- All microsoft windows names
- Windows 1.0
- Windows 2.0
- Windows 3.0
- Windows 95
- Windows 98
- Windows 2000
- Windows XP
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
- Naming conventions in Active Directory for computers, domains, sites, and OUs
- Summary
- Computer names
- NetBIOS computer names
- DNS host names
- Domain names
- NetBIOS domain names
- DNS domain names
- Disjointed namespaces
- Other factors
- Site names
All microsoft windows names
Операционной системе Windows уже более трех десятилетий, и именно в этом году самая известная ОС в ноябре будет отмечать 35 летие. За это время было много версий системы, которые компания Microsoft разрабатывала и предлагала пользователям.
В настоящее время последней версией операционной системы Microsoft является Windows 10. Версия, которая для многих, несомненно, является лучшей в истории, с современным интерфейсом и множеством параметров конфигурации. В нашей статье мы предлагаем посмотреть, как со временем система совершенствовалась и адаптировалась к потребностям пользователей.
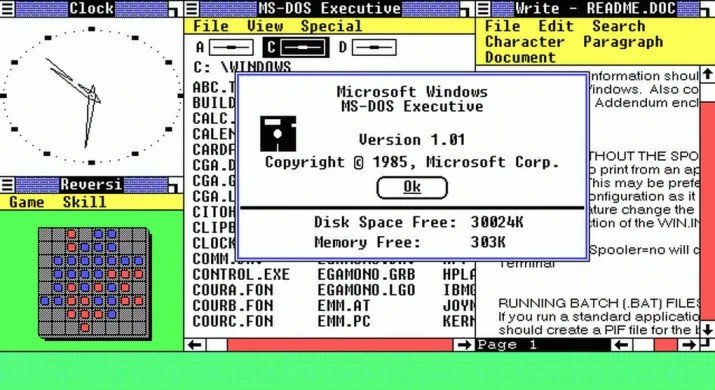
Windows 1.0
Хотя до появления Windows 1.0 уже говорили о существовании первой версии Windows, правда заключается в том, что до 20 ноября 1985 года эта первая версия системы не была официально анонсирована. Версия, которая предлагала мало функциональных возможностей и не была полной операционной системой, поскольку это было скорее графическое расширение MS-DOS.
Windows 1.0 поддерживалась до 31 декабря 2001 года, несмотря на то, что версия почти не обладала функциональностью, Redmond предлагал поддержку чуть более 16 лет.
Windows 2.0
Между тем, всего через два года, в ноябре 1987 года, появилась Windows 2.0. Эта версия была быстро обновлена до v2.03, которая уже включала известные всем окна. Не говоря уже о том, что в неё уже были включены определенные утилиты, которые, можно сказать, должны были стать источником нынешних средств автоматизации делопроизводства.
Эта версия Windows поддерживалась до той же даты, что и предыдущая версия. То есть до 31 декабря 2001 года, когда Microsoft решила прекратить поддержку Windows 1.0 и 2.0.
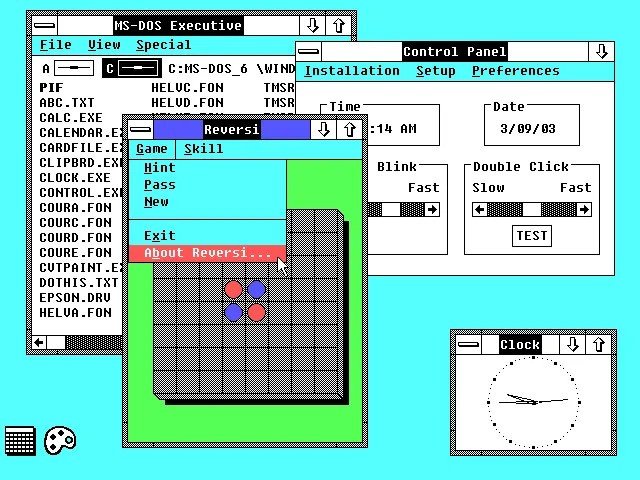
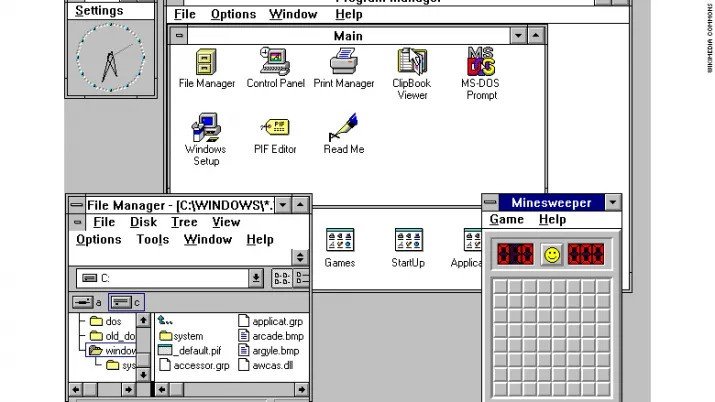
Windows 3.0
22 мая 1990 года была выпущена операционная система Windows 3.0 с графическим интерфейсом. Это была первая коммерчески успешная версия, продавшая до двух миллионов копий всего за несколько месяцев с момента ее запуска.
