- 990x.top
- Простой компьютерный блог для души)
- Microsoft-Windows-Security-SPP — что это за ошибка и как исправить?
- Microsoft-Windows-Security-SPP — что это такое?
- Решение ошибки
- Advanced troubleshooting 802.1X authentication
- Overview
- Scenarios
- Known issues
- Data collection
- Troubleshooting
- Audit policy
- C6273 C6273
- Пример Example
- 6273 microsoft windows security
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
990x.top
Простой компьютерный блог для души)
Microsoft-Windows-Security-SPP — что это за ошибка и как исправить?
Приветствую. Мы пользуемся многими программами, часть из которых — платные. Однако не все хотят платить и предпочитают использовать уже активированные версии, которые могут содержать не только вирусы, но и вызвать ошибки в журнале Windows.
Microsoft-Windows-Security-SPP — что это такое?
Ошибка, которая возникает при проблемах лицензирования ПО.
У некоторых пользователей при этом еще подвисает система.
Может появляться из-за использования взломанного софта. Например часто устанавливают взломанный Офис, при этом могут блокироваться некоторые защитные механизмы Windows, из-за чего собственно и может быть ошибка. Однако ошибка сама некритичная.
Взломанный софт при установке может останавливать службу SPPSVC, полное название которой — Служба платформы защиты программного обеспечения Майкрософт. Разумеется из-за этого могут быть ошибки как в журнале Windows, так и в ее работе.
Есть разные коды ошибки, например 8198. При этом в описании может упоминаться название slui.exe, а это процесс имеет отношение к активации Windows (возможно также и к софту Microsoft). Здесь также — ошибка может быть из-за использования хакерского софта для взлома Windows. Особенно учитывая, что файл slui.exe запускается из папки, в названии которой упоминается SPP:
Вообще существует еще служба Служба уведомления SPP, которая необходима для активации ПО, а также для уведомлений (как понимаю связанных с активацией). Данная служба может спокойно иметь отношение к сообщениям Security-SPP.
Пример ошибки, где в описании сразу указана примерная причина:

Решение ошибки
Способ #1.
Нужно предоставить полные права на папку:
При этом полные права нужно дать именно учетке Network Service.
После этого нужно перезапустить службу SPPSVC при помощи командной строки. Запускаем командную строку от администратора, в Windows 10 достаточно зажать Win + X и выбрать соответствующий пункт. В семерке в диспетчере задач выбираем Файл > пишем cmd и ставим галочку запускать от админа. Сами команды, первая — net stop sppsvc и вторая — net start sppsvc . Первая останавливает, вторая запускает службу.
Также можете посмотреть тему на офф форуме Microsoft, возможно будет полезно.
Способ #2.
Возможно вы недавно ставили взломанный софт, репак какой-то. Попробуйте удалить, возможно ошибка прекратит появляться. Чтобы удалить — используйте штатные возможности Windows:
- Зажмите Win + R, появится окошко Выполнить, вставьте команду appwiz.cpl, нажмите ОК.
- Откроется окно установленного софта. Здесь будет колонка с датой установки, можете нажать по ней и отсортировать программы, так вы сможете понять какое ПО было установлено недавно.
- Удалить просто: нажимаете правой кнопкой > выбираете Удалить. Появится мастер удаления, обычно нужно нажимать Далее/Next/Удалить/Uninstall.
На форуме Microsoft читал что сообщения Security-SPP могут быть также из-за использования всяких чистилок, оптимизаторов системы, удаляторов типа Revo Uninstaller. Поэтому если у вас есть что-то подобное — то возможно стоит удалить и проверить.
Способ #3.
Не уверен что поможет, но не повредит точно. По крайней мере это рекомендуют сделать на форуме Microsoft — проверить систему командой sfc /scannow, которая восстанавливает поврежденные и отсутствующие системные файлы. Запустите командную строку от администратора (выше писал как), далее вставляете команду:

Если будут обнаружены какие-то поврежденные файлы, то они будут заменены на оригинальные, которые хранятся здесь:
Advanced troubleshooting 802.1X authentication
Overview
This article includes general troubleshooting for 802.1X wireless and wired clients. While troubleshooting 802.1X and wireless, it’s important to know how the flow of authentication works, and then figure out where it’s breaking. It involves a lot of third-party devices and software. Most of the time, we have to identify where the problem is, and another vendor has to fix it. We don’t make access points or switches, so it’s not an end-to-end Microsoft solution.
