- Инструкция UPDATE (Microsoft Access SQL) UPDATE statement (Microsoft Access SQL)
- Синтаксис Syntax
- Комментарии Remarks
- Пример Example
- BEST GUIDE: How to Manually Run Windows Updates (7/8/8.1 and 10)
- How to Check If Your Windows Updates are Up to Date
- Windows 7/8/8.1
- Windows 10
- How to Run Windows Updates Manually in Windows 7
- How to Run Windows Updates Manually in Windows 8 and 8.1
- How to Run Windows Update Manually in Windows 10
- PSWindowsUpdate: Managing Windows Updates from PowerShell
- PSWindowsUpdate: Install Windows Update PowerShell Module
- Overview of PSWindowsUpdate Cmdlets
- PowerShell: List All Windows Updates Available for a Computer
- Install-WindowsUpdate: Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
- Install Windows Update on Remote Computers with PowerShell
- Get-WUHistory: Viewing Windows Update History using PowerShell
- Remove-WindowsUpdate: Uninstalling Windows Updates
- Hide-WindowsUpdate: How to Hide Windows Updates with PowerShell?
Инструкция UPDATE (Microsoft Access SQL) UPDATE statement (Microsoft Access SQL)
Область применения: Access 2013, Office 2013 Applies to: Access 2013, Office 2013
Создает запрос на обновление, который изменяет значения в полях в указанной таблице на основании заданных условий. Creates an update query that changes values in fields in a specified table based on specified criteria.
Синтаксис Syntax
UPDATE таблица SET новое_значение WHERE критерии; UPDATE table SET newvalue WHERE criteria;
Инструкция UPDATE состоит из трех указанных ниже частей. The UPDATE statement has these parts:
Имя таблицы, содержащей данные, которые необходимо изменить. The name of the table containing the data you want to modify.
Выражение, указывающее значение, которое необходимо вставить в определенное поле обновляемых записей. An expression that determines the value to be inserted into a particular field in the updated records.
Выражение, определяющее, какие записи необходимо обновить. An expression that determines which records will be updated. Будут обновлены только те записи, которые удовлетворяют условиям выражения. Only records that satisfy the expression are updated.
Комментарии Remarks
Инструкция UPDATE особенно полезна, когда необходимо изменить большое количество записей либо когда записи, которые необходимо изменить, находятся в нескольких таблицах. UPDATE is especially useful when you want to change many records or when the records that you want to change are in multiple tables.
Вы можете изменить одновременно несколько полей. You can change several fields at the same time. В следующем примере показано, как увеличить значения Order Amount на 10 процентов, а значения Freight на 3 процента для грузоотправителей в Соединенном Королевстве: The following example increases the Order Amount values by 10 percent and the Freight values by 3 percent for shippers in the United Kingdom:
- Инструкция UPDATE не создает результирующее множество. UPDATE does not generate a result set. Кроме того, после обновления записи с помощью запроса на обновление вам не удастся отменить эту операцию. Also, after you update records using an update query, you cannot undo the operation. Если вам необходимо узнать, какие записи были обновлены, сначала изучите результаты выполнения запроса на выборку, использующего те же критерии, а затем запустите запрос на обновление. If you want to know which records were updated, first examine the results of a select query that uses the same criteria, and then run the update query.
- Всегда храните резервные копии данных. Maintain backup copies of your data at all times. Если вы обновите не те записи, вы сможете восстановить их из резервных копий. If you update the wrong records, you can retrieve them from your backup copies.
Пример Example
В этом примере показано, как изменить значения в поле ReportsTo на 5 для всех записей сотрудников, у которых поле ReportsTo имеет значение 2. This example changes values in the ReportsTo field to 5 for all employee records that currently have ReportsTo values of 2.
BEST GUIDE: How to Manually Run Windows Updates (7/8/8.1 and 10)
Microsoft updates are continuously released and by default applied and installed on your Windows OS. It is important to let the updates install automatically; because they bring in numerous benefits in terms of security and keeping the software’s and service up to date; The top most reason technically is the security of your operating system. Since there are 100’s of services running on your system, they can become outdated, unreliable and insecure which is when Microsoft pushes an update to patch the system, or update the service or the program. If you don’t run updates regularly; then your computer could be at risk; especially if it connected to a network.
