create a new document on Ubuntu Linux
- 5 Best Ways to create a new file on Linux
- 1. Using Touch command
- 2. Nano Editor
- 3. Vim or Vi text editor
- 4. Echo command using Redirect operator
- 5. Cat command
7 Ways to Create a File in Linux Terminal
In this tutorial, I will show you how to create a file from a Linux terminal. There are many text editors like (vim, nano, vi) and many commands like (cat, echo, printf, touch) to create a file in the Linux operating system via command line. Here will explain the following linux tools.
1) Create a file with touch command
We will use touch command with any extension to create file, this command will create an empty file touch.txt in your current directory as an example below.
To see the file type command below.
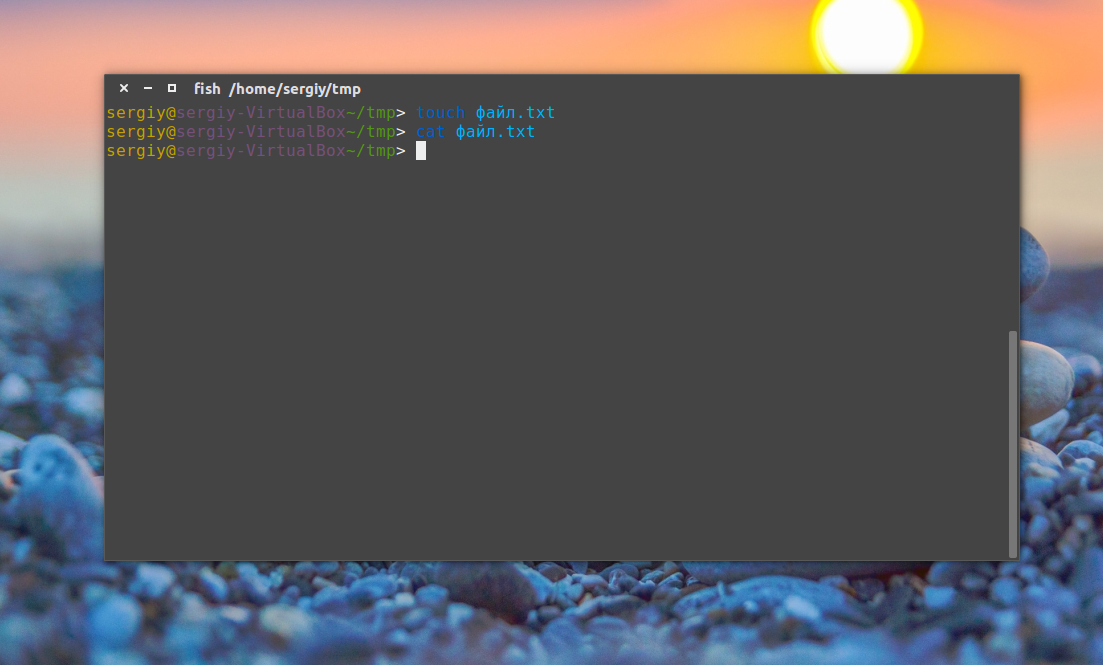
2) Create a file with cat command
We will use cat command to create file, this command will create an empty file cat.txt in your current directory as an example below, but you must add text in the file.
Add the text below.
To save the file hit Ctrl + d , and to see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use cat command to open it.
3) Create a file with echo command
We will use echo command to create file, this command will create a file echo.txt in your current directory as an example below, but you should add text in the line command.
To see the file,type command below.
To open the file, we will use cat command to open it.
4) Create a file with printf command
We will use printf command to create file, this command will create a file printf.txt in your current directory as an example below, but you should add text in the line command.
To see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use cat command to open it.
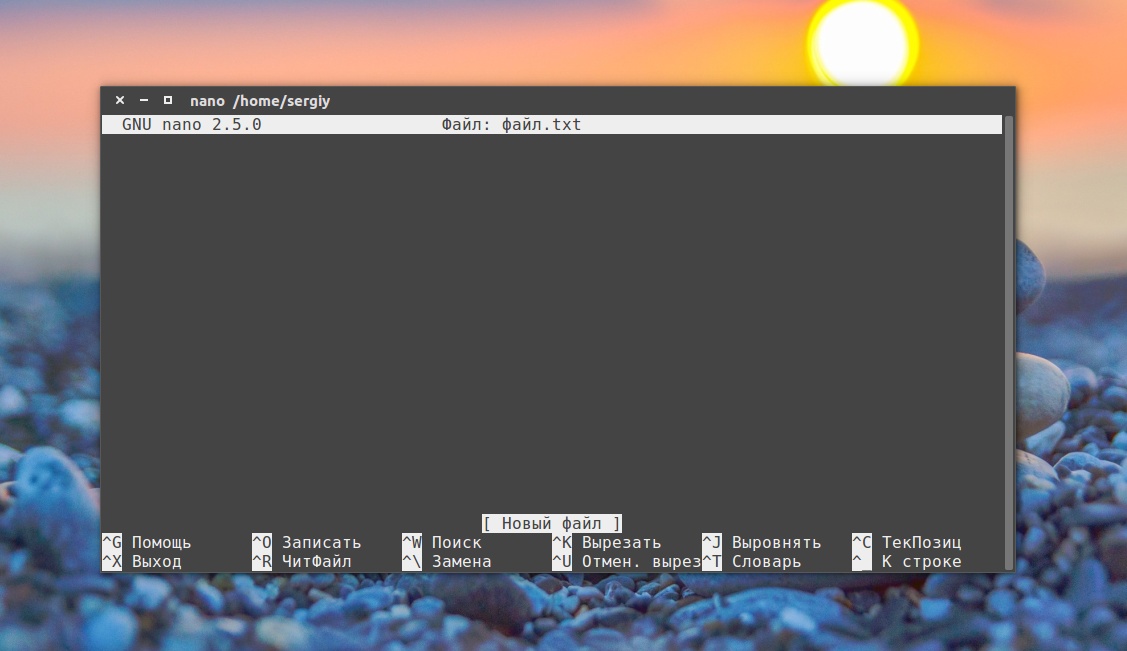
5) Create a file with nano text editor
To create a file using nano text editor, first install it, after that type command below and the text editor will be opened to adding text.