Scenarios
This troubleshooting technique applies to any scenario in which wireless or wired connections with 802.1X authentication is attempted and then fails to establish. The workflow covers Windows 7 through Windows 10 for clients, and Windows Server 2008 R2 through Windows Server 2012 R2 for NPS.
Known issues
Data collection
Troubleshooting
Viewing NPS authentication status events in the Windows Security event log is one of the most useful troubleshooting methods to obtain information about failed authentications.
NPS event log entries contain information about the connection attempt, including the name of the connection request policy that matched the connection attempt and the network policy that accepted or rejected the connection attempt. If you don’t see both success and failure events, see the NPS audit policy section later in this article.
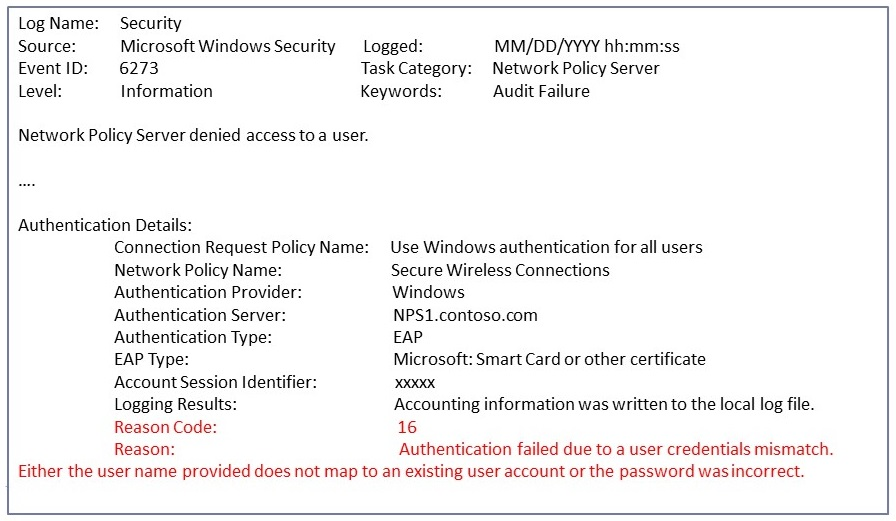
Check Windows Security Event log on the NPS Server for NPS events that correspond to rejected (event ID 6273) or accepted (event ID 6272) connection attempts.
In the event message, scroll to the very bottom, and then check the Reason Code field and the text that’s associated with it.
‎ 
‎The WLAN AutoConfig operational log lists information and error events based on conditions detected by or reported to the WLAN AutoConfig service. The operational log contains information about the wireless network adapter, the properties of the wireless connection profile, the specified network authentication, and, in the event of connectivity problems, the reason for the failure. For wired network access, the Wired AutoConfig operational log is an equivalent one.
On the client side, go to Event Viewer (Local)\Applications and Services Logs\Microsoft\Windows\WLAN-AutoConfig/Operational for wireless issues. For wired network access issues, go to ..\Wired-AutoConfig/Operational. See the following example:
Most 802.1X authentication issues are because of problems with the certificate that’s used for client or server authentication. Examples include invalid certificate, expiration, chain verification failure, and revocation check failure.
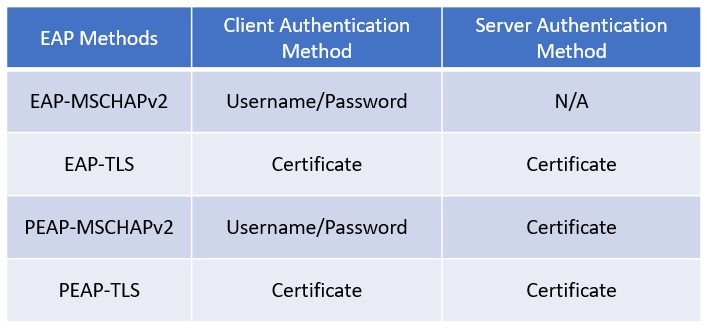
First, validate the type of EAP method that’s used:
If a certificate is used for its authentication method, check whether the certificate is valid. For the server (NPS) side, you can confirm what certificate is being used from the EAP property menu. In NPS snap-in, go to Policies > Network Policies. Select and hold (or right-click) the policy, and then select Properties. In the pop-up window, go to the Constraints tab, and then select the Authentication Methods section.