By default; updates are supposed to run automatically. If for any reason they are not; then you will usually be prompted with an Error Number which can help diagnose the issue.
The aim of this guide is to show how you can make sure that your system is updated and if incase something goes wrong with your Windows Update; then how to push Windows Manually to do the updates and also ensure that you’r e set to receive updates automatically.
How to Check If Your Windows Updates are Up to Date
The easiest way to do this is to click on Start, type Windows Update and Click On It.
Windows 7/8/8.1
Windows 10
see below. It’s easier in Windows 10 therefore exclusive steps are not needed.
How to Run Windows Updates Manually in Windows 7
Press the Windows key on your keyboard. In the search box, type Windows update. In the search results, click on Windows update. Click on Check for updates in the right pane. It will start checking for the latest updates.
If there are any updates available, they will be listed underneath. After it has found updates, you will see an option called Install Updates. Click on it to begin installing updates.
Click Install updates to install them. Click Yes if the UAC warning message appears. You may see a license agreement, click I accept the license terms and click Finish. Updates will start downloading and installing automatically. A reboot maybe required so do it. It may install updates while shutting down and powering on. Be patient, and let the process complete.
Once done; the next step is to ensure that your system is set to install and check updates automatically. To do this, click Change Settings from the left pane; and set the first option to “Install Updates Automatically (Recommended)”
How to Run Windows Updates Manually in Windows 8 and 8.1
Hold the Windows Key and Press X. Choose Command Prompt (Admin)
wuauclt /showcheckforupdates
Windows update’s window will appear and automatically start checking for updates. If there are updates available for your system, click Install to download and install them automatically.
You may be asked to restart your system, click Restart now. It may install updates while shutting down and powering on. Be patient, and let the process complete.
How to Run Windows Update Manually in Windows 10
Hold the Windows Key and Press R. In the run dialog, type the following command
ms-settings:windowsupdate
Windows update’s window will appear. Click on Check for updates. It will start checking for updates. Click Install if any updates are available. This can take a while, and even a couple of reboots. Once done; click on Advanced Options;
then make sure that Automatic (Recommended) option is selected under Choose How Updates Are Installed.
PSWindowsUpdate: Managing Windows Updates from PowerShell
It is very convenient to use the special PSWindowsUpdate module for PowerShell to manage Windows updates from the command line interface. The PSWindowsUpdate is not integrated into Windows and is a third-party module available in Technet Script Gallery. PSWindowsUpdate allows administrators to remotely check, install, remove and hide updates on Windows servers and workstations. The PSWindowsUpdate module is especially valuable to manage updates on Windows Server Core, Hyper-V editions having no graphic interface, as well as when configuring a Windows image in the audit mode.
PSWindowsUpdate: Install Windows Update PowerShell Module
You can install the PSWindowsUpdate module on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 from the online repository (PSGallery) using the PackageManagement with a single command:
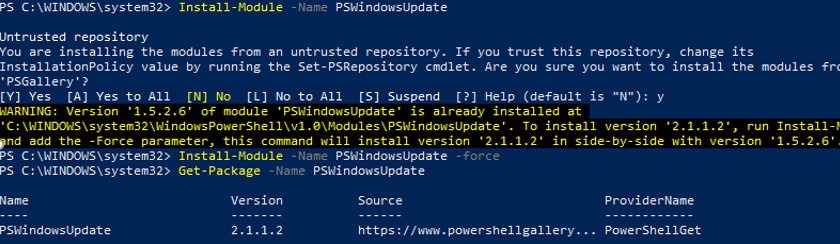
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate
In my case, a warning appeared that PSWindowsUpdate 1.5.2.6 was already installed appeared. To install a newer module version, you need to run the command:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate –Force
After the installation is complete, you need to check the package:
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
If you have an older Windows version (Windows 7/8.1/Windows Server 2008 R2/2012 R2) or you don’t have direct Internet access, you can install PSWindowsUpdate manually.