С обновлением до версии 3.1 система получила знаменитую игру Minesweeper, которая на протяжении многих лет радовала пользователей. Кроме того, мы также должны выделить наличие файлов и менеджера программ. Данную версию компания поддерживала до 31 декабря 2001 года. Та же дата, что и у двух предыдущих ОС.
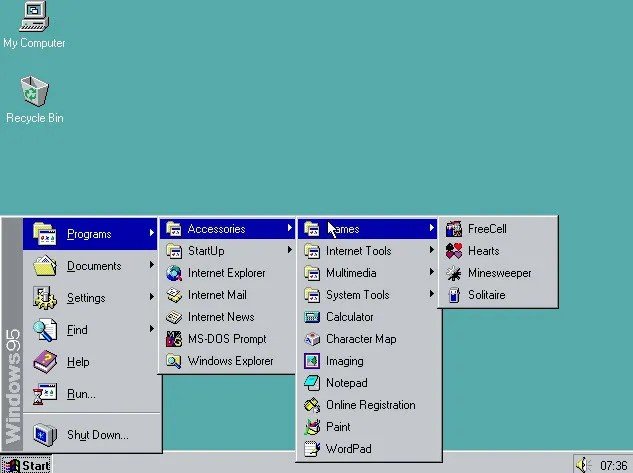
Windows 95
24 августа 1995 года – важная дата в жизни операционной системы Windows, поскольку это день, когда была выпущена знаменитая версия Windows 95. Эта версия предлагает значительно улучшенный интерфейс и в ней уже появляется «Панель задач» и меню «Пуск», два очень важных элемента, которые до сих пор являются частью операционной системы Windows. Также стоит отметить, что Windows 95 включала в себя Internet Explorer, веб-браузер, который сопровождал систему в течение многих лет и, следовательно, поддержку Интернета.
Эта версия, предназначенная для потребительского рынка и с которой переходили от 16-разрядной многозадачной архитектуры к 32-разрядной соответствующей архитектуре, а также многозадачности. Стандартная поддержка для Windows 95 продолжалась до 31 декабря 2000 года, а расширенная до 31 декабря 2001 года.
Windows 98
Хотя до появления Windows 98 мы должны упомянуть, что была версия Windows NT, которая была ориентирована на бизнес-клиентов. Однако 25 июня 1998 года Microsoft выпустила новую версию своей операционной системы. Как и предыдущая, она получила в качестве своего имени последние две цифры года своего запуска, и это была версия, которая шла с файловой системой FAT32 и пыталась расширить доступ к сети. Кроме того, она включала в себя поддержку DVD и USB.
Однако большая сложность системы привела к значительному снижению производительности, что делает ее одной из наиболее критикуемых версий Windows за ее медлительность и ненадежность по сравнению с Windows 95. Несмотря на это, Windows 98 имела стандартную поддержку до 30 июня 2002 года и расширенную поддержку, которая закончилась 11 июля 2006 года.
Windows 2000
29 марта 1999 года была запущена операционная система Windows NT 5.0 EUR Edition, которая представляла собой не что иное, как немецкую версию Windows NET 5.0 и впоследствии называлась Windows 2000.
Windows 2000 включала новые опции для лучшей защиты файлов и даже имела собственную домашнюю версию, Windows 2000 Millennium Edition (ME), которая включала новые инструменты и опции мультимедиа. Стандартная поддержка для этого выпуска закончилась 30 июня 2005 г., а расширенная поддержка – 13 июля 2010 г.