Add the text below.
To save the file type Ctrl + x and type y , to see the file type command below.
To open the file, We will use nano command to open it.
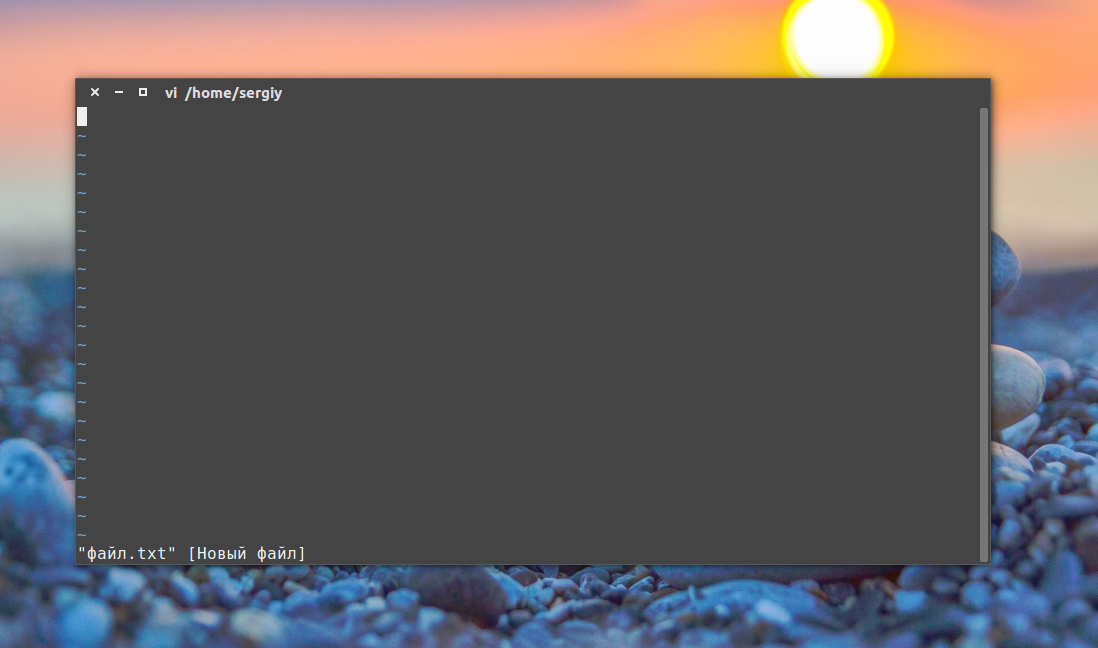
6) Create a file with vi text editor
To create a file using vi text editor, type command below and the text editor will open the file, but you can’t add any text before converting it to insert mode by typing i character.
Add the text below.
To save the file and exit hit Esc after that :wq , To see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use vi command to open it.
7) Create a file with vim text editor
To create a file using vim text editor, type command below and the text editor will open the file, but you can’t add any text before converting it to insert mode by typing i character.
Add the text below.
To save the file and exit hit Esc after that :wq , to see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use vim command to open it.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned the different ways to create a file from Linux terminal. Hope you enjoyed reading and please leave your comments in the below comment section.
Источник
Как создать файл в терминале
Философия Linux гласит — всё в системе есть файл. Мы ежедневно работаем с файлами, и программы, которые мы выполняем, — тоже файлы. В разных случаях нам может понадобиться создать в системе файлы определённого типа. Если вам интересно, какие типы файлов в Linux можно создать, смотрите отдельную статью.
Конечно, всё очень просто делается с помощью мышки и файлового менеджера. Но если вы дружите с клавиатурой, создать файл через терминал Linux намного быстрее и, как вы увидите, эффективнее. В терминале вы можете не только создавать пустые файлы, но и создавать файл с уже готовым содержимым, файлы определённого размера, и с нужными метаданными.
Как всё это делать, вы узнаете из этой статьи. Мы рассмотрим все доступные средства создания файлов в терминале Linux. Поехали!
1. Редактор nano
Самый распространённый способ создать текстовый файл в Linux — это использовать консольные текстовые редакторы. Например nano. После ввода команды открывается редактор, и вы прописываете нужный текст, например:
2. Редактор Vi
Тот же принцип, но программа намного серьёзнее:
Если вы в первый раз столкнулись с vim, то предупрежу — это необычный редактор. Здесь есть два режима: режим вставки и командный. Переключаться между ними можно с помощью кнопки Esc. Для выхода из редактора в командном режиме наберите :q, для сохранения файла — :w. Вообще, Vim — очень полезный инструмент. Чтобы узнать побольше о его возможностях и выучить основы, выполните: vimtutor.