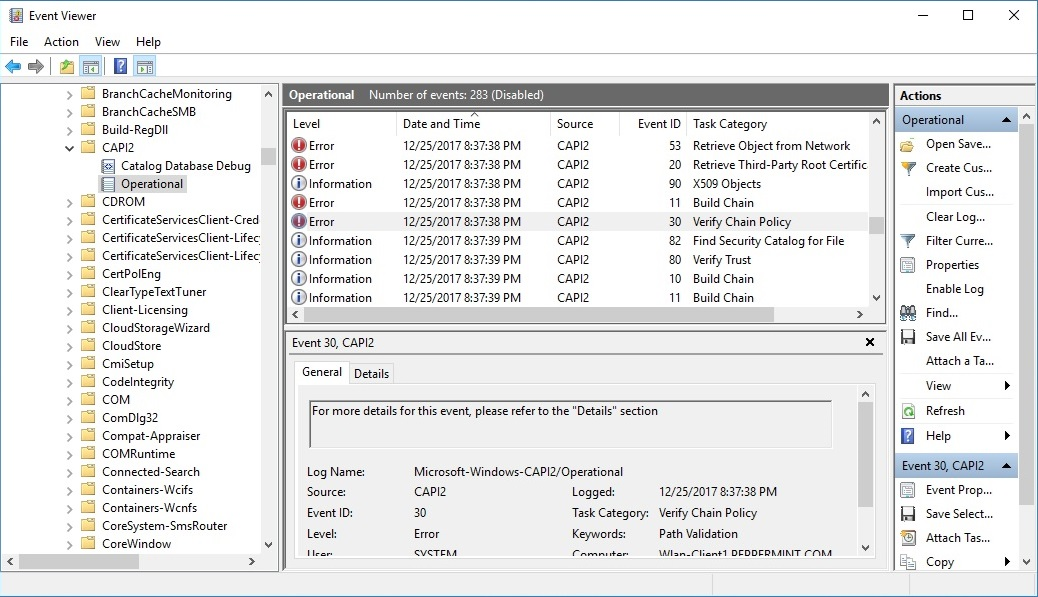
The CAPI2 event log is useful for troubleshooting certificate-related issues. By default, this log isn’t enabled. To enable this log, expand Event Viewer (Local)\Applications and Services Logs\Microsoft\Windows\CAPI2, select and hold (or right-click) Operational, and then select Enable Log.
For information about how to analyze CAPI2 event logs, see Troubleshooting PKI Problems on Windows Vista.
When troubleshooting complex 802.1X authentication issues, it’s important to understand the 802.1X authentication process. Here’s an example of wireless connection process with 802.1X authentication:
If you collect a network packet capture on both the client and the server (NPS) side, you can see a flow like the one below. Type EAPOL in the Display Filter for a client-side capture, and EAP for an NPS-side capture. See the following examples:


‎
If you have a wireless trace, you can also view ETL files with network monitor and apply the ONEX_MicrosoftWindowsOneX and WLAN_MicrosoftWindowsWLANAutoConfig Network Monitor filters. If you need to load the required parser, see the instructions under the Help menu in Network Monitor. Here’s an example:
Audit policy
By default, NPS audit policy (event logging) for connection success and failure is enabled. If you find that one or both types of logging are disabled, use the following steps to troubleshoot.
View the current audit policy settings by running the following command on the NPS server:
If both success and failure events are enabled, the output should be:
If it says, «No auditing,» you can run this command to enable it:
Even if audit policy appears to be fully enabled, it sometimes helps to disable and then re-enable this setting. You can also enable Network Policy Server logon/logoff auditing by using Group Policy. To get to the success/failure setting, select Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Audit Policies > Logon/Logoff > Audit Network Policy Server.
C6273 C6273
предупреждение C6273-нецелочисленное значение, передаваемое в качестве параметра, Если требуется целое число при вызове : при передаче значения указателя следует использовать% p warning C6273 — non-integer passed as parameter when integer is required in call to : if a pointer value is being passed, %p should be used
Это предупреждение означает, что строка формата задает целое число, например, определенную %d длину или спецификацию приоритета для, printf а не целое число, например float , строка или struct передается как параметр. This warning indicates that the format string specifies an integer, for example, a %d , length or precedence specification for printf but a non-integer such as a float , string, or struct is being passed as a parameter. Эта ошибка, скорее всего, приведет к неверным результатам. This defect is likely to result in incorrect output.
Пример Example
В следующем коде создается это предупреждение, поскольку вместо в функции требуется целое число float sprintf : The following code generates this warning because an integer is required instead of a float in the sprintf function:
В следующем коде используется целочисленное приведение для исправления этого предупреждения: The following code uses an integer cast to correct this warning:
В следующем коде используется функция безопасной обработки строк, sprintf_s для устранения этого предупреждения: The following code uses safe string manipulation function, sprintf_s , to correct this warning:
Это предупреждение неприменимо в Windows 9x и Windows NT версии 4, так как на этих платформах не поддерживается% p. This warning is not applicable on Windows 9x and Windows NT version 4 because %p is not supported on these platforms.