Windows XP
Еще один большой скачок в развитии операционной системы Microsoft произошел 25 октября 2001 года, когда была запущена Windows XP. Это был большой успех, поскольку это действительно был высококачественный продукт. Версия, которая была построена из ядра Windows NT и выпускалась в двух разных редакциях: Home и Professional.
В визуальном аспекте необходимо выделить значительные улучшения в пользовательском интерфейсе с новыми значками, меню и параметрами, которые позволили пользователям углубляться и контролировать все виды задач в системе. Но Windows XP не только предлагала графические улучшения, но и значительно увеличила скорость и маневренность.
В Windows XP встроены такие функции, как шифрование системных файлов, поддержка сетей WiFi, удаленная помощь и 64-разрядная версия, что вызвало взрыв на рынке операционных систем. Эта версия имела стандартную поддержку от Microsoft до 14 апреля 2009 года, в то время как расширенная поддержка продолжалась до 8 апреля 2014 года.
Windows Vista
Windows Vista, выпущенная Microsoft 30 января 2007 года и включающая в себя бесчисленное количество новых функций, переработанную оболочку и интерфейс с серьезными изменениями, нацеленные на повышение безопасности, однако не понравилась подавляющему большинству пользователей.
С Windows Vista мы смогли увидеть интерфейс Aero UI, который, несомненно, предлагал отличную визуальную привлекательность, но оказался слишком проблематичным на менее мощных компьютерах. Множество обстоятельств сделало Windows Vista провалом в истории операционных систем, несмотря на большие ожидания компании.
Постоянные проблемы, медлительность и перегрузки затмили все графические новинки. Эта версия получала стандартную поддержку от компании до 10 апреля 2012 года, а расширенная поддержка была продлена до 11 апреля 2017 года.
Windows 7
22 октября 2009 года Microsoft объявила о выпуске Windows 7 в качестве замены Windows Vista и стала одной из самых важных версий ОС компании.
В данную систему была добавлена поддержка мультитач, переработанная оболочка Windows, новая панель задач, сетевая система, улучшения производительности и скорости, а также сокращение потребления ресурсов. Кроме того, Windows 7 представила новый дизайн панели задач, сделав ее более широкой, и систему с большими значками. Стандартная поддержка Windows 7 продолжалась до 13 января 2015 года, а расширенная поддержка до 14 января 2020 года.
Windows 8
Почти три года спустя, 26 октября 2012 г., была выпущена Windows 8. Версия, в которой была добавлена поддержка микропроцессоров ARM. Интерфейс в новой системе был изменен, чтобы сделать ее более удобной для устройств с сенсорными экранами. Также в системе было удалено меню «Пуск», что не нравилось подавляющему большинству пользователей.
Плохие отзывы пользователей о новом интерфейсе Metro заставили Microsoft запустить Windows 8.1, чтобы добавить некоторые улучшения. Стандартная и расширенная поддержка для Windows 8 закончилась 12 января 2016 года, тогда как для Windows 8.1 стандартная поддержка продолжалась до 9 января 2018 года, а расширенная поддержка все еще действует до 10 января 2023 года.
Windows 10
29 июля 2015 года Microsoft выпустила последнюю и ожидаемую версию своей операционной системы Windows 10. Версия, которая имеет большой набор приложений и современный интерфейс с отличной производительностью. Кросс-платформенность новой системы позволяет использовать ее на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах.
Но это не единственные новинки, поскольку также стоит отметить универсальные приложения: новый браузер Edge, помощник Cortana, новая страница конфигурации системы, TimeLine и возвращение меню «Пуск», которое жаждали подавляющее большинство пользователей. Одним словом – это лучшая версия системы на сегодняшний день и продукт, отвечающий потребностям пользователей.
Windows 10 имеет стандартную поддержку, действующую до 9 января 2024 года, в то время как расширенная поддержка продлится до 9 января 2029 года.
Naming conventions in Active Directory for computers, domains, sites, and OUs
This article describes the naming conventions for computer accounts in Windows, NetBIOS domain names, DNS domain names, Active Directory sites, and organizational units (OUs) that are defined in the Active Directory directory service.
Original product version: В Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: В 909264
Summary
This article discusses the following topics:
- The valid characters for names
- The minimum and maximum name lengths
- Reserved names
- Names that we don’t recommend
- General recommendations that are based on supporting Active Directory in small, medium, and large deployments
All objects that are named within Active Directory, or within AD/AM and LDS, are subject to name matching based on the algorithm described in the following article:
In that article, this naming convention applies to computer, OU, and site names.