Понятное дело, в этом пункте можно говорить и о других редакторах, в том числе и с графическим интерфейсом. Но мы их опустим и перейдём к другим командам создания файла в Linux.
3. Оператор перенаправления >
Это, наверное, самая короткая команда для создания файла в Linux:
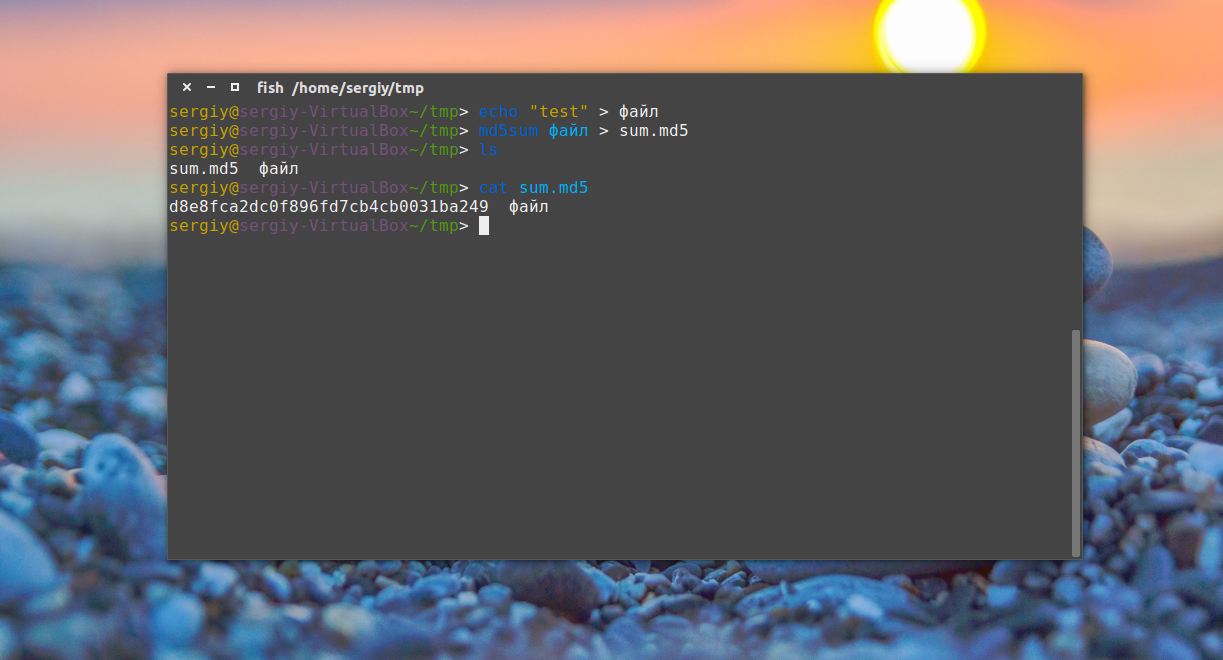
Оператор оболочки для перенаправления вывода позволяет записать вывод любой команды в новый файл. Например, можно подсчитать md5 сумму и создать текстовый файл в Linux с результатом выполнения.
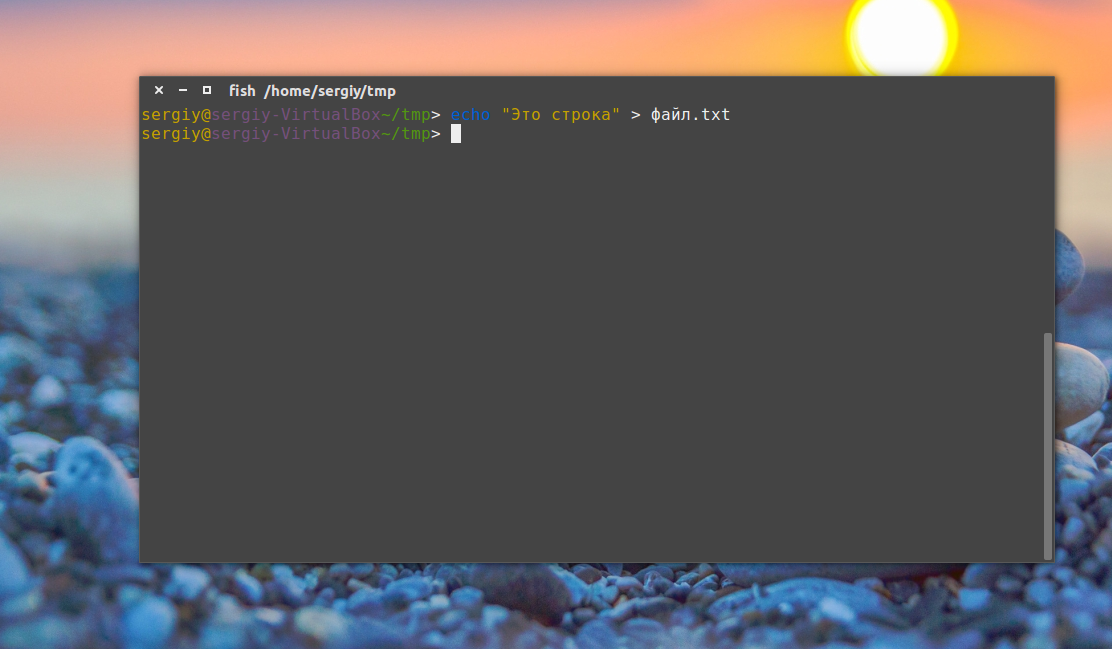
Это рождает ещё несколько способов создания файла в Linux, например, выведем строку в файл с помощью команды echo:
echo «Это строка» > файл.txt
Этот способ часто используется для создания конфигурационных файлов в Linux, так сказать, на лету. Но заметьте, что sudo здесь работать не будет. С правами суперпользователя выполниться echo, а запись файла уже будет выполнять оболочка с правами пользователя, и вы всё равно получите ошибку Access Denied.