6273 microsoft windows security
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
I am having a hard time figuring what is wrong with my NPS server (Windows 2008 R2 Standard), I have a Controller base Cisco wireless network infrastructuire with Cisco AP’s. Everytime that I tried to authenticate my wireless client through the NPS server I am getting Event ID: 6273 with the below problem description on the NPS Event Viewer. Please help me with this issue because I cannot figure it out what is going on. I tried calling Cisco but they said that my Wireless LAN Controller is configured properly and they are pointing to my my NPS server not properly configured. Please help. Thank you.
Log Name: Security
Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Date: 5/13/2010 12:32:08 PM
Event ID: 6273
Task Category: Network Policy Server
Level: Information
Keywords: Audit Failure
User: N/A
Computer: phcmisad02.PeninsulaAD.local
Description:
Network Policy Server denied access to a user.
Contact the Network Policy Server administrator for more information.
User:
Security ID: DOMAIN\wireless_user
Account Name: DOMAIN\wireless_user
Account Domain: DOMAIN
Fully Qualified Account Name: DOMAIN\wireless_user
Client Machine:
Security ID: NULL SID
Account Name: —
Fully Qualified Account Name: —
OS-Version: —
Called Station Identifier: WLC mac address:SSID
Calling Station Identifier: wireless client mac address
NAS:
NAS IPv4 Address: x.x.x.x
NAS IPv6 Address: —
NAS Identifier: 4402WLC50P1
NAS Port-Type: Wireless — IEEE 802.11
NAS Port: 1
RADIUS Client:
Client Friendly Name: WAP-Controller1
Client IP Address: x.x.x.x
Authentication Details:
Proxy Policy Name: Secure Wireless Connections
Network Policy Name: Secure Wireless Connections
Authentication Provider: Windows
Authentication Server: phcmisad02.PeninsulaAD.local
Authentication Type: PEAP
EAP Type: —
Account Session Identifier: —
Reason Code: 301
Reason: Received Crypto-Binding TLV is invalid.
6273
0
0
12552
0
0x8010000000000000
76556189
Security
l
S-1-5-21-1922845083-1694484325-3216510869-3720
DOMAIN\wireless_user
DOMAIN
DOMAIN\wireless_user
S-1-0-0
—
—
—
WLC mac address:SSID
wireless client mac address
x.x.x.x
—
4402WLC50P1
Wireless — IEEE 802.11
1
WAP-Controller1
x.x.x.x
Secure Wireless Connections
Secure Wireless Connections
Windows
PEAP
—
—
301
Received Crypto-Binding TLV is invalid.
Answers
Hmm, there is also a setting on the client for this. You should also check that this is disabled. I explained how this works in a previous post — which I’ve copied below FYI.
I believe cryptobinding TLV is a method to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. When this fails, it essentially means that the message appears to have been tampered with. It is possible that the Wireless AP is causing this simply due to an incompatibility (not necessarily a misconfiguration). If the client-side setting is also disabled, can you possibly test with a different AP and see if you get the same thing?
The NPS server will always send a cryptobinding TLV, and there is no option to disable this. However, it does not require cryptobinding from the client unless the option (disconnect clients without cryptobinding) is enabled. I’ve provided a description below of what happens when you enable or disable the settings on NPS or on the client. I hope this helps you.
On the NPS server, you can access the cryptobinding option through properties of your network policy. On the Settings tab, click Authentication Methods. In EAP Types, click Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP), and then click Edit. One of the available options in the Edit Protected EAP Properties dialog box is to Disconnect Clients Without Cryptobinding. On the NAP client, you can access a similar option by reviewing PEAP settings or properties on the Authentication tab of your VPN connection. In the Protected EAP Properties dialog box, an available option is Disconnect If Server Does Not Present Cryptobinding TLV.
If you enable disconnection of clients without cryptobinding as described above, it will additionally enforce receipt of a cryptobinding response from the client computer. If this is not received, the server will reject the connection attempt. On the client side, enabling the cryptobinding option will require that the server send a cryptobinding TLV, and authentication will fail if this is not received by the client. If the cryptobinding option is not enabled on the client and it receives a cryptobinding TLV from the server, it will reply with a cryptobinding TLV response.