- Windows Subsystem for Linux Installation Guide for Windows 10
- Simplified Installation for Windows Insiders
- Manual Installation Steps
- Step 1 — Enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux
- Step 2 — Check requirements for running WSL 2
- Step 3 — Enable Virtual Machine feature
- Step 4 — Download the Linux kernel update package
- Step 5 — Set WSL 2 as your default version
- Step 6 — Install your Linux distribution of choice
- Install Windows Terminal (optional)
- Set your distribution version to WSL 1 or WSL 2
- Troubleshooting installation
- Ubuntu Wiki
- BuildYourOwnKernel
- Build Environment
- Obtaining the source for an Ubuntu release
- apt-get
- Modifying the configuration
- Building the kernel
- Testing the new kernel
- Debug Symbols
- See also
Windows Subsystem for Linux Installation Guide for Windows 10
There are two options available for installing Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL):
Simplified install (preview release): wsl —install
The wsl —install simplified install command requires that you join the Windows Insiders Program and install a preview build of Windows 10 (OS build 20262 or higher), but eliminates the need to follow the manual install steps. All you need to do is open a command window with administrator privileges and run wsl —install , after a restart you will be ready to use WSL.
Manual install: Follow the six steps listed below.
The manual install steps for WSL are listed below and can be used to install Linux on any version of Windows 10.
If you run into an issue during the install process, check the Troubleshooting installation section at the bottom of this page.
Simplified Installation for Windows Insiders
The installation process for Windows Subsystem for Linux has been significantly improved in the latest Windows Insiders preview builds of Windows 10, replacing the manual steps below with a single command.
In order to use the wsl —install simplified install command, you must:
- Join the Windows Insiders Program
- Install a preview build of Windows 10 (OS build 20262 or higher).
- Open a command line windows with Administrator privileges
Once those requirements are met, to install WSL:
- Enter this command in the command line you’ve opened in Admin mode: wsl.exe —install
- Restart your machine
The first time you launch a newly installed Linux distribution, a console window will open and you’ll be asked to wait for files to de-compress and be stored on your PC. All future launches should take less than a second.
CONGRATULATIONS! You’ve successfully installed and set up a Linux distribution that is completely integrated with your Windows operating system!
The —install command performs the following actions:
- Enables the optional WSL and Virtual Machine Platform components
- Downloads and installs the latest Linux kernel
- Sets WSL 2 as the default
- Downloads and installs a Linux distribution (reboot may be required)
By default, the installed Linux distribution will be Ubuntu. This can be changed using wsl —install -d . (Replacing with the name of your desired distribution.) Additional Linux distributions may be added to your machine after the initial install using the wsl —install -d command.
To see a list of available Linux distributions, enter wsl —list —online .
Manual Installation Steps
If you are not on a Windows Insiders build, the features required for WSL will need to be enabled manually following the steps below.
Step 1 — Enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux
You must first enable the «Windows Subsystem for Linux» optional feature before installing any Linux distributions on Windows.
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
We recommend now moving on to step #2, updating to WSL 2, but if you wish to only install WSL 1, you can now restart your machine and move on to Step 6 — Install your Linux distribution of choice. To update to WSL 2, wait to restart your machine and move on to the next step.
Step 2 — Check requirements for running WSL 2
To update to WSL 2, you must be running Windows 10.
- For x64 systems: Version 1903 or higher, with Build 18362 or higher.
- For ARM64 systems: Version 2004 or higher, with Build 19041 or higher.
- Builds lower than 18362 do not support WSL 2. Use the Windows Update Assistant to update your version of Windows.
To check your version and build number, select Windows logo key + R, type winver, select OK. Update to the latest Windows version in the Settings menu.
If you are running Windows 10 version 1903 or 1909, open «Settings» from your Windows menu, navigate to «Update & Security» and select «Check for Updates». Your Build number must be 18362.1049+ or 18363.1049+, with the minor build # over .1049. Read more: WSL 2 Support is coming to Windows 10 Versions 1903 and 1909. See the troubleshooting instructions.