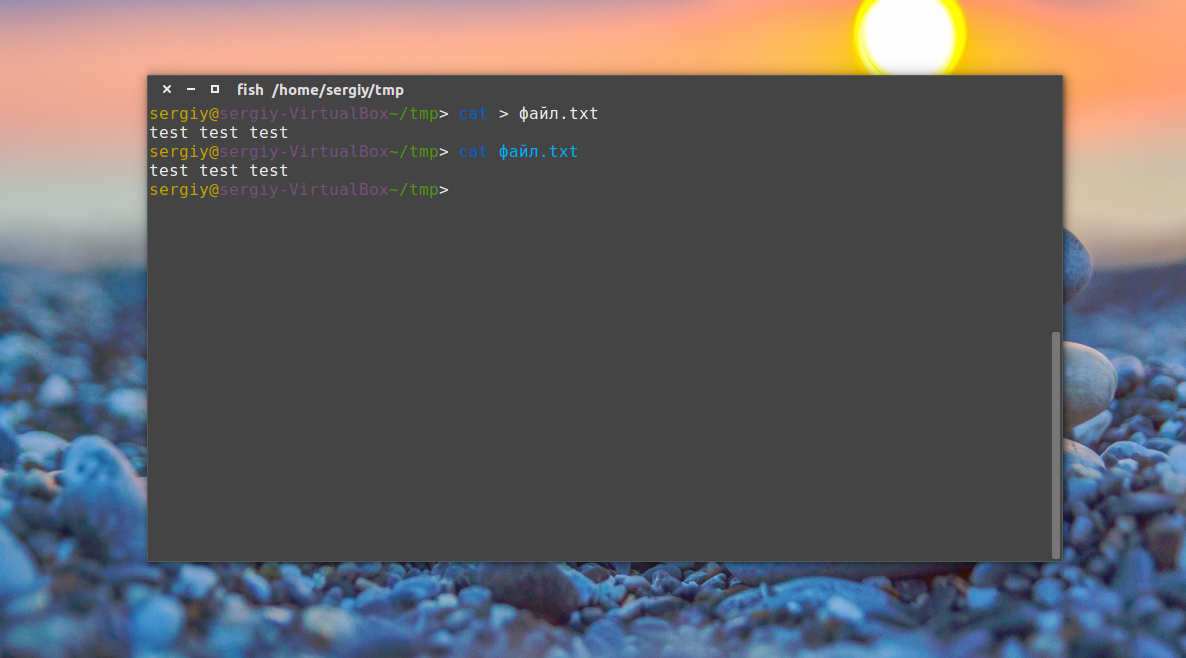
Ещё тем же способом можно сделать примитивный текстовый редактор для создания файла. Утилита cat без параметров принимает стандартный ввод, используем это:
После выполнения команды можете вводить любые символы, которые нужно записать в файл, для сохранения нажмите Ctrl+D.
А ещё есть утилита printf, и здесь она тоже поддерживает форматирование вывода:
printf «Это %d текстовая строка\n» 1 > файл
Этот способ создать файл в Linux используется довольно часто.
4. Оператор перенаправления вывода >>
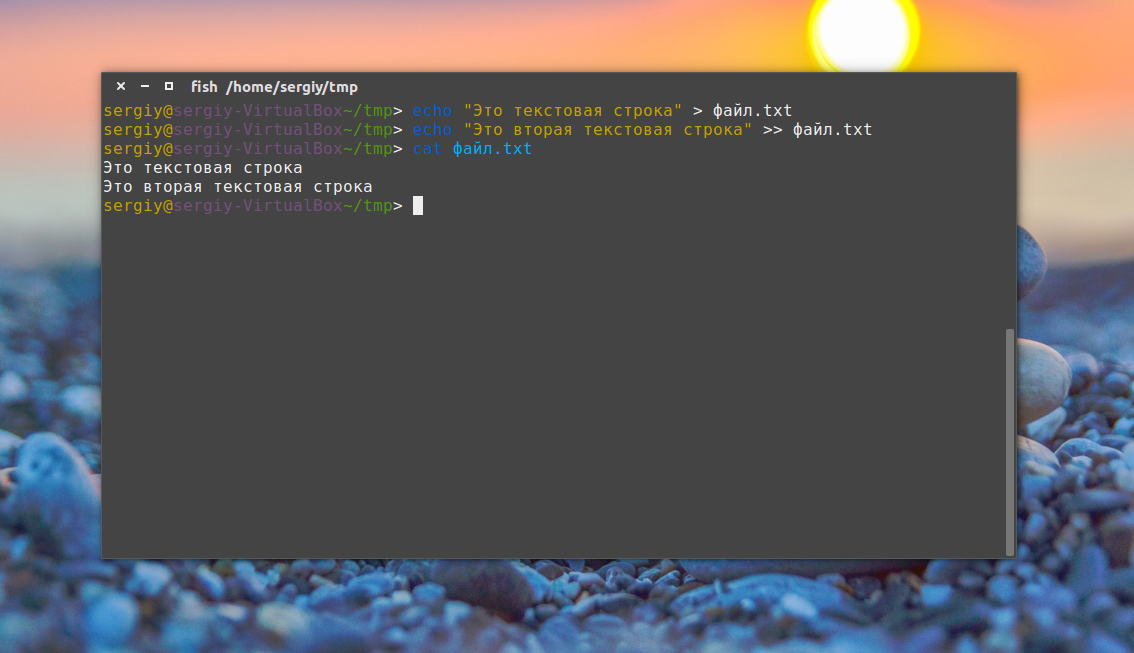
Также можно не только перезаписывать файл, а дописывать в него данные, с помощью перенаправления оператора >>. Если файла не существует, будет создан новый, а если существует, то строка запишется в конец.