Computer names
NetBIOS computer names
NetBIOS computer names can contain all alphanumeric characters except for the extended characters that are listed in Disallowed characters. Names can contain a period, but names can’t start with a period.
NetBIOS computer names can’t contain the following characters:
Names can contain a period (.). But the name can’t start with a period. The use of non-DNS names with periods is allowed in Microsoft Windows NT. Periods should not be used in Microsoft Windows 2000 or later versions of Windows. If you’re upgrading a computer whose NetBIOS name contains a period, change the machine name. For more information, see Special characters.
In Windows 2000 and later versions of Windows, computers that are members of an Active Directory domain can’t have names that are composed completely of numbers. This restriction is because of DNS restrictions.
For more information about the NetBIOS name syntax, see NetBIOS name syntax.
Minimum name length: 1 character
Maximum name length: 15 characters
The 16th character is reserved to identify the functionality that is installed on the registered network device.
Special characters: Period (.)
A period character separates the name into a NetBIOS scope identifier and the computer name. The NetBIOS scope identifier is an optional string of characters that identify logical NetBIOS networks that run on the same physical TCP/IP network. For NetBIOS to work between computers, the computers must have the same NetBIOS scope identifier and unique computer names.
The use of NetBIOS scopes in names is a legacy configuration. It shouldn’t be used with Active Directory forests. For more information about NetBIOS scopes, see the following web sites:
DNS host names
DNS names can contain only alphabetical characters (A-Z), numeric characters (0-9), the minus sign (-), and the period (.). Period characters are allowed only when they are used to delimit the components of domain style names.
In the Windows 2000 domain name system (DNS) and the Windows Server 2003 DNS, Unicode characters are supported. Other implementations of DNS don’t support Unicode characters. Avoid Unicode characters if queries will be passed to the servers that use non-Microsoft implementations of DNS.
For more information, see the following websites:
DNS host names can’t contain the following characters:
white space (blank)
The underscore has a special role. It is permitted for the first character in SRV records by RFC definition. But newer DNS servers may also allow it anywhere in a name. For more information, see Complying with Name Restrictions for Hosts and Domains.
All characters preserve their case formatting except for American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) characters.
The first character must be alphabetical or numeric.
The last character must not be a minus sign or a period.
Two-character SDDL user strings that are listed in well-known SIDs list can’t be used. Otherwise, import, export, and take control operations fail.
In Windows 2000 and later versions of Windows, computers that are members of an Active Directory domain can’t have names that are composed completely of numbers. This restriction is because of DNS restrictions.
DNS Host Name Registration substitutes a hyphen (-) character for invalid characters.
Minimum name length: 2 characters
Maximum name length: 63 characters
The maximum length of the host name and of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is 63 bytes per label and 255 bytes per FQDN.
Windows doesn’t permit computer names that exceed 15 characters, and you can’t specify a DNS host name that differs from the NETBIOS host name. You might however create host headers for a web site hosted on a computer and that is then subject to this recommendation.
In Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003, the maximum host name and the FQDN use the standard length limitations that are mentioned earlier, with the addition of UTF-8 (Unicode) support. Because some UTF-8 characters exceed one octet in length, you can’t determine the size by counting the characters.
Domain controllers must have an FQDN of less than 155 bytes.
Reserved names per RFC 952
For more information, see rfc952.
Reserved names in Windows
When you create names for the DNS computers in a new Windows Server 2003 DNS infrastructure, use the following guidelines:
- Choose computer names that are easy for users to remember.
- Identify the owner of the computer in the computer name.
- Choose a name that describes the purpose of the computer.
- For ASCII characters, don’t use character case to indicate the owner or the purpose of a computer. For ASCII characters, DNS is not case-sensitive, Windows and Windows applications are not case-preserving in all places.
- Match the Active Directory domain name to the primary DNS suffix of the computer name. For more information, see the Disjointed namespaces section below.
- Use a unique name for every computer in your organization. Avoid the same computer name for computers in different DNS domains.
- Use ASCII characters. This guarantees interoperability with computers that are running versions of Windows that are earlier than Windows 2000.