This module can be installed on any supported Windows versions starting from Vista / Windows Server 2008 with PowerShell 2.0 installed (though, PoSh 3.0 or newer is recommended).
After installing the PSWindowsUpdate module on your computer, you can remotely install it on other computers or servers using the Update-WUModule cmdlet. For example, to copy the PSWindowsUpdate module from your computer to two remote servers, run the commands (you need to access the remote servers via SMB protocol, TCP port 445):
$Targets = «lon-fs02», «lon-db01»
Update-WUModule -ComputerName $Targets –Local
To save (export) the PoSh module to a shared network folder for further importing of the module on other computers, run:
Save-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate –Path \\lon-fs02\psmodules\
Overview of PSWindowsUpdate Cmdlets
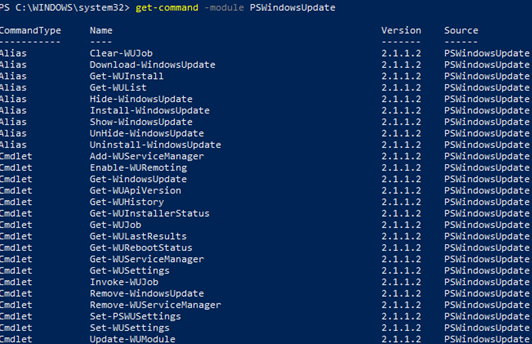
You can display the list of available cmdlets in the PSWindowsUpdate module as follows:
get-command -module PSWindowsUpdate
Let’s describe the usage of the module commands in brief:
- Clear-WUJob – use the Get-WUJob to call the WUJob in Task Scheduler;
- Download-WindowsUpdate (alias for Get-WindowsUpdate –Download ) — get a list of updates and download them;
- Get-WUInstall, Install-WindowsUpdate (alias for Get-WindowsUpdate –Install ) – install updates;
- Hide-WindowsUpdate (alias for Get-WindowsUpdate -Hide:$false ) – hide update;
- Uninstall-WindowsUpdate – remove update using Remove-WindowsUpdate;
- Add-WUServiceManager – register the update server (Windows Update Service Manager) on the computer;
- Enable-WURemoting — enable Windows firewall rules to allow remote use of the PSWindowsUpdate cmdlets;
- Get-WindowsUpdate (Get-WUList) — displays a list of updates that match the specified criteria, allows you to find and install the updates. This is the main cmdlet of the PSWindowsUpdate module. Allows to download and install updates from a WSUS server or Microsoft Update. Allows you to select update categories, specific updates and set the rules of a computer restart when installing the updates;
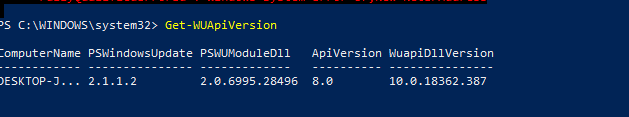
- Get-WUApiVersion – get the Windows Update Agent version on the computer;
- Get-WUHistory – display a list of installed updates (update history);
- Get-WUInstallerStatus — check the Windows Installer service status;
- Get-WUJob – run WUJob update tasks in the Task Scheduler;
- Get-WULastResults — dates of the last search and installation of updates (LastSearchSuccessDate and LastInstallationSuccessDate);
- Get-WURebootStatus — allows you to check whether a reboot is needed to apply a specific update;
- Get-WUServiceManager – list update sources;
- Get-WUSettings – get Windows Update client settings;
- Invoke-WUJob – remotely call WUJobs jobs in the Task Scheduler to immediately execute PSWindowsUpdate commands;
- Remove-WindowsUpdate – allows to uninstall an update by KB ID;
- Remove-WUServiceManager – disable Windows Update Service Manager;
- Set-PSWUSettings – save PSWindowsUpdate module settings to the XML file;
- Set-WUSettings – configure Windows Update client settings;
- Update-WUModule – update the PSWindowsUpdate module version (you can update the module on a remote computer by copying it from the current one, or updating from PSGallery).