echo «Это текстовая строка» > файл.txt
$ echo «Это вторая текстовая строка» >> файл.txt
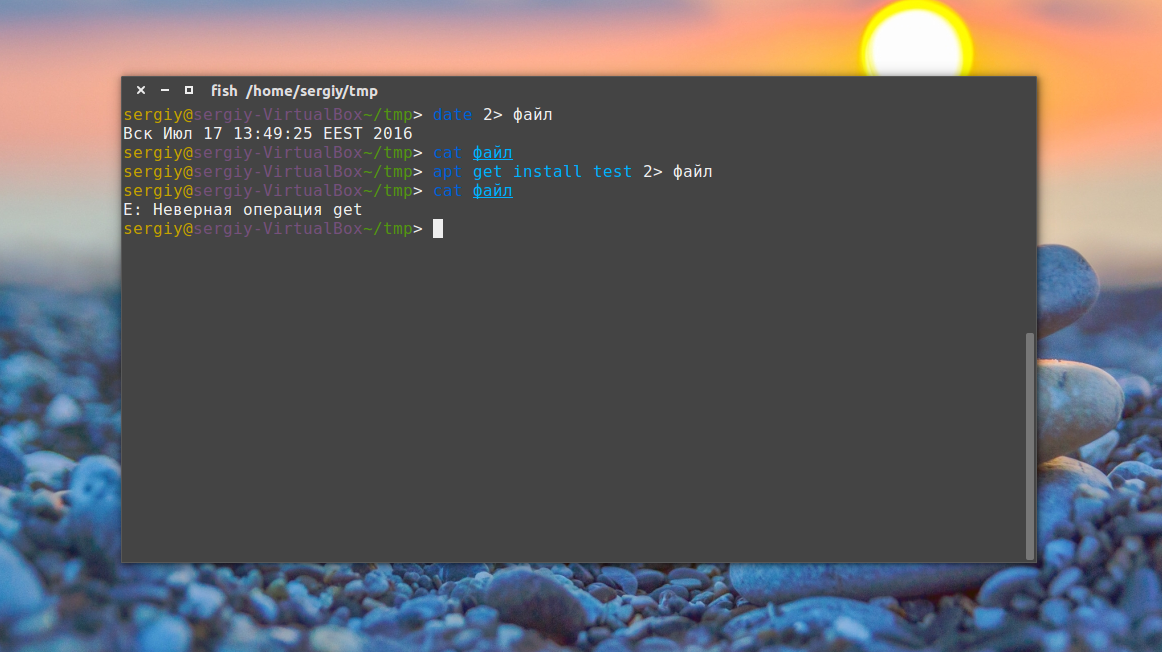
5. Оператор перенаправления 2>
Первые два оператора перенаправления вывода команды в файл использовали стандартный вывод. Но можно создать файл в терминале Ubuntu и перенаправить в него вывод ошибок:
Если команда не выдает ошибок, файл будет пустым.
6. Оператор перенаправления и head
С помощью команды head можно выбрать определённый объем данных, чтобы создать текстовый файл большого размера. Данные можно брать, например, с /dev/urandom. Для примера создадим файл размером 100 мегабайт:
base64 /dev/urandom | head -c 100M > файл
7. Команда cp
Команда cp используется для копирования файлов в Linux. Но с её помощью можно и создать файл. Например, чтобы создать пустой файл, можно просто скопировать /dev/null:
cp /dev/null файл
8. touch
Вот мы и подобрались к непосредственному созданию файлов через терминал, для этого в Linux есть специальная утилита touch. Она позволяет создать пустой файл в Linux, при этом указывать дату создания, права доступа и другие метаданные.