- In DNS computer names, use only the characters that are listed in RFC 1123. These characters include A-Z, a-z, 0-9, and the hyphen (-). In Windows Server 2003, DNS allows most UTF-8 characters in names. Don’t use extended ASCII or UTF-8 characters unless all the DNS servers in your environment support them.
Domain names
Here are details for NetBIOS domain names and DNS domain names.
NetBIOS domain names
NetBIOS domain names can contain all alphanumeric characters except for the extended characters that are listed in Disallowed characters. Names can contain a period, but names can’t start with a period.
NetBIOS computer names can’t contain the following characters:
Names can contain a period (.). But the name can’t start with a period. The use of non-DNS names with periods is allowed in Microsoft Windows NT. Periods shouldn’t be used in Active Directory domains. If you are upgrading a domain whose NetBIOS name contains a period, change the name by migrating the domain to a new domain structure. Do not use periods in new NetBIOS domain names.
In Windows 2000 and later versions of Windows, computers that are members of an Active Directory domain can’t have names that are composed completely of numbers. This restriction is because of DNS restrictions.
Minimum name length: 1 character
Maximum name length: 15 characters.
The 16th character is reserved to identify the functionality that is installed on the registered network device.
Reserved names in Windows
The names of an upgraded domain can include a reserved word. However, trust relationships with other domains fail in this situation.
Special characters: Period (.).
A period character separates the name into a NetBIOS scope identifier and the computer name. The NetBIOS scope identifier is an optional string of characters that identify logical NetBIOS networks that run on the same physical TCP/IP network. For NetBIOS to work between computers, the computers must have the same NetBIOS scope identifier and unique computer names.
The use of NetBIOS scopes in names is a legacy configuration. It shouldn’t be used with Active Directory forests. There is no inherent problem with this, but there may be applications that filter the name and assume a DNS name when a period is found.
DNS domain names
DNS names can contain only alphabetical characters (A-Z), numeric characters (0-9), the minus sign (-), and the period (.). Period characters are allowed only when they are used to delimit the components of domain style names.
In the Windows 2000 domain name system (DNS) and the Windows Server 2003 DNS, Unicode characters are supported. Other implementations of DNS don’t support Unicode characters. Avoid Unicode characters if queries will be passed to the servers that use non-Microsoft implementations of DNS.
For more information, visit the following web sites:
DNS domain names can’t contain the following characters:
white space (blank)
The underscore has a special role. It’s permitted for the first character in SRV records by RFC definition. But newer DNS servers may also allow it anywhere in a name. For more information, see Complying with Name Restrictions for Hosts and Domains.
When promoting a new domain, you get a warning that an underscore character might cause problems with some DNS servers. But it still lets you create the domain.
All characters preserve their case formatting except for ASCII characters.
The first character must be alphabetical or numeric.
The last character must not be a minus sign or a period.
Minimum name length: 2 characters
Maximum name length: 255 characters
The maximum length of the host name and of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is 63 bytes per label and 255 characters per FQDN. The latter is based on the maximum path length possible with an Active Directory Domain name with the paths needed in SYSVOL , and it needs to obey to the 260 character MAX_PATH limitation.
An example path in SYSVOL contains:
The might contain user input such as the logon script file name, thus it can also reach a significant length.
The AD FQDN domain name appears in the path twice, due to that the length of an AD FQDN domain name is restricted to 64 characters.
In Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003, the maximum host name and the FQDN use the standard length limitations that are mentioned earlier, with the addition of UTF-8 (Unicode) support. Because some UTF-8 characters exceed one octet in length, you can’t determine the size by counting the characters.
Single-label domain namespaces
Single-label DNS names are names that don’t contain a suffix, such as .com , .corp , .net , .org , or companyname . For example, host is a single-label DNS name. Most Internet registrars don’t allow the registration of single-label DNS names.
Generally, we recommend that you register DNS names for internal and external namespaces with an Internet registrar. This includes the DNS names of Active Directory domains, unless such names are subdomains of DNS names that are registered by your organization name. For example, corp.example.com is a subdomain of example.com . Registering your DNS name with an Internet registrar may help prevent a name collision. A name collision may occur if another organization tries to register the same DNS name, or if your organization merges with another organization that uses the same DNS name.
Problems that are associated with single-label namespaces include:
Single-label DNS names can’t be registered by using an Internet registrar.
Domains that have single-label DNS names require additional configuration.
The DNS Server service may not be used to locate domain controllers in domains that have single-label DNS names.