Step 3 — Enable Virtual Machine feature
Before installing WSL 2, you must enable the Virtual Machine Platform optional feature. Your machine will require virtualization capabilities to use this feature.
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
Restart your machine to complete the WSL install and update to WSL 2.
Step 4 — Download the Linux kernel update package
Download the latest package:
If you’re using an ARM64 machine, please download the ARM64 package instead. If you’re not sure what kind of machine you have, open Command Prompt or PowerShell and enter: systeminfo | find «System Type» . Caveat: On non-English Windows versions, you might have to modify the search text, for example, in German it would be systeminfo | find «Systemtyp» .
Run the update package downloaded in the previous step. (Double-click to run — you will be prompted for elevated permissions, select вЂyes’ to approve this installation.)
Once the installation is complete, move on to the next step — setting WSL 2 as your default version when installing new Linux distributions. (Skip this step if you want your new Linux installs to be set to WSL 1).
Step 5 — Set WSL 2 as your default version
Open PowerShell and run this command to set WSL 2 as the default version when installing a new Linux distribution:
Step 6 — Install your Linux distribution of choice
Open the Microsoft Store and select your favorite Linux distribution.
The following links will open the Microsoft store page for each distribution:
From the distribution’s page, select «Get».
The first time you launch a newly installed Linux distribution, a console window will open and you’ll be asked to wait for a minute or two for files to de-compress and be stored on your PC. All future launches should take less than a second.
CONGRATULATIONS! You’ve successfully installed and set up a Linux distribution that is completely integrated with your Windows operating system!
Install Windows Terminal (optional)
Windows Terminal enables multiple tabs (quickly switch between multiple Linux command lines, Windows Command Prompt, PowerShell, Azure CLI, etc), create custom key bindings (shortcut keys for opening or closing tabs, copy+paste, etc.), use the search feature, and custom themes (color schemes, font styles and sizes, background image/blur/transparency). Learn more.
Set your distribution version to WSL 1 or WSL 2
You can check the WSL version assigned to each of the Linux distributions you have installed by opening the PowerShell command line and entering the command (only available in Windows Build 18362 or higher): wsl -l -v
To set a distribution to be backed by either version of WSL please run:
Make sure to replace with the actual name of your distribution and with the number ‘1’ or ‘2’. You can change back to WSL 1 at anytime by running the same command as above but replacing the ‘2’ with a ‘1’.
The update from WSL 1 to WSL 2 may take several minutes to complete depending on the size of your targeted distribution. If you are running an older (legacy) installation of WSL 1 from Windows 10 Anniversary Update or Creators Update, you may encounter an update error. Follow these instructions to uninstall and remove any legacy distributions.
If wsl —set-default-version results as an invalid command, enter wsl —help . If the —set-default-version is not listed, it means that your OS doesn’t support it and you need to update to version 1903, Build 18362 or higher. If you are on Build 19041 for ARM64, this command may fail when using PowerShell in which case you can use a Command Prompt instead to issue the wsl.exe command.
If you see this message after running the command: WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component. For information please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel . You still need to install the MSI Linux kernel update package.
Additionally, if you want to make WSL 2 your default architecture you can do so with this command:
This will set the version of any new distribution installed to WSL 2.
Troubleshooting installation
Below are related errors and suggested fixes. Refer to the WSL troubleshooting page for other common errors and their solutions.
Installation failed with error 0x80070003
- The Windows Subsystem for Linux only runs on your system drive (usually this is your C: drive). Make sure that distributions are stored on your system drive:
- Open Settings -> **System —>Storage ->More Storage Settings: Change where new content is saved
WslRegisterDistribution failed with error 0x8007019e
- The Windows Subsystem for Linux optional component is not enabled:
- Open Control Panel ->Programs and Features ->Turn Windows Feature on or off -> Check Windows Subsystem for Linux or using the PowerShell cmdlet mentioned at the beginning of this article.
Installation failed with error 0x80070003 or error 0x80370102
- Please make sure that virtualization is enabled inside of your computer’s BIOS. The instructions on how to do this will vary from computer to computer, and will most likely be under CPU related options.