Чтобы создать пустой файл Linux, просто наберите:
Можно создать несколько пустых файлов сразу:
touch файл1 файл2
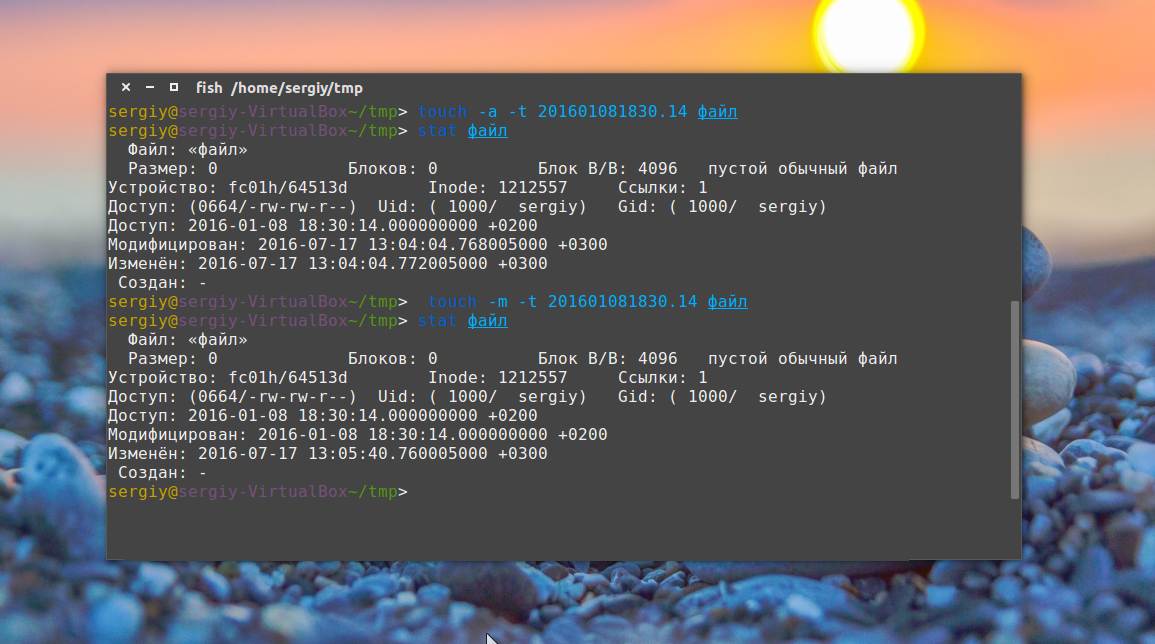
Опция -t позволяет установить дату создания. Дата указывается опцией -t в формате YYMMDDHHMM.SS. Если не указать, будет установлена текущая дата. Пример:
touch -t 201601081830.14 файл
Можно использовать дату создания другого файла:
touch -r шаблон файл
Также можно установить дату последней модификации, с помощью опции -m:
touch -m -t 201601081830.14 файл
Или дату последнего доступа:
touch -a -t 201601081830.14 файл
Чтобы посмотреть, действительно ли задаётся информация, которую вы указали, используйте команду stat:
9. Утилита dd
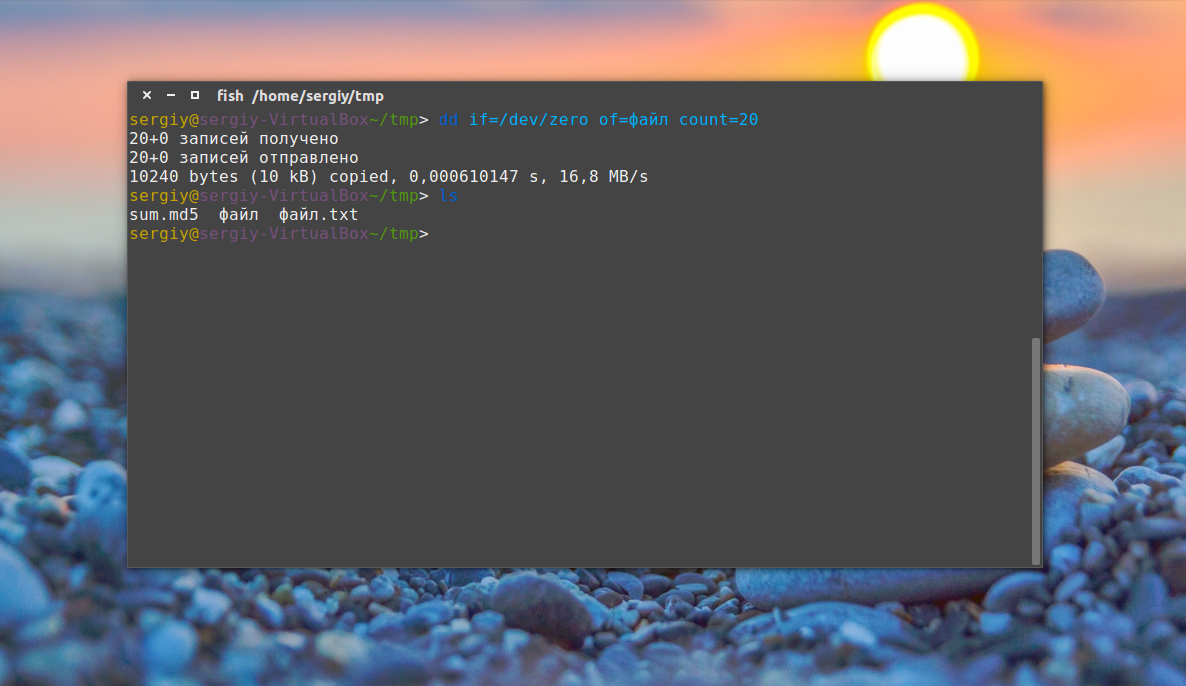
Это утилита для копирования данных из одного файла в другой. Иногда необходимо создать файл определённого размера в Linux, тогда можно просто создать его на основе /dev/zero или /dev/random, вот так:
dd if=/dev/zero of=
Параметр if указывает, откуда брать данные, а of — куда записывать, count — необходимый размер. Ещё можно указать размер блока для записи с помощью bs, чем больше размер блока, тем быстрее будет выполняться копирование.