PowerShell: List All Windows Updates Available for a Computer
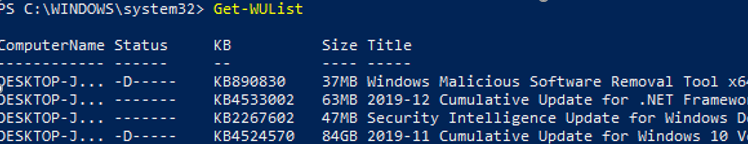
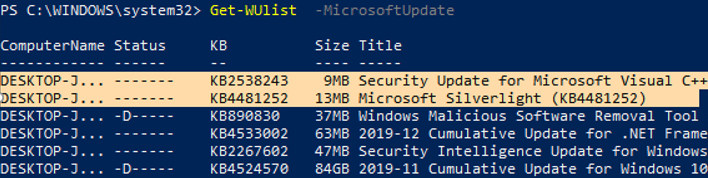
You can list the updates available for this computer on the update server using the Get-WindowsUpdate or Get-WUList commands.
To check the list of available updates on a remote computer, run this command:
Get-WUList –ComputerName server2
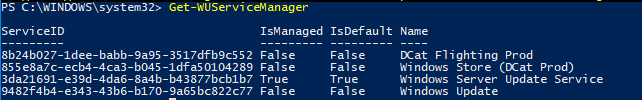
You can check where your Windows should get updates from. Run the following command:
As you can see, the computer is configured to receive updates from the local WSUS server (Windows Server Update Service = True). In this case, you should see a list of updates approved for your computer.
If you want to scan your computer on Microsoft Update servers in the Internet (in addition to Windows updates, these servers contain Office and other Microsoft product updates), run this command:
You will get this warning:
To allow scanning on Microsoft Update, run this command:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID «7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d» -AddServiceFlag 7
You can now scan to Microsoft Update. As you can see, in this case, additional updates were found for Microsoft Visual C ++ 2008 and Microsoft Silverlight.
To check the version of the Windows Update Agent on the computer, run the command:
To remove certain products or packages from the list of updates received by your computer, you can exclude them by:
- Category (-NotCategory);
- Title (-NotCategory);
- Update number (-NotKBArticleID).
For example, let’s exclude OneDrive, drivers and the specific KB from the list of updates:
Get-WUlist -NotCategory «Drivers» -NotTitle «OneDrive» -NotKBArticleID KB4489873
Install-WindowsUpdate: Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
To automatically download and install all available updates for your computer, run the command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
The AcceptAll key accepts installation of all update packages, and AutoReboot allows Windows to automatically restart after the updates are installed.
You can save the update installation history to the log file (you can use it instead of WindowsUpdate.log file).
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot | Out-File «c:\logs\$(get-date -f yyyy-MM-dd)-WindowsUpdate.log» -force
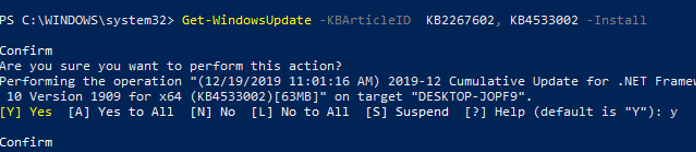
You can install only the specific update packages by KB number:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602, KB4533002 -Install
In this case, you need to confirm the installation of each update manually.
If you want to exclude some updates from the installation list, run this command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -NotCategory «Drivers» -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4011670 -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
Install Windows Update on Remote Computers with PowerShell
The PSWindowsUpdate module allows you to install updates remotely on multiple workstations or servers at once (the PSWindowsUpdate must be installed/imported on these computers). It is very convenient since an administrator doesn’t have to log on manually to all servers when update installation is scheduled.