- WSL2 requires that your CPU supports the Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) feature, which was introduced in Intel Nehalem processors (Intel Core 1st Generation) and AMD Opteron. Older CPUs (such as the Intel Core 2 Duo) will not be able to run WSL2, even if the Virtual Machine Platform is successfully installed.
Error when trying to upgrade: Invalid command line option: wsl —set-version Ubuntu 2
- Enure that you have the Windows Subsystem for Linux enabled, and that you’re using Windows Build version 18362 or higher. To enable WSL run this command in a PowerShell prompt with admin privileges: Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux .
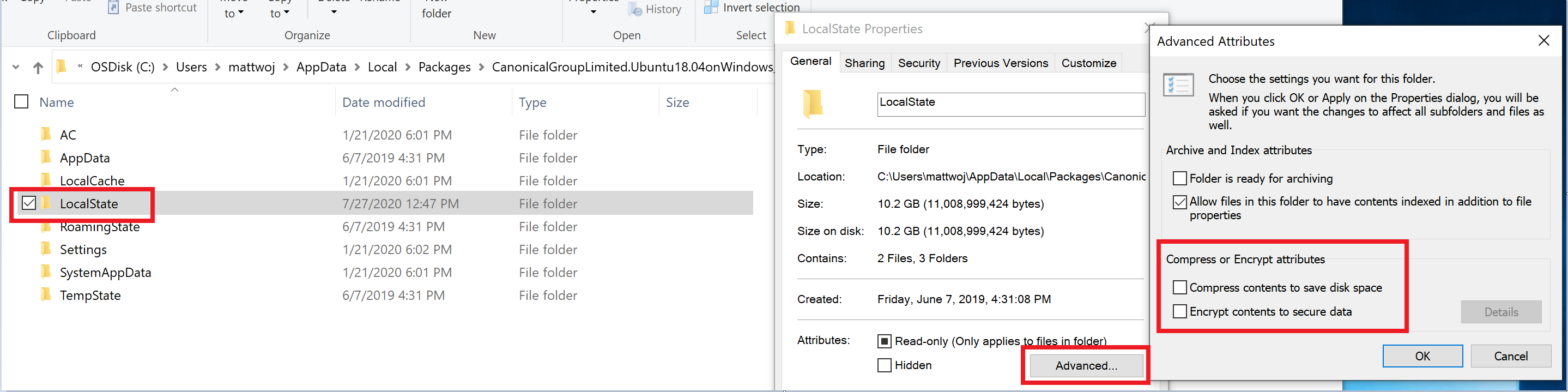
The requested operation could not be completed due to a virtual disk system limitation. Virtual hard disk files must be uncompressed and unencrypted and must not be sparse.
- Deselect “Compress contents” (as well as “Encrypt contents” if that’s checked) by opening the profile folder for your Linux distribution. It should be located in a folder on your Windows file system, something like: USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.
- In this Linux distro profile, there should be a LocalState folder. Right-click this folder to display a menu of options. Select Properties > Advanced and then ensure that the “Compress contents to save disk space” and “Encrypt contents to secure data” checkboxes are unselected (not checked). If you are asked whether to apply this to just to the current folder or to all subfolders and files, select “just this folder” because you are only clearing the compress flag. After this, the wsl —set-version command should work.
In my case, the LocalState folder for my Ubuntu 18.04 distribution was located at C:\Users \AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu18.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc
Check WSL Docs GitHub thread #4103 where this issue is being tracked for updated information.
The term ‘wsl’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program.
- Ensure that the Windows Subsystem for Linux Optional Component is installed. Additionally, if you are using an ARM64 device and running this command from PowerShell, you will receive this error. Instead run wsl.exe from PowerShell Core, or Command Prompt.
Error: This update only applies to machines with the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
- To install the Linux kernel update MSI package, WSL is required and should be enabled first. If it fails, it you will see the message: This update only applies to machines with the Windows Subsystem for Linux .