Создание специальных файлов в Linux
В Linux, кроме выше рассмотренных обычных текстовых и бинарных файлов, существуют ещё и специальные файлы. Это файлы сокетов и туннелей. Их нельзя создать обычными программами, но для этого существуют специальные утилиты, смотрите подробнее в статье, ссылку на которую я дал вверху.
Выводы
Это были все возможные команды для создания файла в Linux. Если вы знаете другие, которые следовало бы добавить в статью — поделитесь в комментариях.
Источник
How to Create a file in Ubuntu Linux using command & GUI
Creating files on Linux is not a cumbersome task, however those who are new to it or just shifting from Windows to Ubuntu like systems, they may face some problem to create files using command line especially.
Well, even on Linux anybody can create files and folders using a graphical user interface that works just like a charm. Simply right-click and select the New folder or New Document for text files. However, this is not true with every Linux system. For example on Ubuntu right-clicking will give you the only option to create a new folder, thus when it comes to creating a text using GUI you will get stuck.
Therefore, to create a file on Ubuntu Linux, there are two options either using the command terminal or enable the “new document” option in the right-click context menu of Ubuntu. We will show both the methods.
Create a file in Ubuntu 20.04 using GUI & right-click
Although here we are using Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, the steps given below are applicable for Ubuntu 19.04/18.04 and previous versions.
By default, when we right-click inside anywhere in Ubuntu Nautilus file manager, it will not give us the “New document” option. Thus, to get this missing option, we need to run a command.
- Open Ubuntu command terminal.
- Run command- touch
/Templates/Text\ document
For example, I want to create some text document files on my Linux Desktop, then inside the Desktop folder I will right-click, rest of the below picture can describe.
Command-Line to create a new document on Ubuntu Linux
There are a couple of ways to create an empty file without any content or one with some on Linux, here we show all the best possible ways to do that using the command terminal. The below-given commands are applicable for all types of Linux distros.
5 Best Ways to create a new file on Linux
- Using Touch command
- Nano Text editor
- VIM/VI text editor
- Echo command
- Cat command
Note: Inside any folder that was created with root rights, to create a file there. we have to use sudo with every command given below.
1. Using Touch command
As we already have seen in the GUI method, how we have created an empty document using the Touch command in the terminal. Thus, in the same way anywhere in any directory, we can use the touch tool to create an empty file.
The command syntax is:
touch file-name
Now, here we can define the extension to let the system what kind of file we want to create such as a txt, docx.
For example, I want to create a Text file or Docx, thus the command will be:
or
Here is the example screenshot, where we have created a file on the Ubuntu Desktop using command terminal and touch command:
2. Nano Editor
Nano is the popular and easy-to-use command-line visual text editor that not allows users to edit any existing file on the system using the terminal but also lets us create a new file to add some content and save it anywhere on Linux.
Some Linux may not have nano editor by default, thus to install it run:
For Ubuntu/Debian – sudo apt install nano
For REHL based Linux- sudo yum install nano
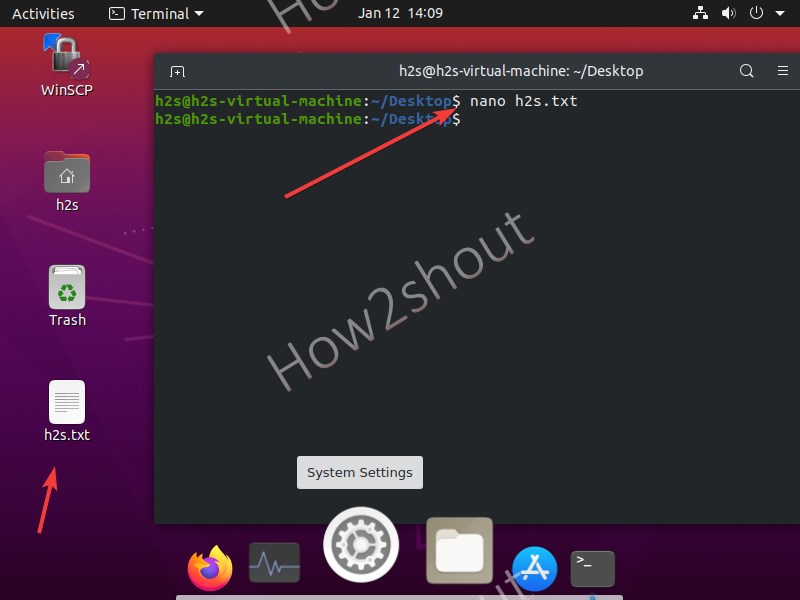
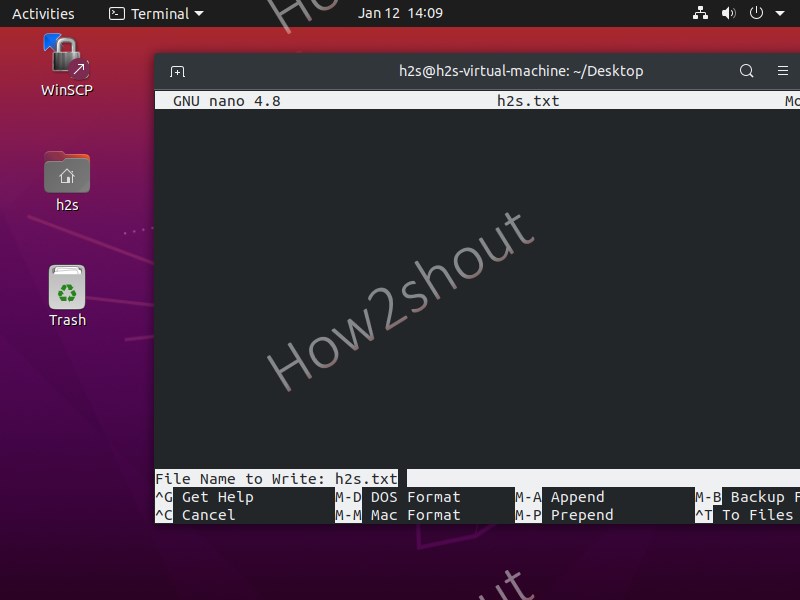
Now, how to use a nano text editor to create a new file? Well, it is quite simple, on command terminal type- nano along with the filename.