Almost all PSWindowsUpdate module cmdlets allow you to manage and install updates on remote computers. To do this, use the attribute: -Computername server1, server2, server3
In order to manage updates on remote computers, you need to add host names to your winrm trusted host list:
Install the PSWindowsUpdate module on remote computers and allow to access the process dllhost.exe via dynamic RPC ports in the Windows Defender Firewall.
The following command will install all available updates on three remote servers:
In newer versions of the PSWindowsUpdate module, use the following command to remotely install updates on multiple computers:
You can install updates on a remote computer and send an email report to the administrator:
Install-WindowsUpdate -ComputerName nysrv1 -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll — IgnoreReboot -SendReport –PSWUSettings @
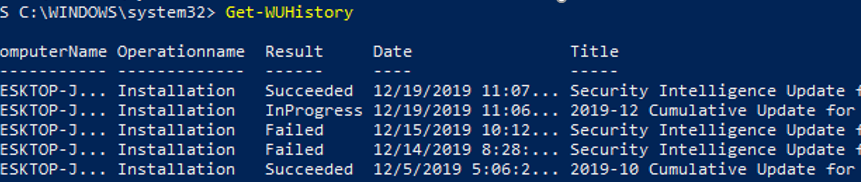
Get-WUHistory: Viewing Windows Update History using PowerShell
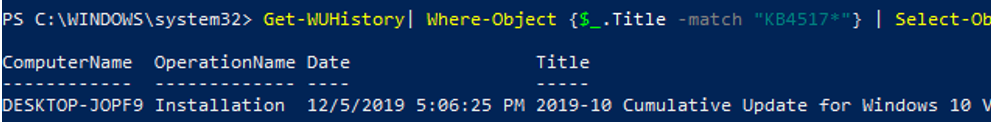
Using the Get-WUHistory cmdlet, you can get the list of updates installed on a computer earlier automatically or manually.
You can get the information about the date of installation of a specific update:
Get-WUHistory| Where-Object <$_.Title -match "KB4517389">| Select-Object *|ft
To find out if the update has been installed on multiple remote computers, you can use this PowerShell code:
«server1″,»server2» | Get-WUHistory| Where-Object <$_.Title -match "KB4011634">| Select-Object *|ft
Remove-WindowsUpdate: Uninstalling Windows Updates
To correctly uninstall the updates from PowerShell, you can use the Remove-WindowsUpdate cmdlet. Just specify the KB number as an argument of the KBArticleID parameter. To delay automatic computer restart, add the –NoRestart key:
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4489873 -NoRestart
Hide-WindowsUpdate: How to Hide Windows Updates with PowerShell?
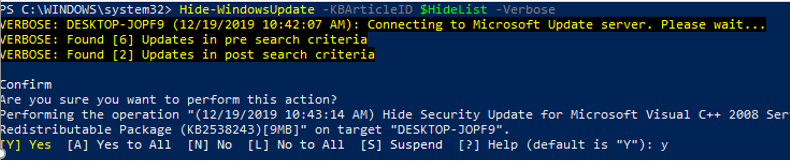
You can hide the specific updates so they will be never installed by Windows Update service on your computer (most often you need to hide the driver updates). For example, to hide the KB4489873 and KB4489243 updates, run these commands:
$HideList = «KB4489873», «KB4489243»
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList –Hide
Now the next time you scan for updates using the Get-WUInstall command, the hidden updates won’t be displayed in the list of updates available for installation.
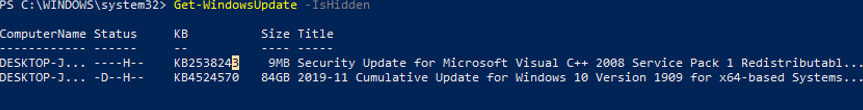
This is how you can display the list of updates hidden on this computer:
Notice that the H (Hidden) attribute has appeared in the Status column of hidden updates.
To remove an update from hidden ones, run this command:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -WithHidden -Hide:$false
Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList
For those who feel uncomfortable in the PowerShell console, I would recommend a graphic Windows Update MiniTool to manage Windows 10 updates.