- There are three possible reason you see this message:
- If the Linux kernel package is missing in the %SystemRoot%\system32\lxss\tools folder, you will encounter this error. Resolve it by installing the Linux kernel update MSI package in step #4 of these installation instructions. You may need to uninstall the MSI from ‘Add or Remove Programs’, and install it again.
You are still in old version of Windows which doesn’t support WSL 2. See step #2 for version requirements and links to update.
WSL is not enabled. You will need to return to step #1 and ensure that the optional WSL feature is enabled on your machine.
After you enabled WSL, a reboot is required for it to take effect, reboot your machine and try again.
Error: WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component. For information please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel .
—>
Ubuntu Wiki
BuildYourOwnKernel
This page describes how to build the kernel.
The majority of users that are interested in building their own kernel are doing so because they have installed Ubuntu on their system and they wish to make a small change to the kernel for that system. In many cases the user just wants to make a kernel configuration change.
The purpose of this page is to give that user a minimum amount of information for them to meet the goal of making a simple change to the kernel, building it and installing their kernel. It is not intended to be the definitive guide to doing Ubuntu kernel development.
Build Environment
If you have not built a kernel on your system before, there are some packages needed before you can successfully build. You can get these installed with:
Unfortunately, the above does not install all of the necessary dependencies. The current Disco Dingo release requires the following additional packages.
If you are going to be using git, install it via:
The above command requires your system to have the correct deb-src lines in /etc/apt/sources.list. For example, on Disco Dingo you should have:
Obtaining the source for an Ubuntu release
There are a number of different ways of getting the kernel sources. The two main ways will be documented here.
If you have installed a version of Ubuntu and you want to make changes to the kernel that is installed on your system, use the apt-get method (described below) to obtain the sources.
However, if you wish to get the most up to date sources for the Ubuntu release you are running and make changes to that, use the git method (described below) to obtain the sources.
apt-get
The source code which generated a specific binary package may be obtained using the apt-get source
command. For example to obtain the source for the currently running kernel you can use the command:
All of the Ubuntu Kernel source is maintained under git. The source for each release is maintained in its own git repository on kernel.ubuntu.com. To obtain a local copy you can simply git clone the repository for the release you are interested in as shown below.
For example to obtain the Disco Dingo tree:
Modifying the configuration
This step can be skipped if no configuration changes are wanted. The build process will use a configuration that is put together from various sub-config files. The simplest way to modify anything here is to run:
This takes the current configuration for each architecture/flavour supported and calls menuconfig to edit its config file. The chmod is needed because the way the source package is created, it loses the executable bits on the scripts.
In order to make your kernel "newer" than the stock Ubuntu kernel from which you are based you should add a local version modifier. Add something like "+test1" to the end of the first version number in the debian.master/changelog file, before building. This will help identify your kernel when running as it also appears in uname -a. Note that when a new Ubuntu kernel is released that will be newer than your kernel (which needs regenerating), so care is needed when upgrading. NOTE: do not attempt to use CONFIG_LOCALVERSION as this _will_ break the build.
Building the kernel
Building the kernel is quite easy. Change your working directory to the root of the kernel source tree and then type the following commands:
If the build is successful, a set of three .deb binary package files will be produced in the directory above the build root directory. For example after building a kernel with version "4.8.0-17.19" on an amd64 system, these three (or four) .deb packages would be produced:
on later releases you will also find a linux-extra- package which you should also install if present.
Testing the new kernel
Install the three-package set (on your build system, or on a different target system) with dpkg -i and then reboot:
Debug Symbols
Sometimes it is useful to have debug symbols built as well. Two additional steps are needed. First pkg-config-dbgsym needs to be installed. Second when executing the binary-* targets you need to add 'skipdbg=false'.
See also
The above instructions provide a very simple recipe for obtaining the sources and then building them. If you are going to be doing more kernel development than simple configuration changes you may want to look at:
More information about using git to pull down the kernel sources.
For more info about ARM and cross compilation.
Kernel/BuildYourOwnKernel (последним исправлял пользователь rs2009 2021-02-03 17:41:47)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details.