for example, I want to create a text file then the command will be:
Add some line or just press the Enter key. Then save the file by pressing Ctrl+X , type Y , and hit the Enter key.
3. Vim or Vi text editor
Vi is a command-line text editor that is available to use on every Linux including Ubuntu out of the box, thus no need to install anything, just use its command to create or edit an existing file on your system.
Now, what is the difference between VIM and VI text editors? Vi is the early implementation of a visual text editor and that is why it is available on all Linux systems, whereas VIM that stands for Vi IMproved, is the enhanced version for Vi text editor with many additions. Thus, you may not find VIM by default on all Linux distros and need to install it manually.
To install VIM on Ubuntu/Debian type- sudo apt install vim
For RHEL based– sudo yum install vim
Nevertheless, the syntax to create a new file on Linux using both the editors will be the same. However, they are slightly complex to use as compared to nano .
To create a file using Vim or Vi type
vi filename.txt
Example:
To add the content, press the “INSERT” key on your keyboard. Once you are done and want to save the created file’s content press the Esc key and then type :wq , and finally hit the Enter key to exit.
4. Echo command using Redirect operator
The echo command is another one available on all Linux distros to not only create a new file but also add the text in the same. I mean you can add the text into your file right the moment you are creating it.
echo > file-name
Let’s see some example using the Echo command:
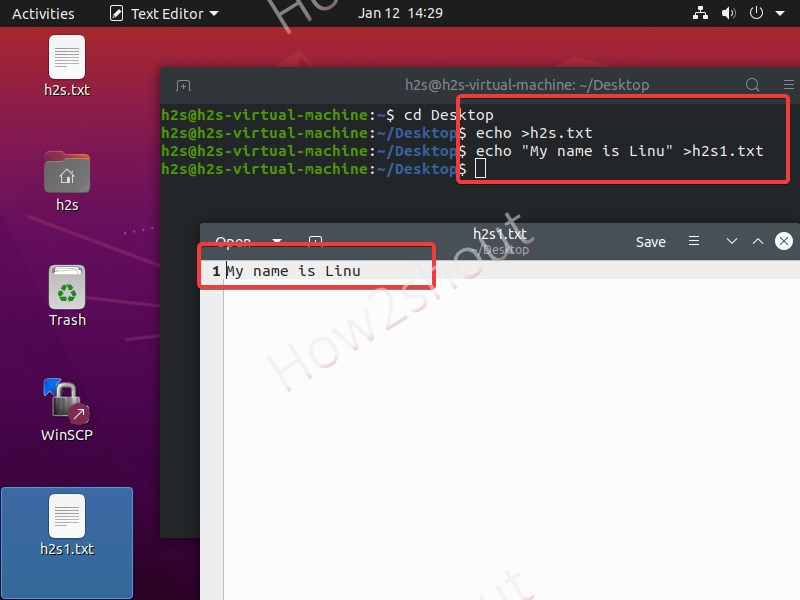
So, if I want to create a new file on Linux with echo and at the same time I also want to add some text into it, let’s say “My name is Linux” thus the command will be like this:
echo «My name is linux» > h2s.txt
In the above, the command h2s.txt file will be created having the content “My name is Linux“.
If you want to create a blank file with echo then don’t type anything before Redirect > operator i.e >
5. Cat command
Cat is also easy to use Linux command that can create a file using a command-line interface.
Example
Add the text you want in your file and hit the Enter button. To save the file, press- Ctrl+D .
Note: For empty files don’t add any text and use only the shortcut to save it.
If you want to read the text of any existing file without opening it, then cat can be used.
For example, let’s create a file demo.txt and then added the text “My name is Linux” into it. Once done, save it and again call the same using the cat to read its text directly inside the terminal but without actually opening the file.
Add text and hit the Enter key
Save the file – Ctrl + d
If you want to read the text of the file using the cat command then type:
Источник