By default, Windows Server 2003-based domain members, Windows XP-based domain members, and Windows 2000-based domain members don’t perform dynamic updates to single-label DNS zones.
Don’t use top-level Internet domain names on the intranet, such as .com , .net , and .org . If you use top-level Internet domain names on the intranet, computers on the intranet that are also connected to the Internet may experience resolution errors.
Disjointed namespaces
A disjointed namespace occurs when a computer’s primary DNS suffix doesn’t match the DNS domain of which it is a member. For example, a disjointed namespace occurs when a machine that has the DNS name of dc1.contosocorp.com is in a domain that has the DNS name of contoso.com .
How disjointed namespaces occur:
A Windows NT 4.0 primary domain controller is upgraded to a Windows 2000 domain controller by using the original release version of Windows 2000. In the Networking item in Control Panel, multiple DNS suffixes are defined.
The domain is renamed when the forest is at the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level. And the primary DNS suffix isn’t changed to reflect the new DNS domain name.
Effects of a disjointed namespace:
Suppose a domain controller named DC1 resides in a Windows NT 4.0 domain whose NetBIOS domain name is contoso. This domain controller is upgraded to Windows 2000. When this upgrade occurs, the DNS domain is renamed contoso.com . In the original release version of Windows 2000, the upgrade routine clears the check box that links the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller to its DNS domain name. So, the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller is the Windows NT 4.0 DNS suffix that was defined in the Windows NT 4.0 suffix search list. In this example, the DNS name is DC1.northamerica.contoso.com .
The domain controller dynamically registers its service location (SRV) records in the DNS zone that corresponds to its DNS domain name. However, the domain controller registers its host records in the DNS zone that corresponds to its primary DNS suffix.
For more information about a disjoint namespace, see the following articles:
Other factors
Forests that are connected to the Internet
A DNS namespace that is connected to the Internet must be a subdomain of a top-level or second-level domain of the Internet DNS namespace.
Maximum number of domains in a forest
In Windows 2000, the maximum number of domains in a forest is 800. In Windows Server 2003 and later versions, the maximum number of domains at Forest Functional Level 2 is 1200. This restriction is a limitation of multivalued non-linked attributes in Windows Server 2003.
The DNS names of all the nodes that require name resolution include the Internet DNS domain name for the organization. So, choose an Internet DNS domain name that is short and easy to remember. Because DNS is hierarchical, DNS domain names grow when you add subdomains to your organization. Short domain names make the computer names easy to remember.
If the organization has an Internet presence, use names that are relative to the registered Internet DNS domain name. For example, if you have registered the Internet DNS domain name contoso.com , use a DNS domain name such as corp.contoso.com for the intranet domain name.
Don’t use the name of an existing corporation or product as your domain name. You can run into a name collision later on.
Avoid a generic name like maybe domain.localhost. Another company you merge with in a few years might follow the same thinking.
Don’t use an acronym or an abbreviation as a domain name. Users may have difficulty recognizing the business unit that an acronym represents.
Avoid the use of underscores (_) in domain names. Applications might be very RFC obedient and reject the name, and will not install or work in your domain. And you might experience problems with older DNS servers.
Don’t use the name of a business unit or of a division as a domain name. Business units and other divisions will change, and these domain names can be misleading or become obsolete.
Don’t use geographic names that are difficult to spell and remember.
Avoid extending the DNS domain name hierarchy more than five levels from the root domain. You can reduce administrative costs by limiting the extent of the domain name hierarchy.
If you are deploying DNS in a private network, and you don’t plan to create an external namespace, register the DNS domain name that you create for the internal domain. Otherwise, you may find that the name is unavailable if you try to use it on the Internet, or if you connect to a network that is connected to the Internet.
Site names
We recommend that you use a valid DNS name when you create a new site name. Otherwise, your site will be available only where a Microsoft DNS server is used. For more information about valid DNS names, see the DNS host names section.
DNS names can contain only alphabetical characters (A-Z), numeric characters (0-9), the minus sign (-), and the period (.). Period characters are allowed only when they are used to delimit the components of domain style names.
In the Windows 2000 domain name system (DNS) and the Windows Server 2003 DNS, Unicode characters are supported. Other implementations of DNS don’t support Unicode characters. Avoid Unicode characters if queries will be passed to the servers that use non-Microsoft implementations of DNS.
For more information, visit the following web sites:
DNS names can’t contain the following characters: